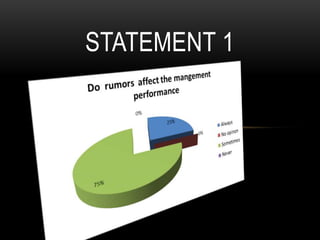
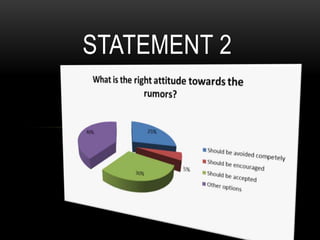
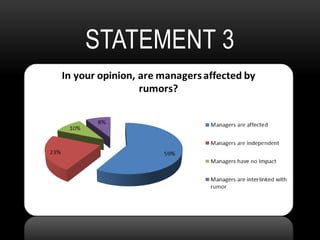
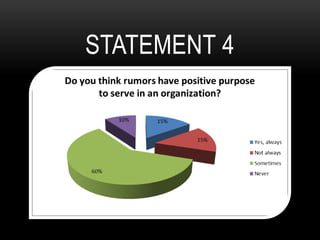
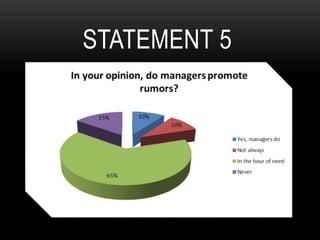
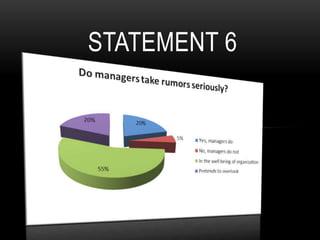
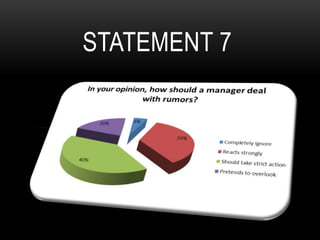
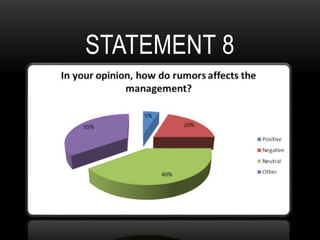
This document discusses how rumors affect managers' decision making in organizations. It defines rumors and identifies four common types: wish fulfillment, bogey rumors, wedge drivers, and home stretchers. The purpose is to understand how rumors impact decision making, employee morale, and organizational behavior. A survey was conducted to understand employee perspectives on multiple choice and true/false statements regarding rumors and their effects. Responses highlighted how rumors can justify employee demands and introduce bias into decision making processes. The document concludes that both positive and negative rumors have become part of organizational structures, and provides recommendations for minimizing rumors such as improving communication and screening suspicious individuals.