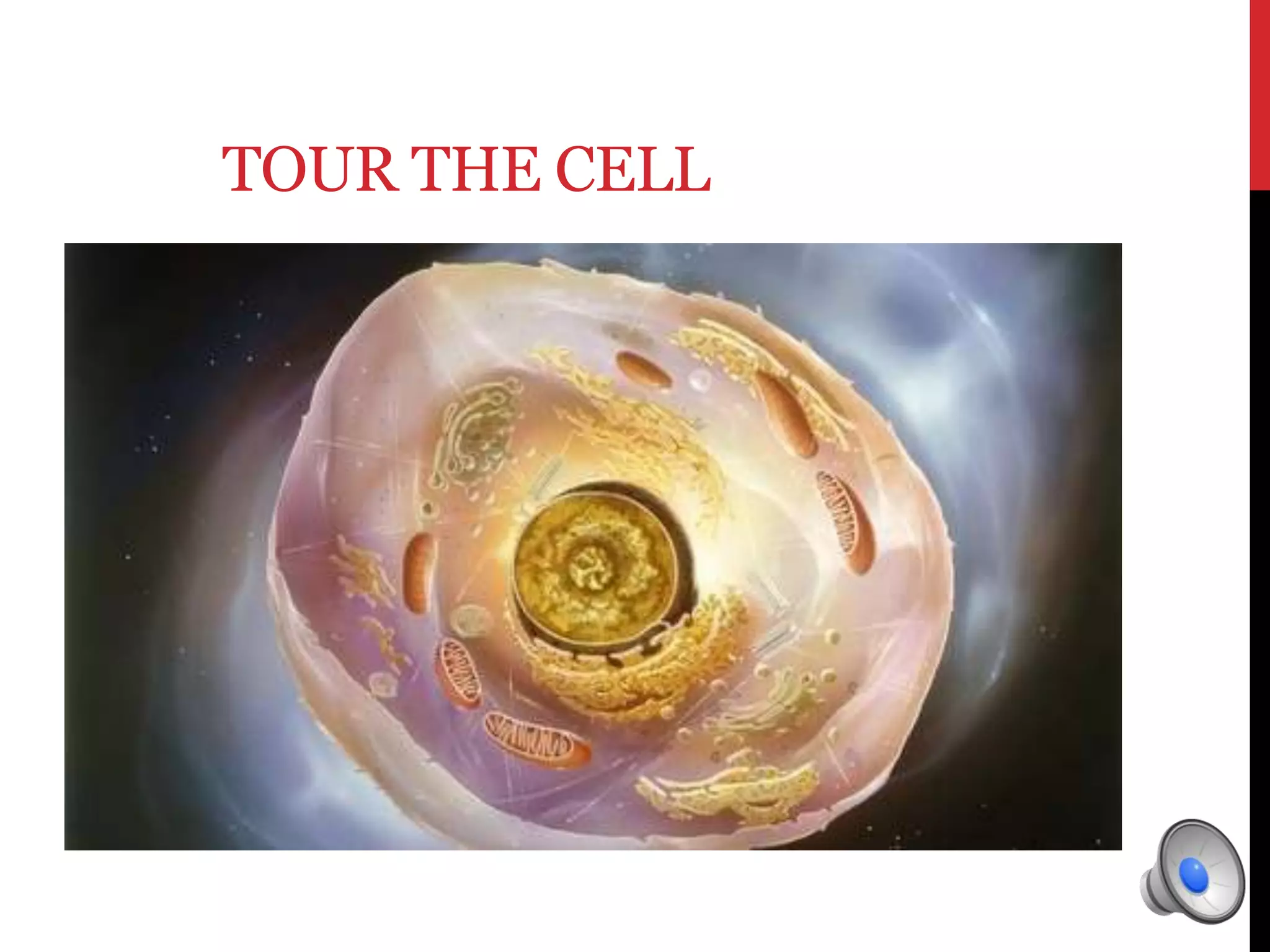
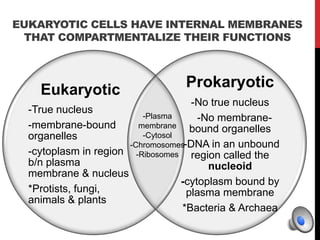
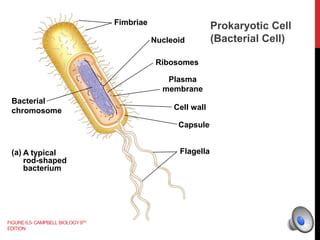
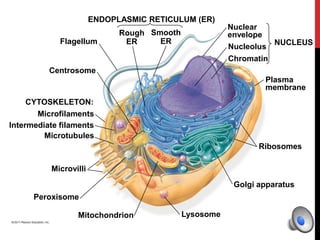
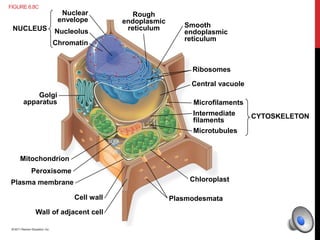
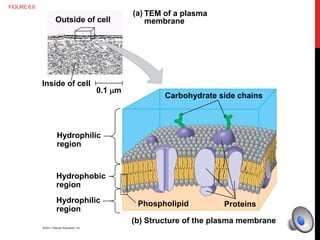
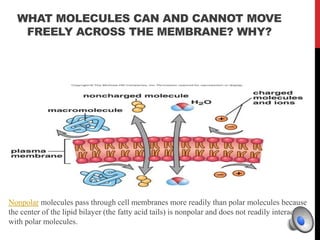
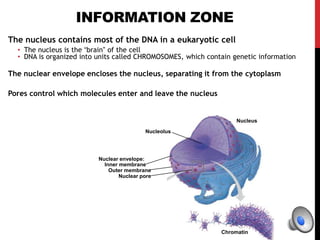
Here is a mind map of the major structures found in a typical eukaryotic cell:
Cell Membranes
- Plasma Membrane
- Nuclear Envelope
Organelles
- Nucleus
- Nucleolus
- Chromatin
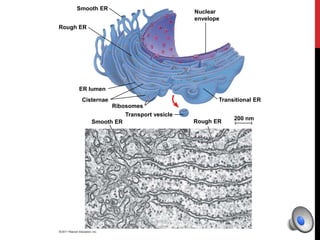
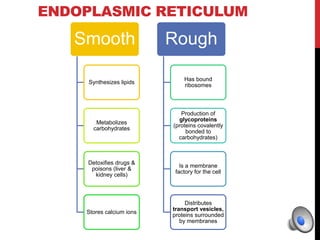
- Endoplasmic Reticulum
- Rough ER
- Smooth ER
- Golgi Apparatus
- Lysosomes
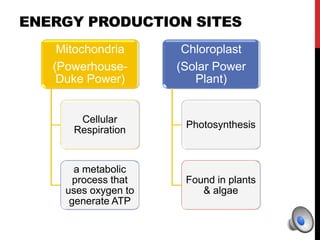
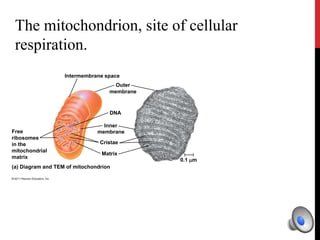
- Mitochondria
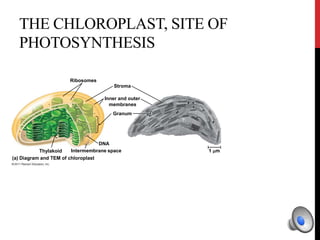
- Chloroplasts (in plant cells)
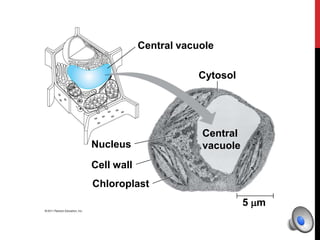
- Vacuoles (in plant and fungal cells)
- Cytoskeleton
- Microtubules
- Microfilaments
- Intermediate Filaments
Other Structures
- Ribosomes
- Centros