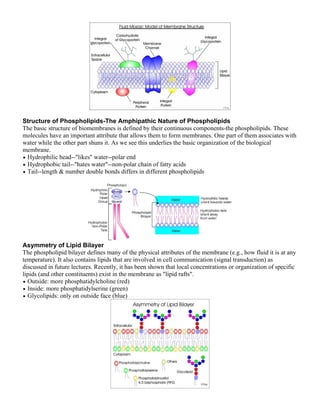
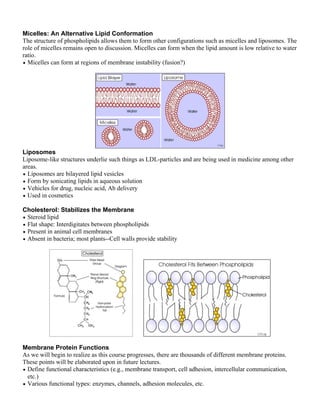
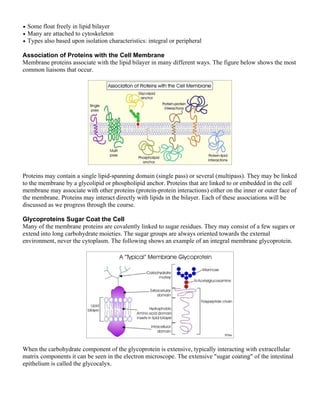
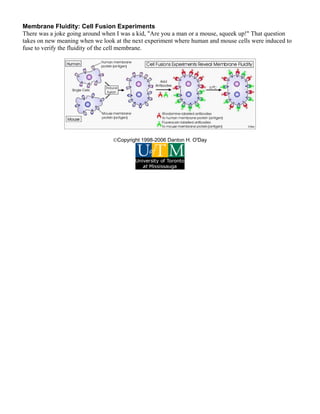
The document summarizes the key components and structure of the cell membrane according to the fluid mosaic model. It describes that the cell membrane is a lipid bilayer with embedded and associated proteins. The major constituents are phospholipids that form the bilayer, cholesterol that provides stability, and various types of membrane proteins. The fluid mosaic model and experimental evidence demonstrate that the cell membrane is fluid and dynamic in nature.