This document provides an overview of a course on advanced cell biology. It focuses on the topic of membranes, including their structure and key components. The main points are:
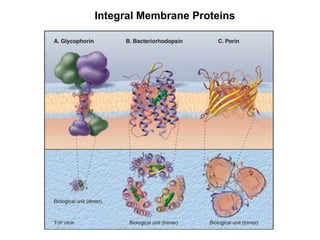
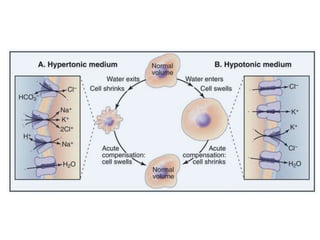
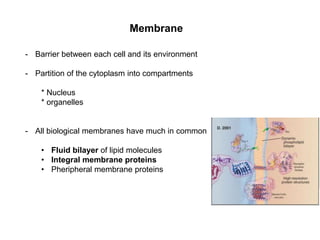
- Biological membranes act as barriers that compartmentalize the cell and contain lipids, integral proteins, and peripheral proteins.
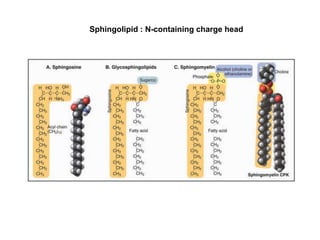
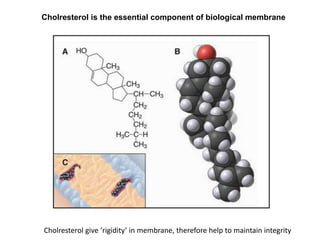
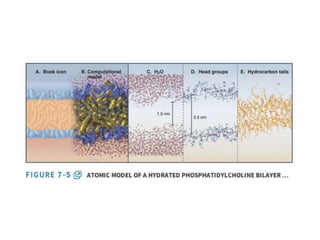
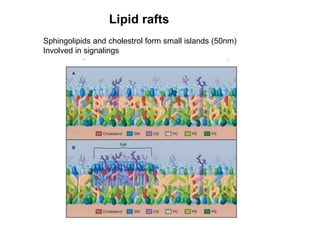
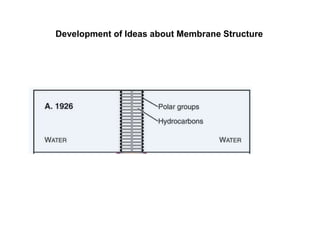
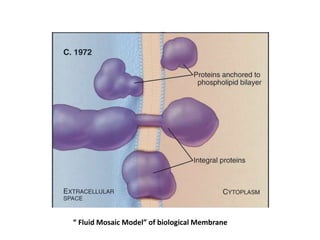
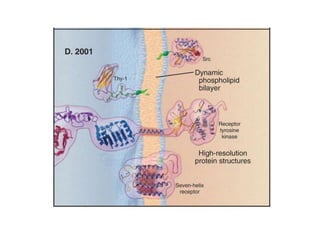
- The fluid mosaic model describes membranes as a fluid bilayer of lipids with integral proteins embedded. Key lipids include phospholipids and sphingolipids. Cholesterol provides rigidity.
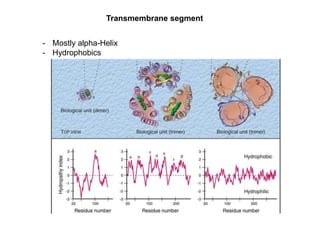
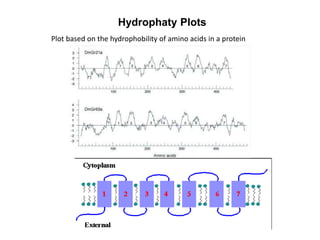
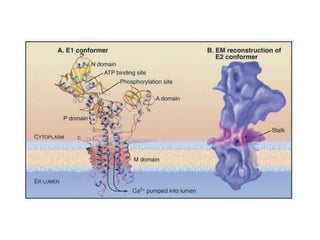
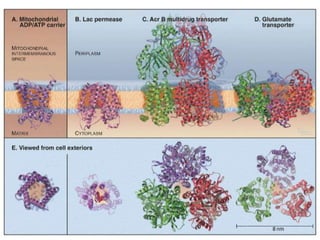
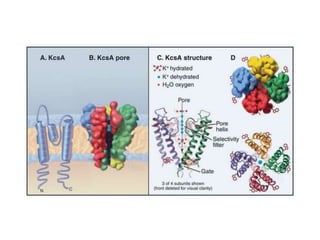
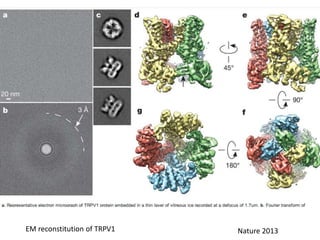
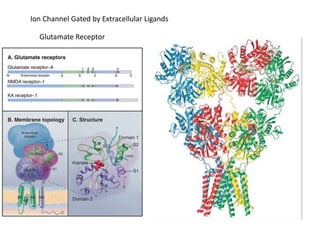
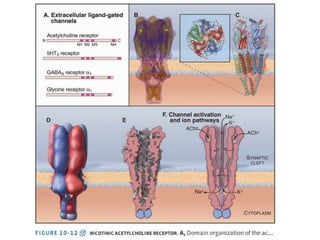
- Integral membrane proteins span the membrane and include transmembrane alpha helices. Their structure can be predicted using hydropathy plots.
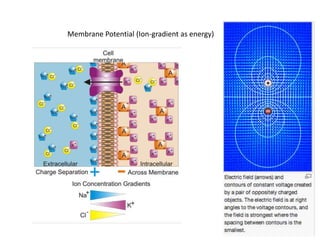
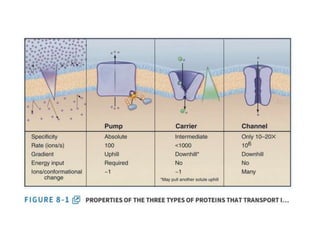
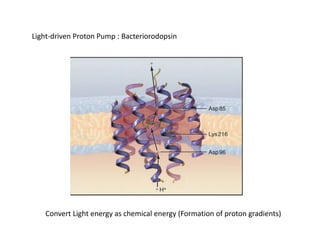
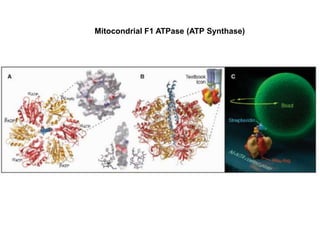
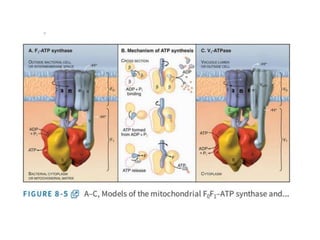
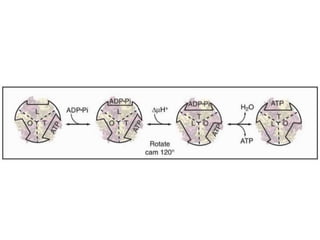
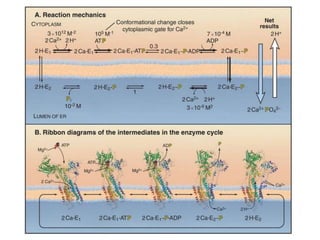
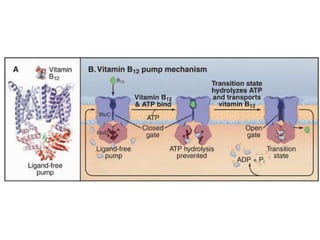
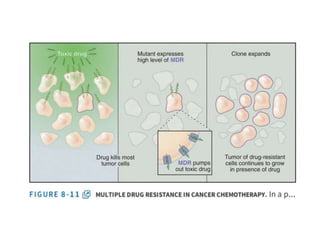
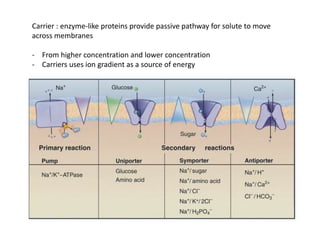
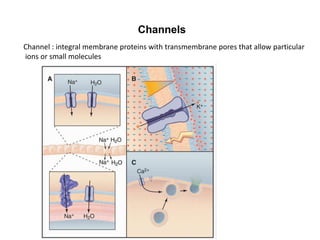
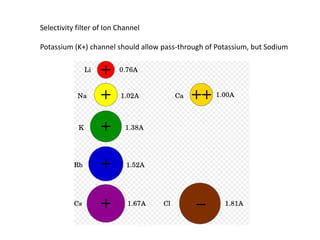
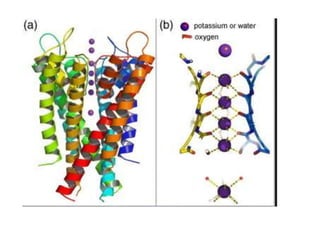
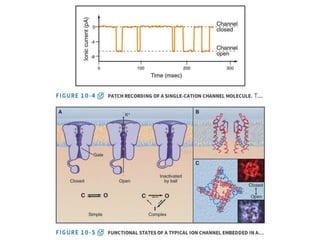
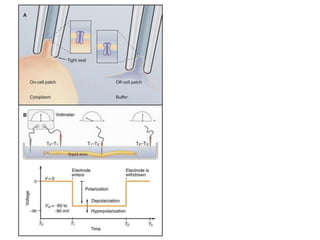
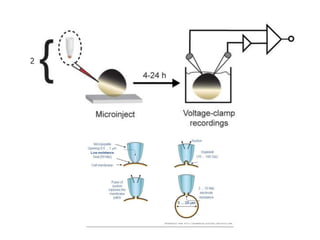
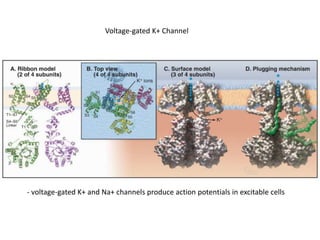
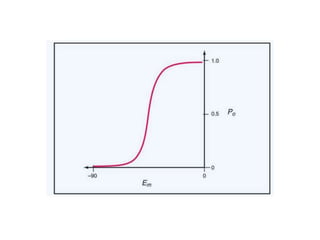
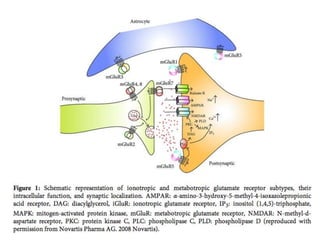
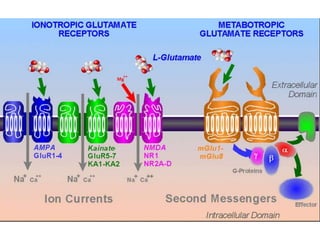
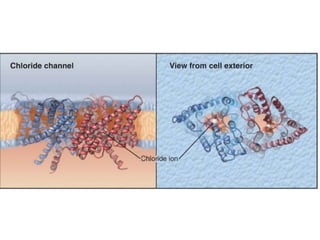
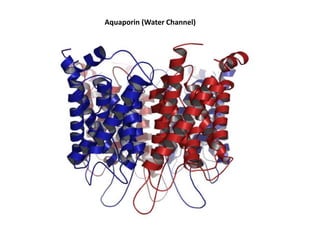
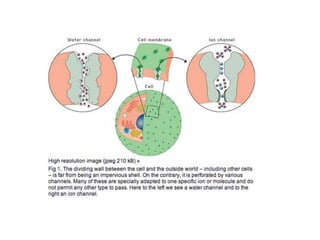
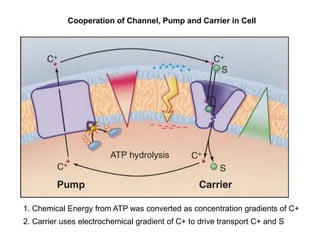
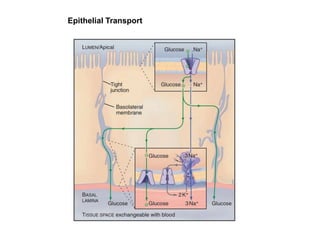
- Membranes establish gradients using pumps, carriers, and channels. Pumps actively transport ions using ATP.



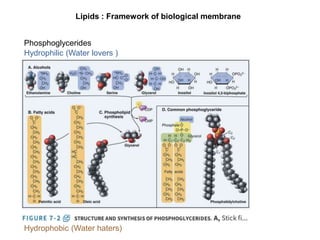
![• Main lipid constitutes of membranes
• Glycerol + two fatty acids + phosphoric acids +
alchohol
• Depend on alcohols esterified to the phosphates
- Phosphatidic acid [PA]
- Phosphatidylglycerol [PG]
- Phosphatidiylethanolamine [PE]
- Phosphatidylcholine [PC]
- Phosphatidylserine [PS]
- Phophatidylinositol [PI]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cellbio4-140610210708-phpapp01/85/Cell-Biology-Lecture-3-9-320.jpg)