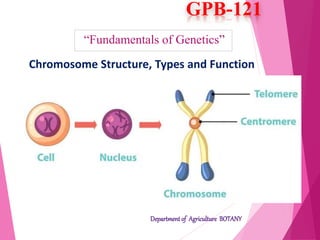
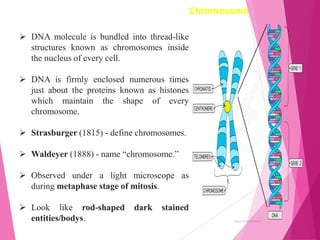
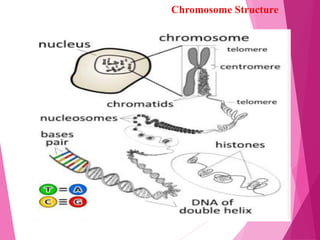
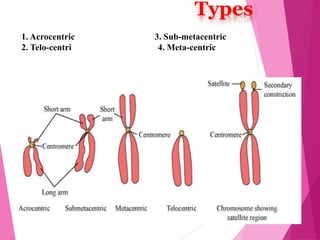
This document discusses chromosome structure and types. It describes how DNA is bundled into chromosomes within cell nuclei. Chromosomes are divided into three structural segments: the pellicle outer covering, matrix ground substance, and chromonemata coiled DNA threads. The centromere is a constriction that attaches the two chromonemata and separates the chromosome into arms. Telomeres are specialized chromosome ends. Chromosomes are also classified based on centromere position as acrocentric, telocentric, submetacentric, or metacentric. The centromere provides attachment points for spindle fibers during cell division and acts as a nucleation center for microtubule formation.