Fibrous proteins collagen, elastin, and keratin have structural functions.
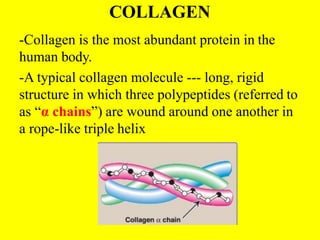
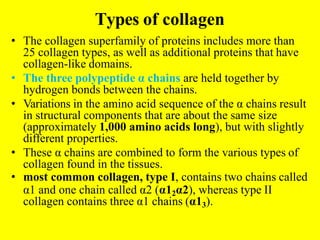
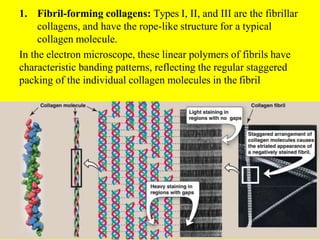
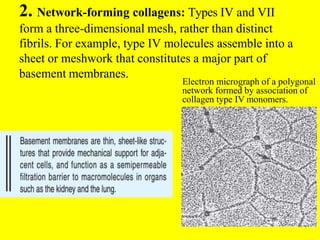
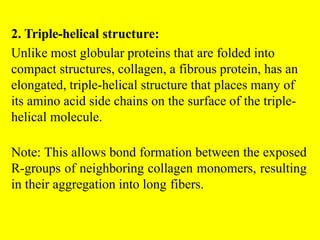
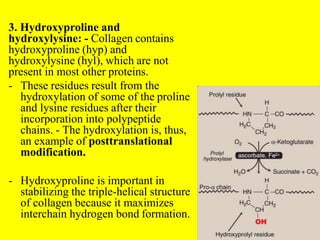
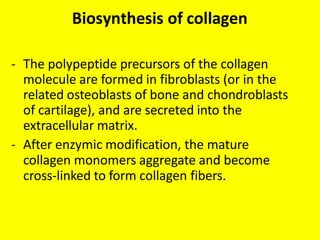
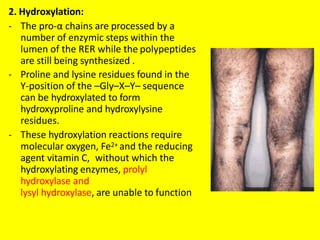
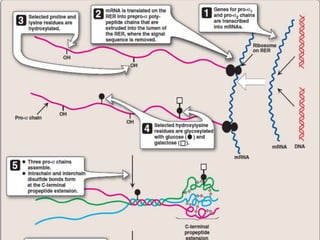
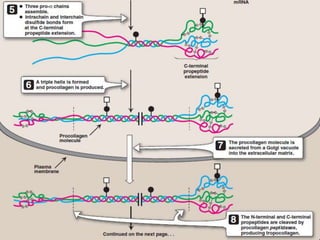
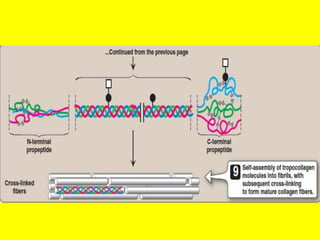
Collagen forms rope-like triple helices that assemble into strong fibrils in connective tissues. Variations in collagen's alpha chains result in over 25 types with different properties. Defects in collagen synthesis can cause collagenopathies like osteogenesis imperfecta.
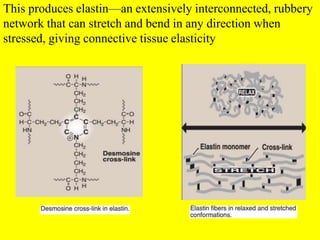
Elastin also forms fibrils but has rubber-like properties, being able to stretch and recoil through crosslinking.
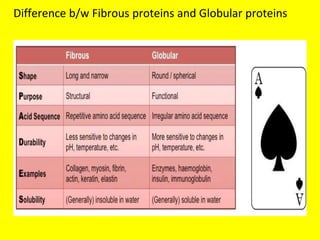
In contrast, fibrous proteins form regular structures while globular proteins rely on complex folding interactions.