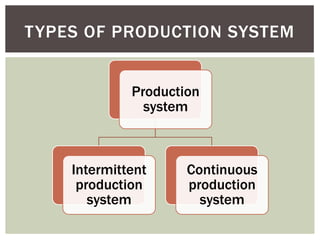
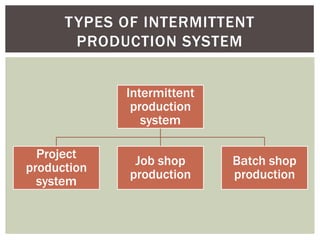
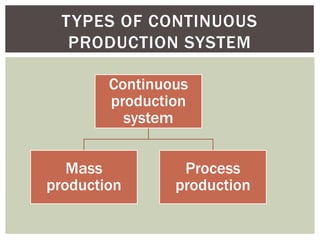
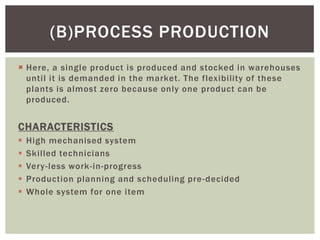
The document discusses the importance of production facilities and systems in production management, including elements such as plant location, layout, and types of production systems. It highlights different production methods, including intermittent and continuous systems, as well as the Toyota Production System and Just-In-Time strategies. The conclusion emphasizes the necessity of having the right facilities installed according to product requirements for efficient production.