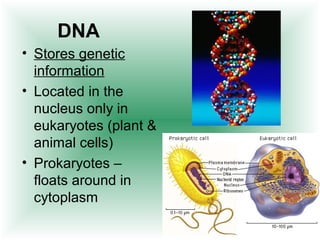
This document discusses the differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. Prokaryotic cells lack internal membranes and organelles, while eukaryotic cells contain membrane-bound organelles. It then describes the major organelles found in plant and animal cells and their functions, such as the nucleus containing DNA, mitochondria producing energy, and chloroplasts facilitating photosynthesis in plant cells. Cell membranes surround and protect cells, while plant cells also contain a cell wall for additional support.