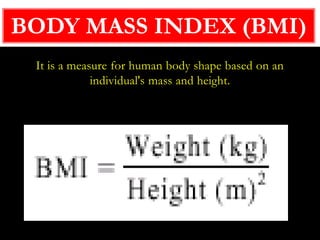
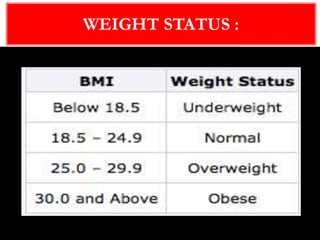
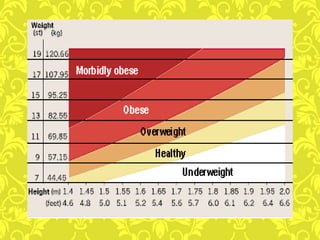
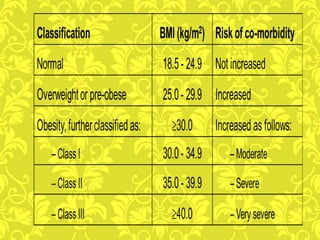
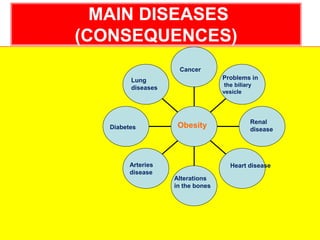
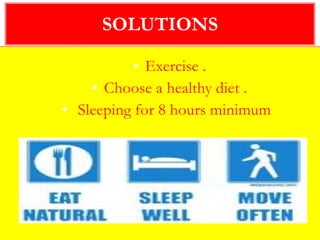
Obesity is caused by an imbalance between calories consumed and calories expended, leading to excess body fat. It is measured by body mass index (BMI) and defined as a BMI of 30 or higher. Obesity can lead to serious health conditions like heart disease, diabetes, and certain cancers. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle through balanced nutrition, regular physical activity, and managing stress can help prevent and treat obesity.