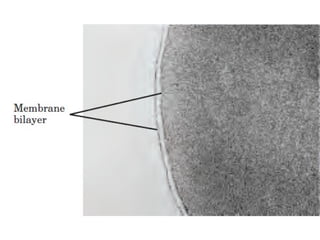
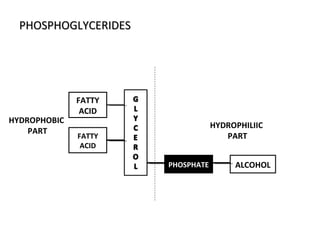
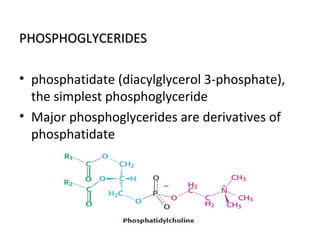
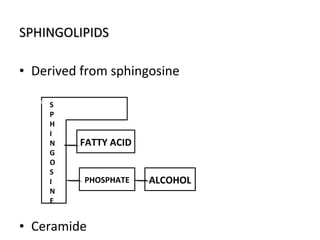
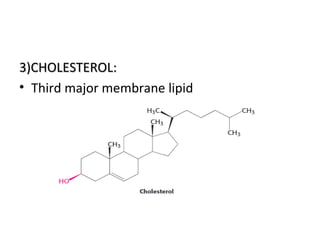
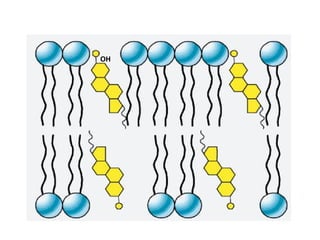
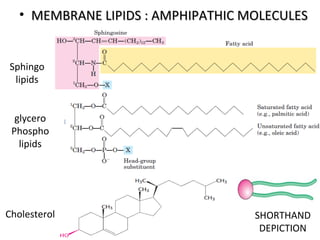
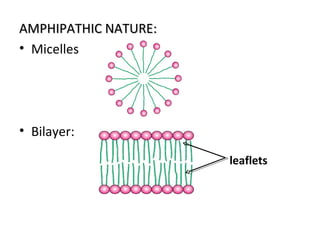
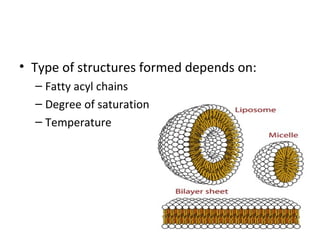
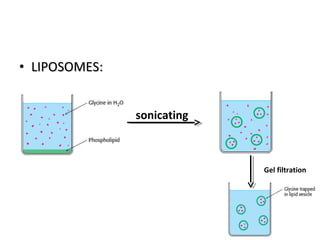
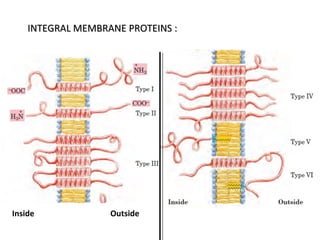
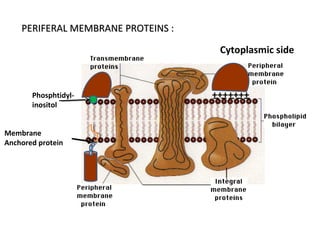
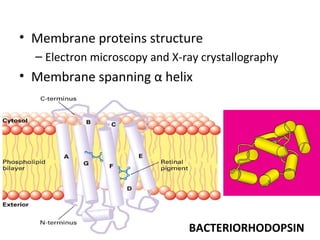
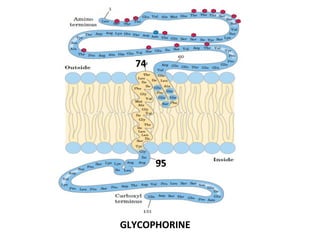
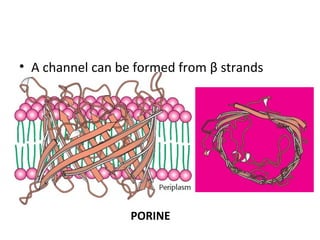
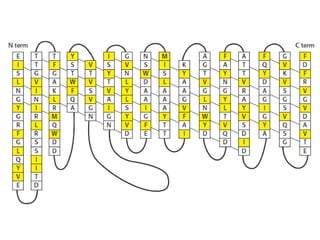
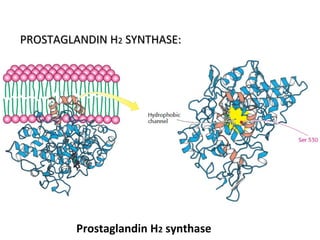
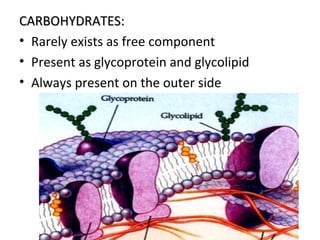
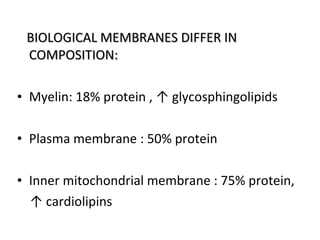
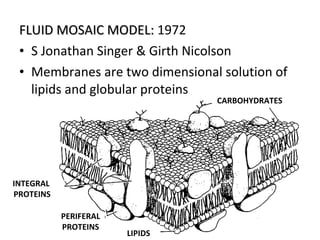
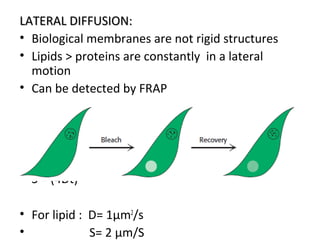
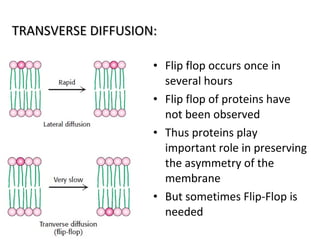
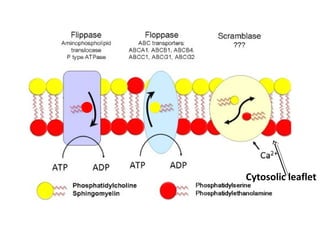
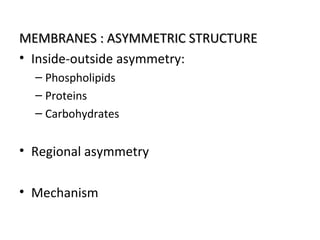
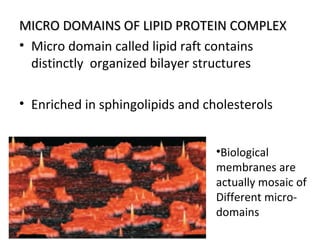
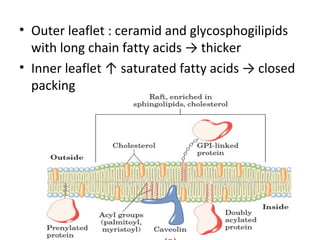
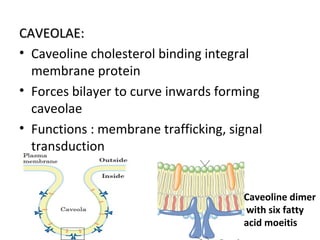
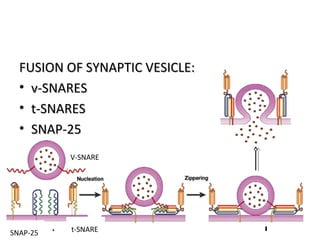
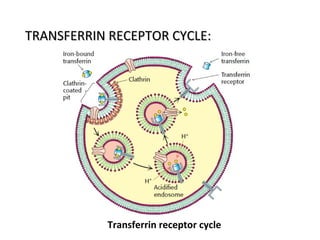
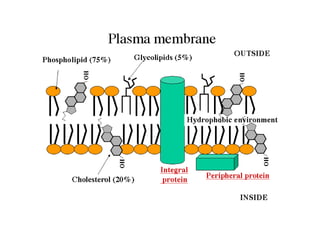
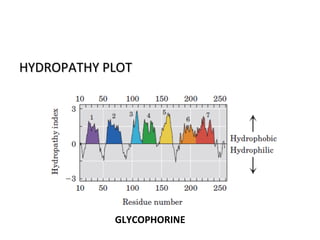
The cell membrane is composed mainly of lipids and proteins that form a fluid bilayer. Phospholipids are the major lipids and form a bilayer with their hydrophobic tails facing inward and hydrophilic heads facing outward. Membrane proteins can be integral or peripheral. The fluid mosaic model describes membranes as a fluid bilayer with proteins diffusing laterally. Membranes exhibit asymmetry, fluidity, and formation of microdomains. Specific proteins mediate membrane fusion and curvature essential for cellular processes.