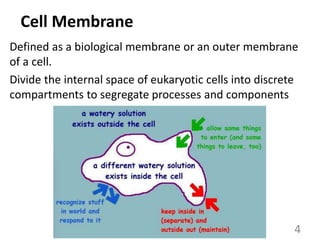
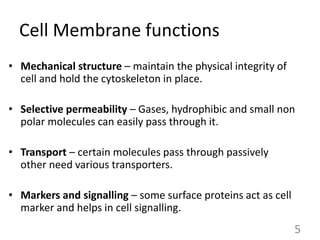
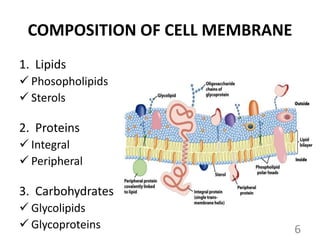
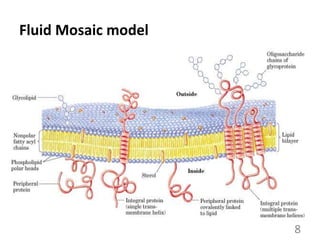
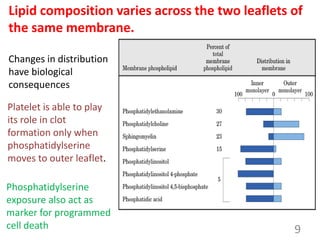
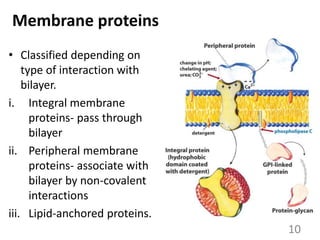
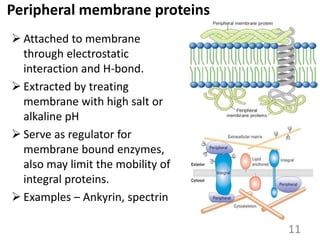
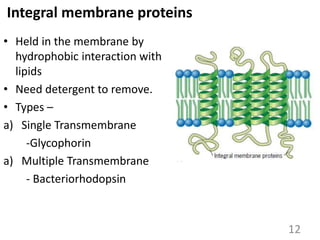
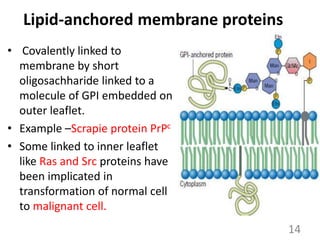
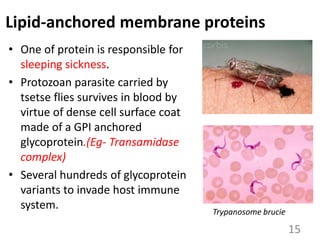
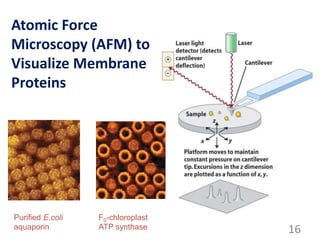
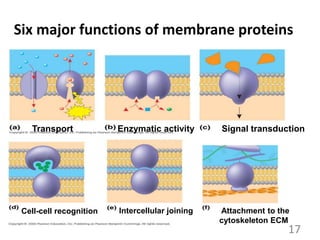
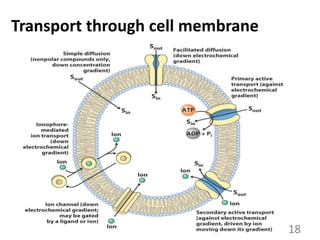
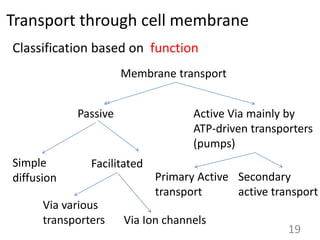
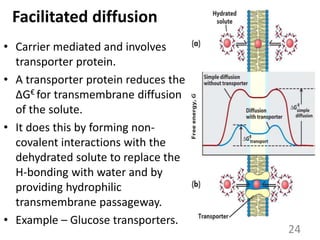
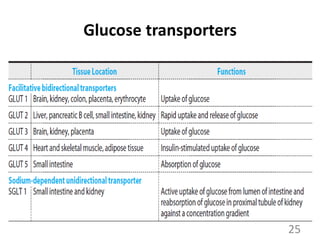
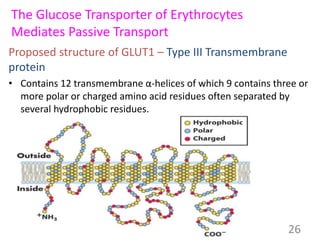
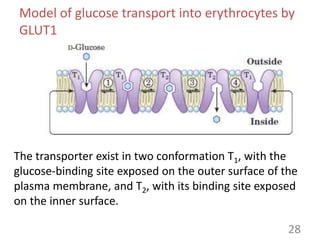
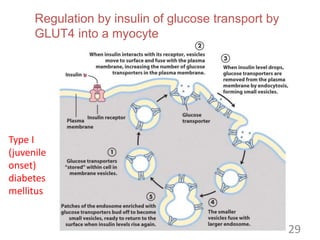
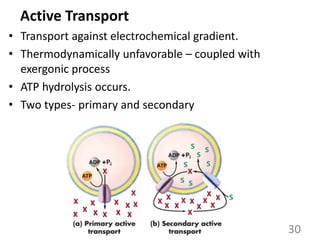
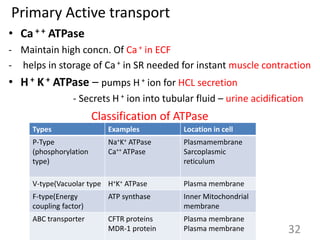
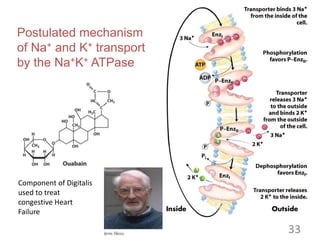
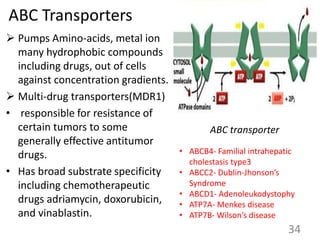
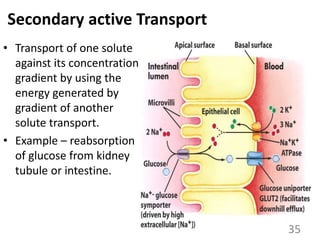
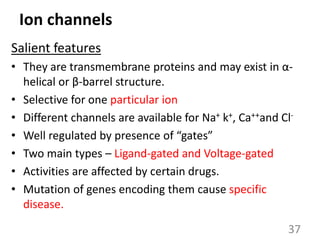
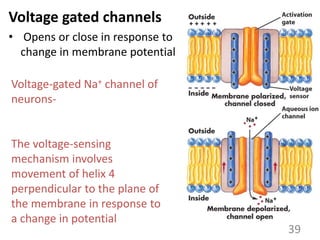
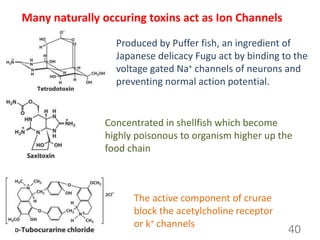
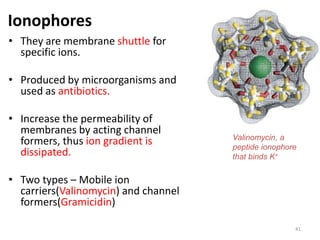
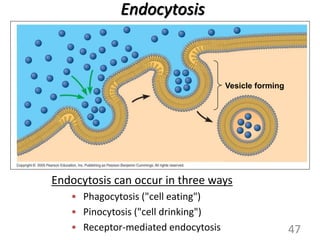
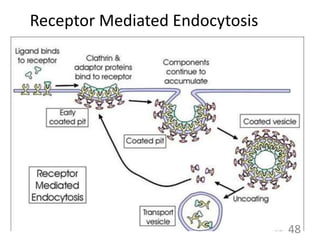
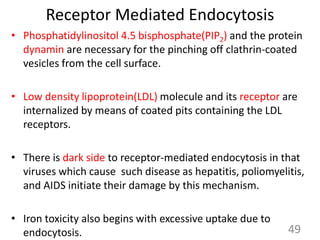
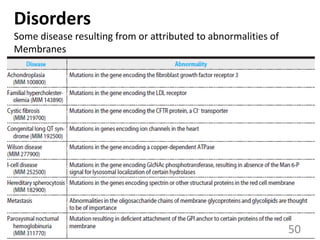
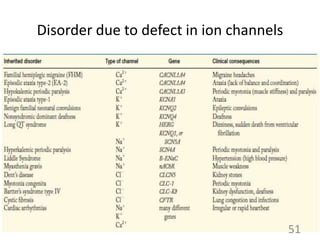
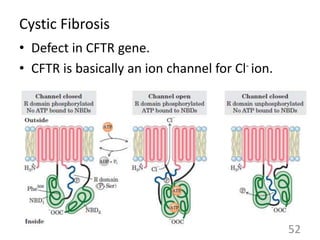
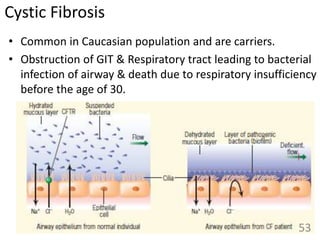
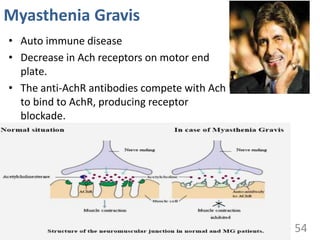
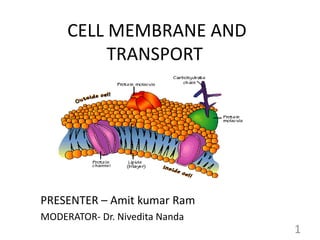
This document provides an overview of cell membranes and transport systems. It begins by defining the cell membrane and outlining its key functions, including maintaining cell integrity, selective permeability, and transport. It then describes the fluid mosaic model of the cell membrane's structure, which is composed of a phospholipid bilayer with embedded and peripheral proteins. Various types of membrane proteins and their functions are also discussed. The document focuses on different mechanisms of transport across the membrane, including simple diffusion, facilitated diffusion, active transport (primary and secondary), ion channels, and transporter proteins. Specific transport proteins like glucose transporters and ion pumps/channels are highlighted as examples.

![Cell Membrane
“Possibly the decisive step [in the
origin of life] was the formation of
the first cell, in which chain
molecules were enclosed by a semi-
permeable membrane which kept
them together but let their food in.”
James Danielli
(1911-1984)
3](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cellmembraneandtransport-150831114501-lva1-app6891/85/Cell-membrane-and-transport-3-320.jpg)