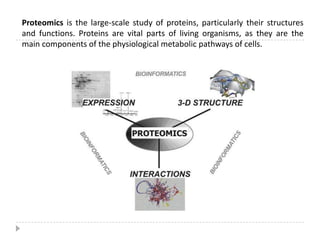
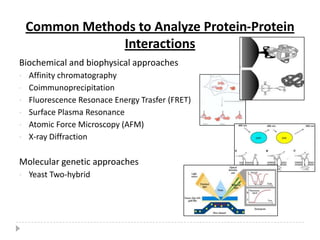
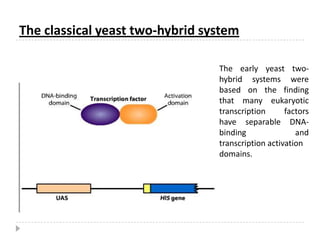
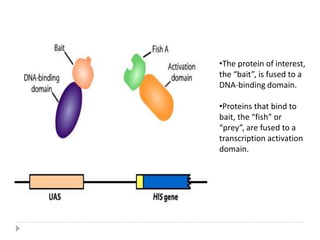
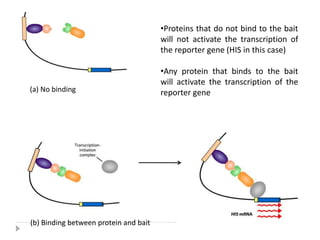
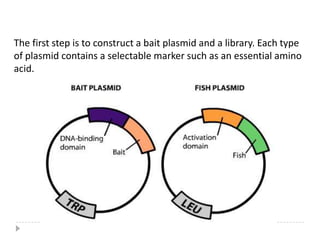
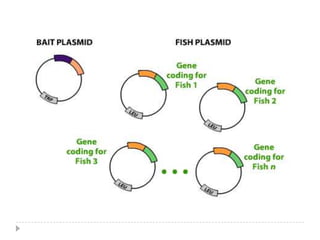
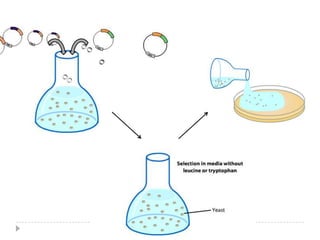
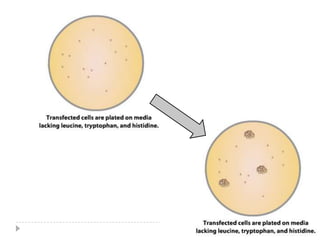
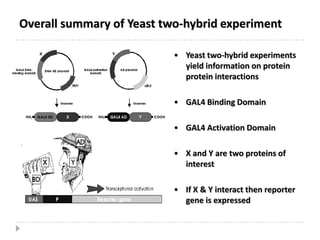
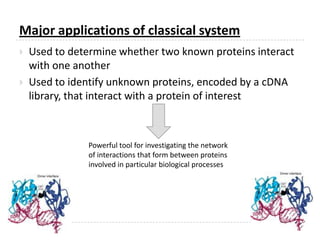
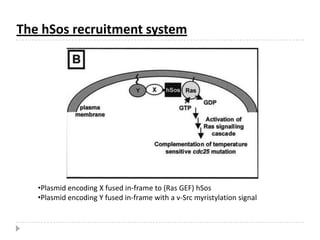
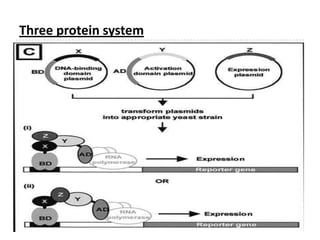
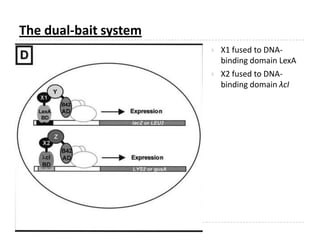
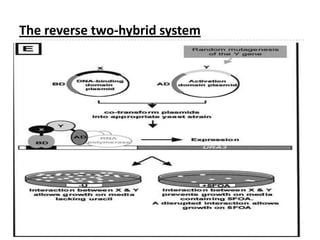
The yeast two-hybrid system is used to identify protein-protein interactions. It involves fusing two interacting proteins to a DNA-binding domain and transcriptional activation domain. If the proteins interact, it brings the domains together and activates a reporter gene. This allows identification of novel interactions and domains involved. Some advantages are it occurs in vivo, can find weak interactions, and doesn't require purified proteins. Disadvantages include false positives and some proteins may not fold correctly in yeast.