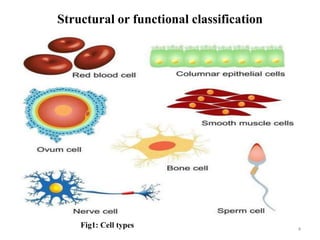
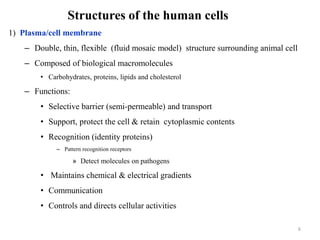
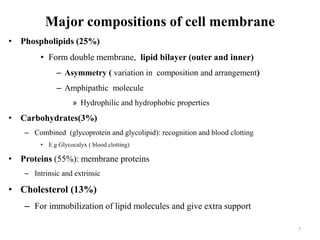
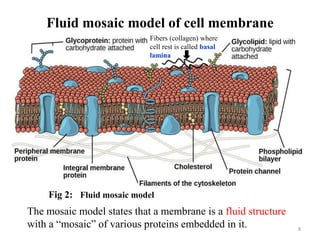
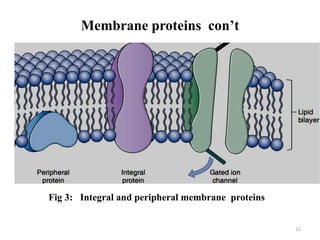
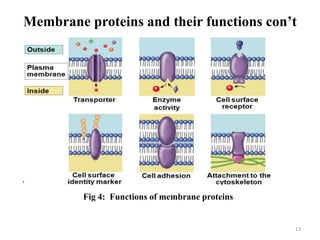
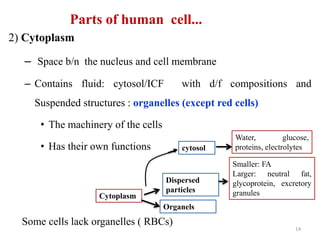
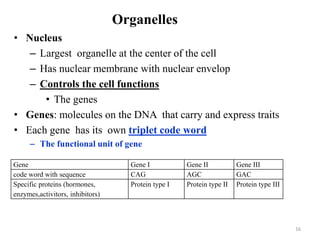
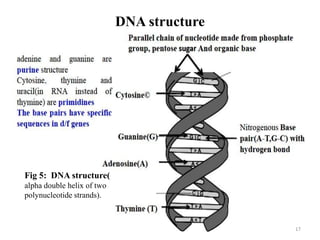
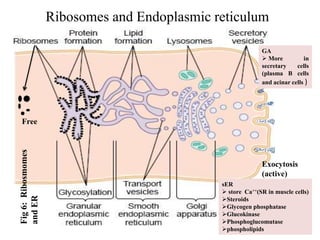
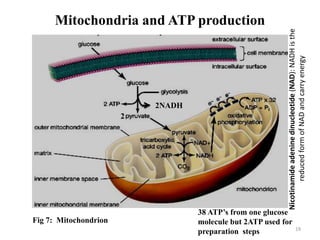
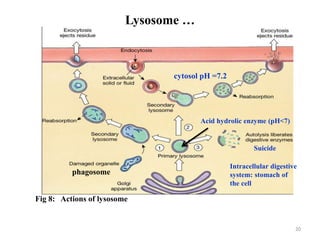
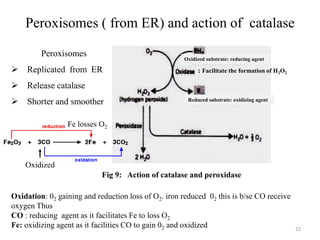
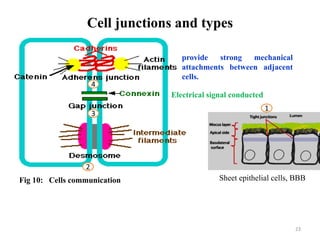
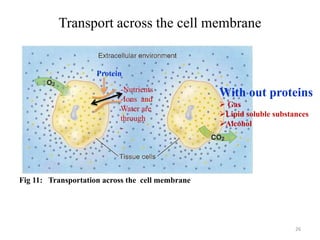
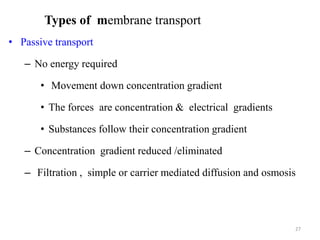
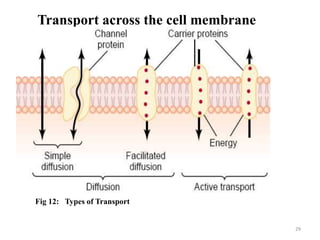
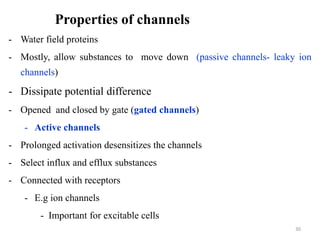
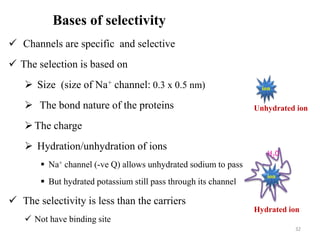
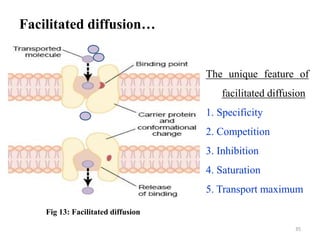
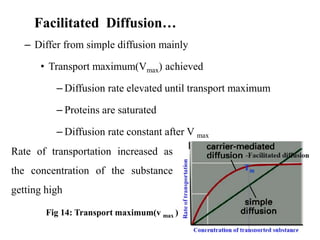
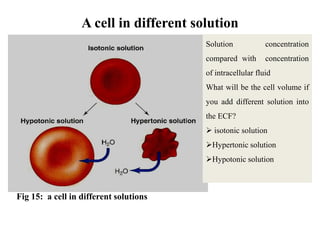
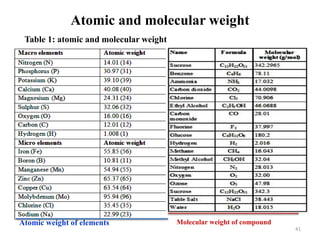
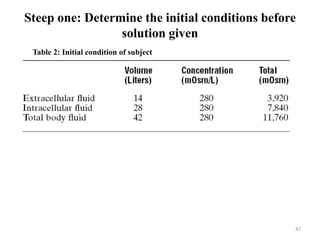
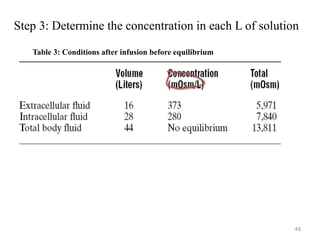
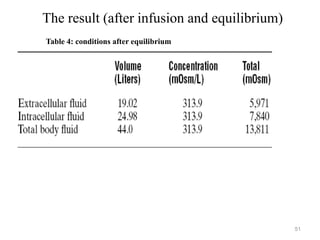
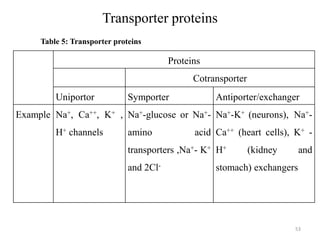
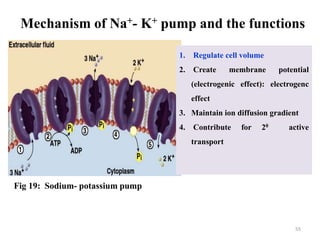
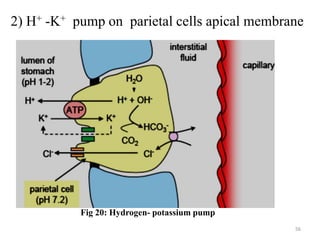
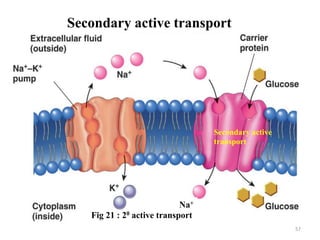
The document is a set of lecture notes from Addis Ababa University focusing on cell physiology and transportation, aimed at medical students. It covers objectives like understanding cell structures, membrane proteins, and cell transport mechanisms, including passive and active transport. Key components discussed include the human cell structure, the fluid mosaic model of membranes, types of membrane transport, osmosis, osmotic pressure, and active transport mechanisms.