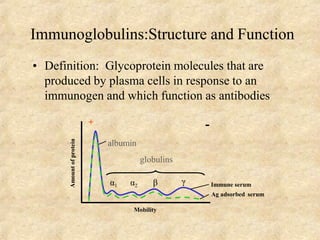
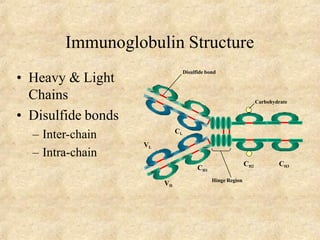
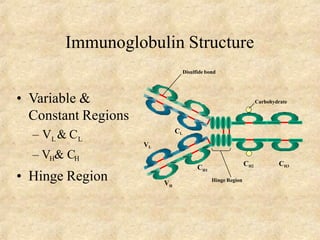
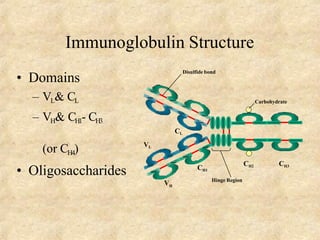
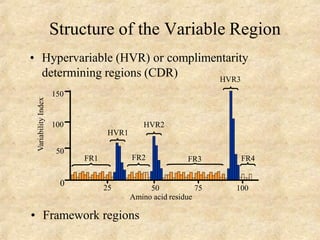
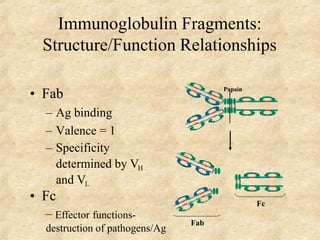
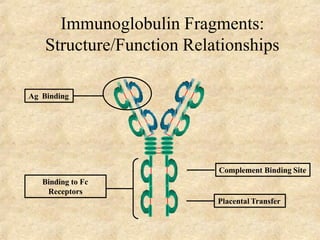
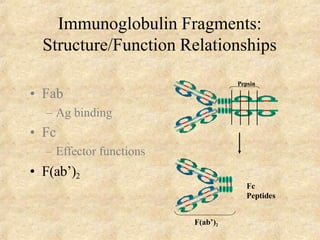
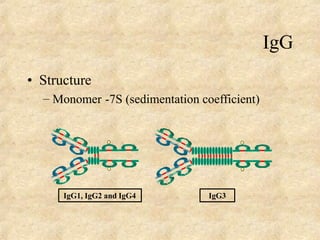
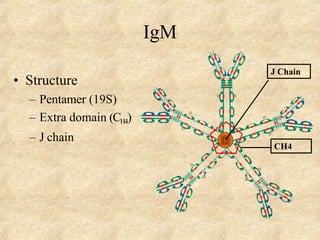
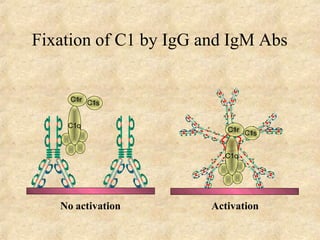
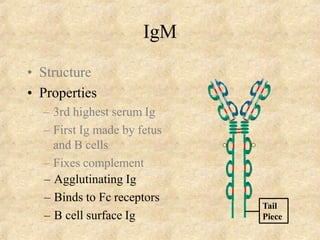
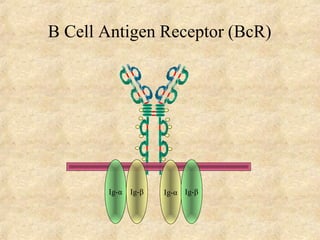
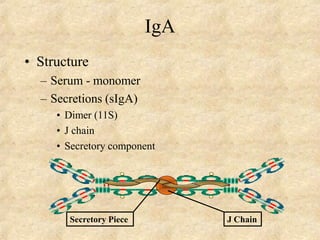
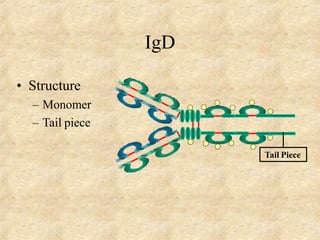
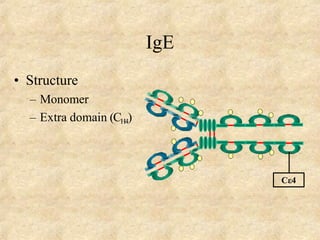
Immunoglobulins are glycoprotein molecules produced by plasma cells that function as antibodies. They have a basic Y-shaped structure composed of two heavy chains and two light chains connected by disulfide bonds. The variable regions at the tips of the Y determine antigen binding specificity. The constant regions define the five major classes - IgG, IgM, IgA, IgD, and IgE - which have different effector functions like complement activation. IgG is the most abundant antibody and provides systemic immunity while IgA dominates mucosal immunity through secretions. IgE mediates allergic reactions by binding basophils and mast cells.