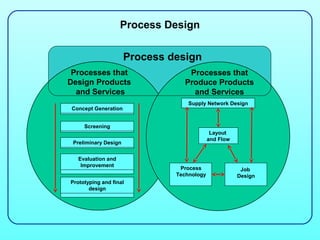
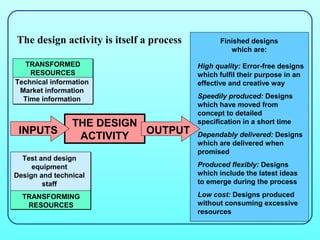
1) Process design involves planning the processes that transform inputs like resources, information, and time into outputs like products and services.
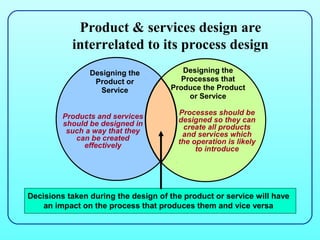
2) Product and service design influence and are influenced by process design - decisions in one area impact the other. Processes must be designed to effectively produce the products and services.
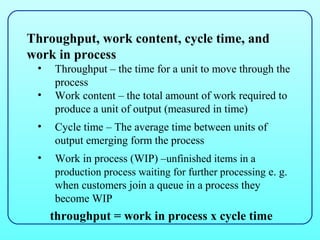
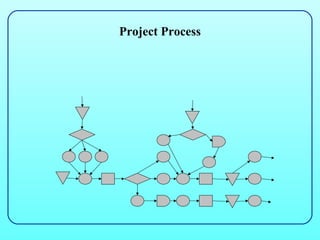
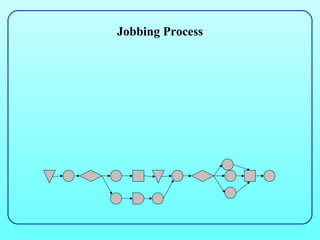
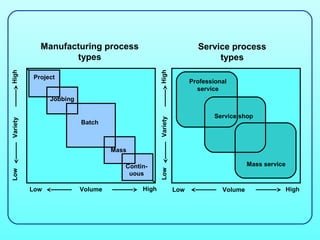
3) There are different types of processes like project, jobbing, batch, mass, and continuous, as well as service types like professional and mass service, which vary in factors like volume, variety, and skills required. Process mapping and analysis can improve processes.