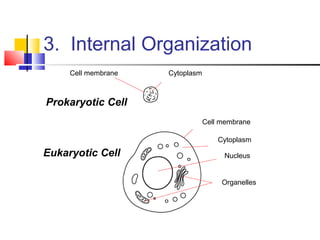
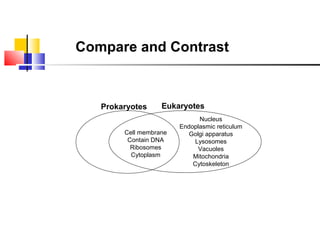
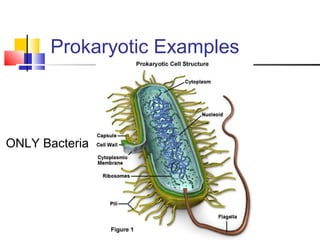
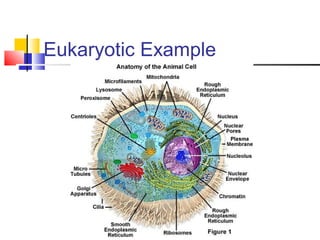
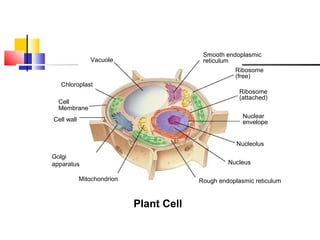
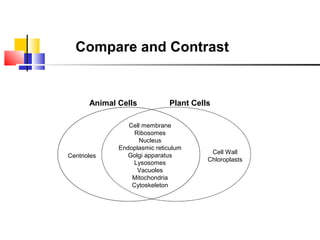
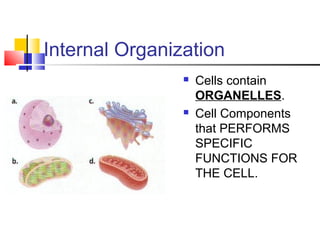
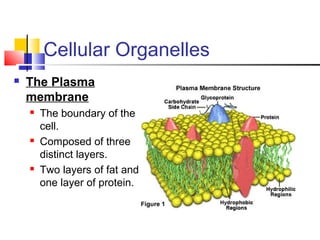
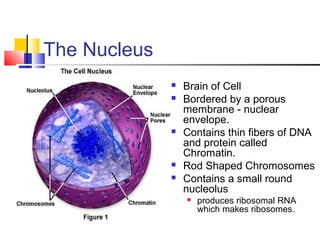
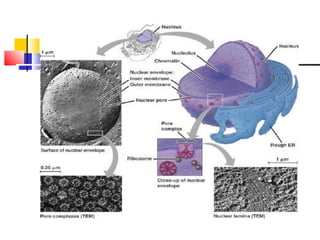
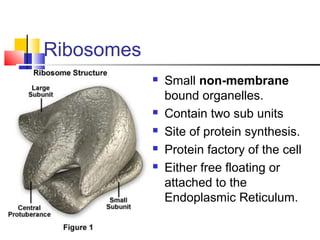
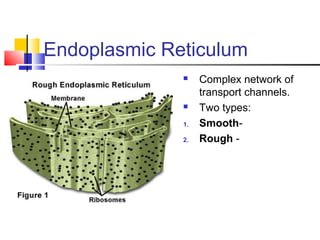
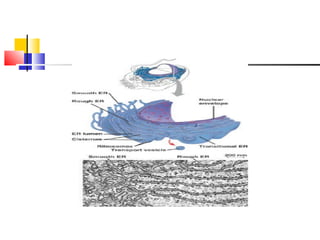
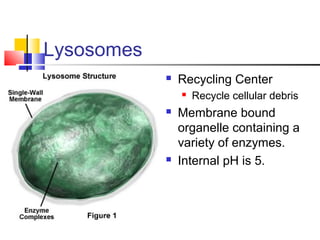
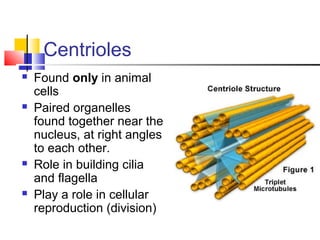
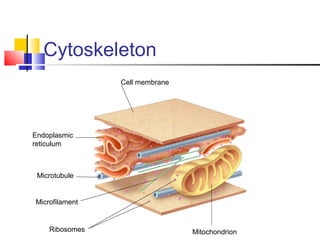
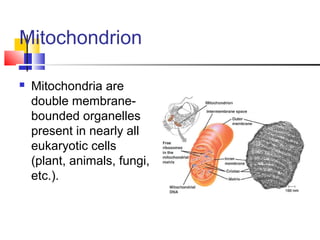
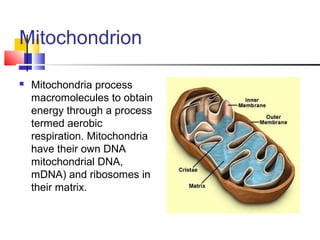
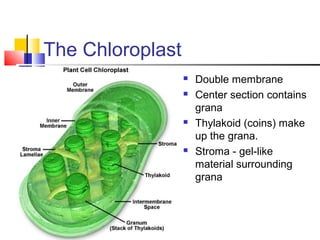
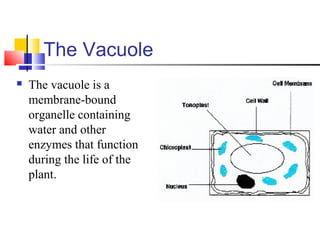
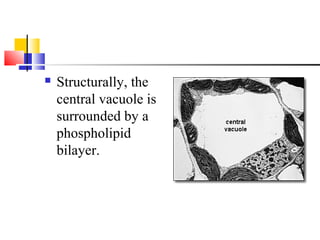
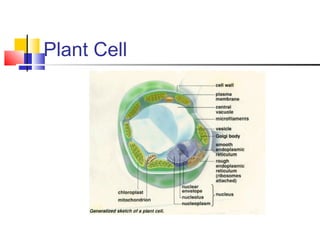
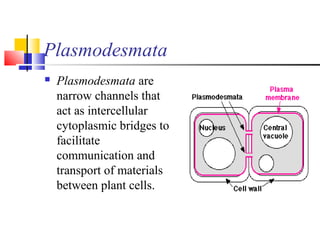
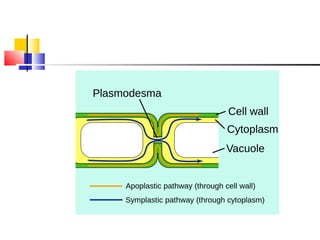
Cells are the fundamental units of life, varying in size and shape to perform specific functions. They contain organelles, each with dedicated roles, such as the nucleus for genetic material, ribosomes for protein synthesis, and mitochondria for energy production. Eukaryotic cells (plant and animal) have complex structures, including a cell membrane, endoplasmic reticulum, and chloroplasts for photosynthesis in plants.