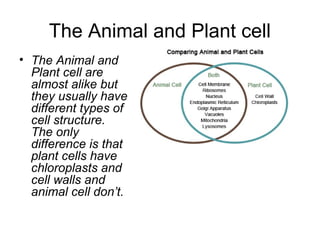
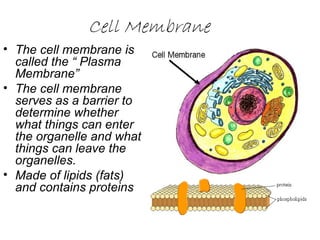
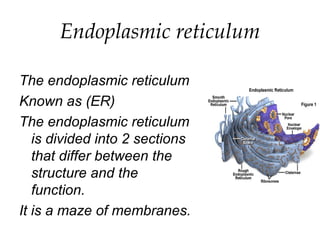
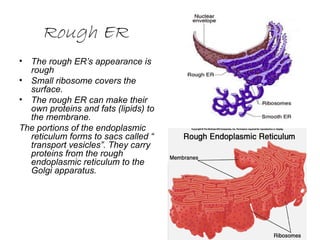
This document summarizes the key structures and functions of animal and plant cells. It describes the cell membrane, nucleus, cytoplasm, cytoskeleton, ribosomes, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, lysosomes, vacuoles, mitochondria, cell wall, and chloroplasts. The main differences between animal and plant cells are that plant cells contain chloroplasts and a cell wall, while animal cells do not.