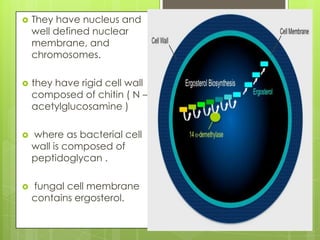
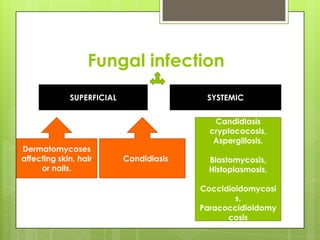
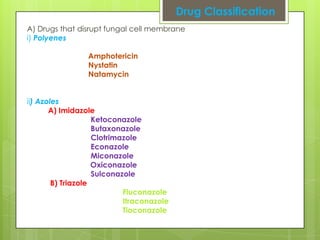
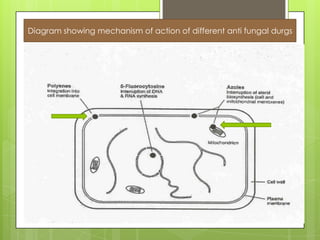
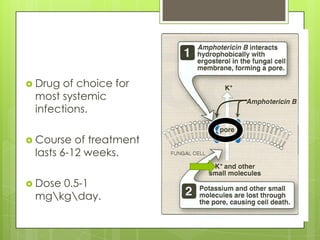
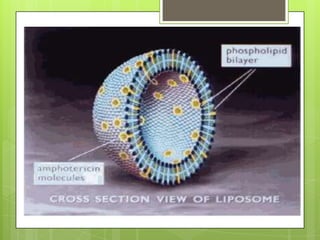
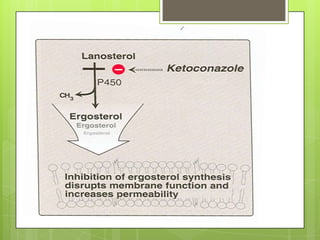
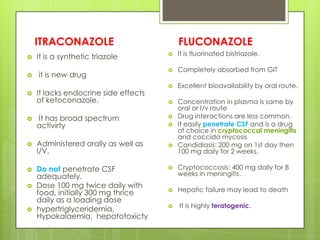
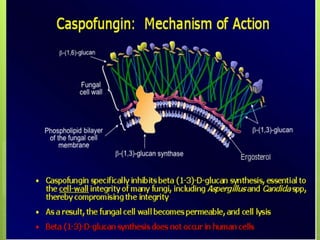
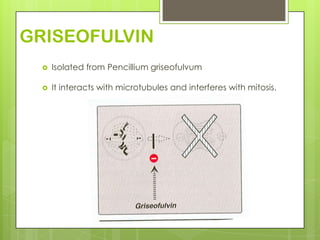
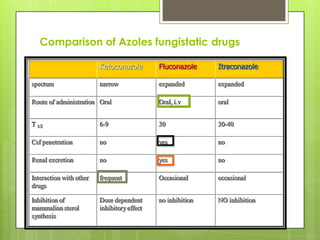
This document provides an overview of antifungal agents including their classification, mechanisms of action, indications, and adverse effects. It discusses several classes of antifungals such as azoles, polyenes, and echinocandins. Azoles like ketoconazole and fluconazole inhibit ergosterol synthesis, while polyenes like amphotericin B bind to ergosterol in the fungal cell membrane. Echinocandins target glucan synthesis. The document reviews specific drugs, their dosages, mechanisms, and side effects in treating superficial and systemic fungal infections. Future antifungal agents that may be effective for resistant fungal strains are also mentioned.