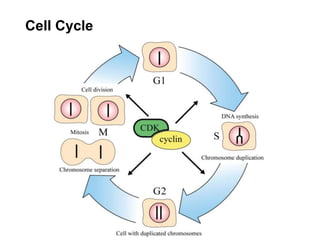
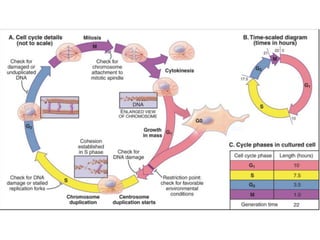
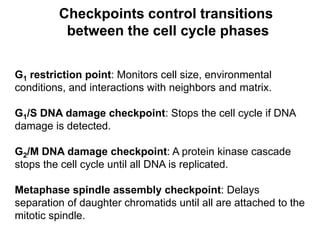
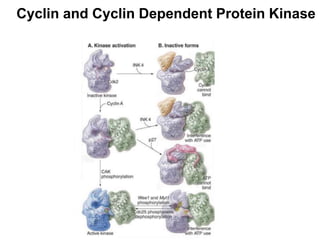
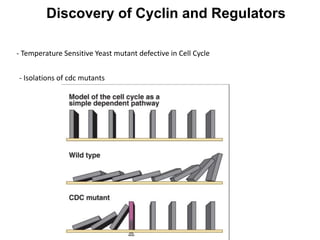
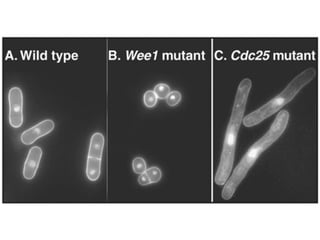
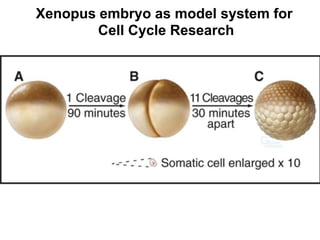
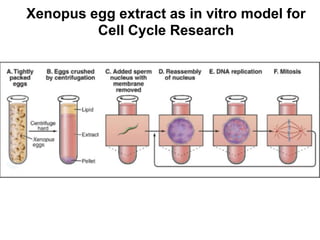
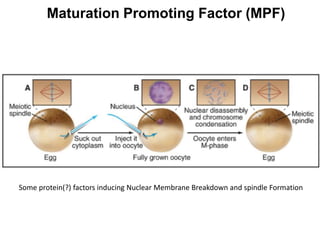
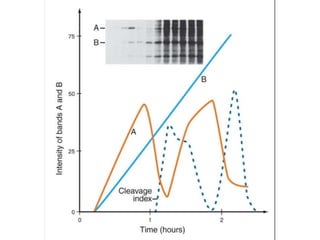
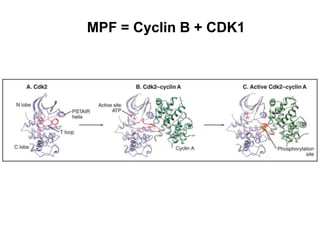
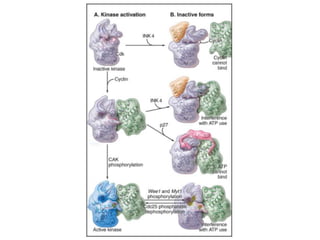
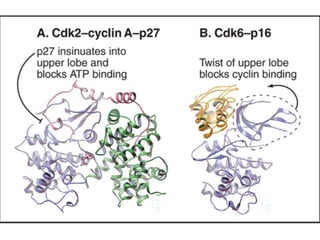
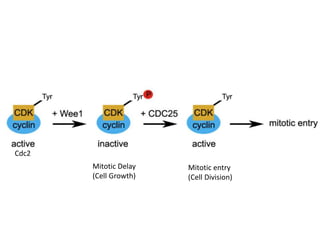
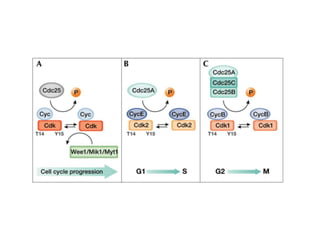
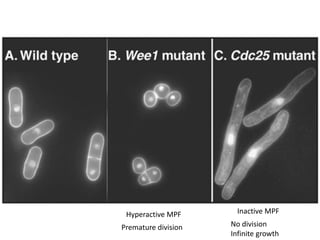
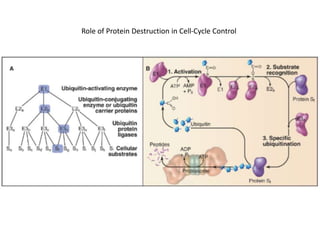
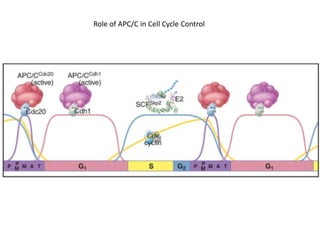
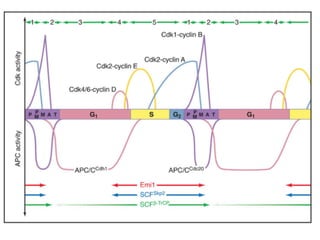
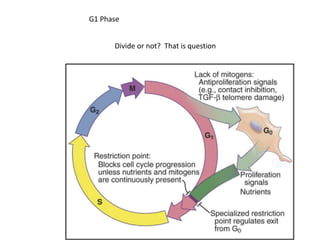
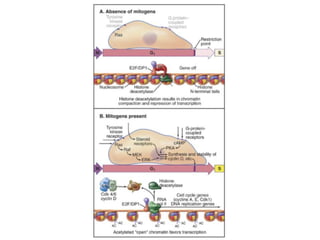
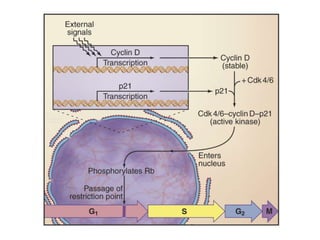
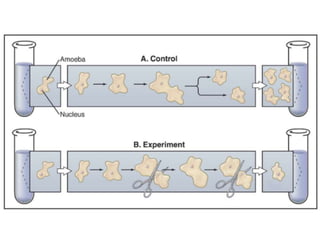
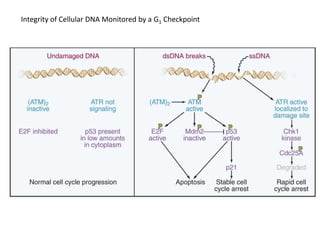
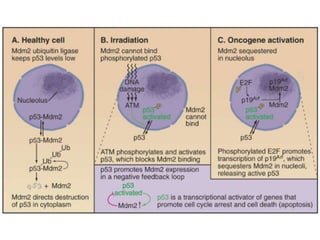
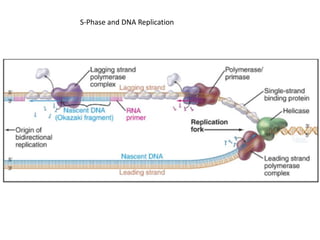
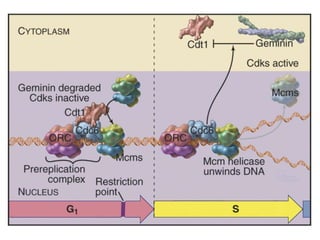
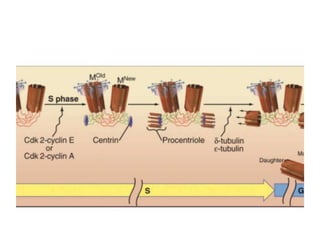
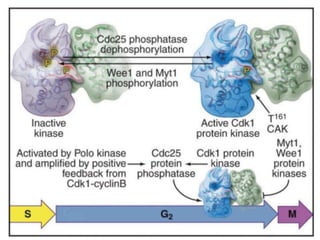
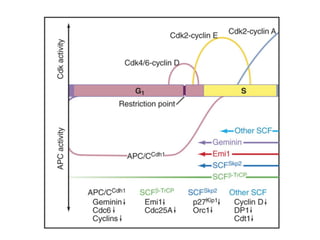
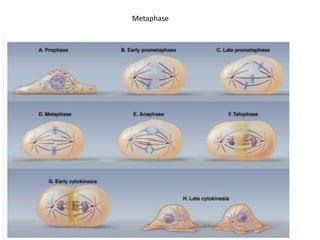
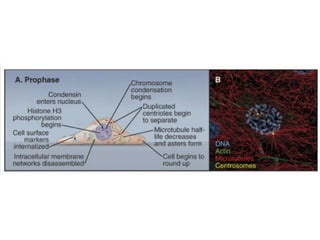
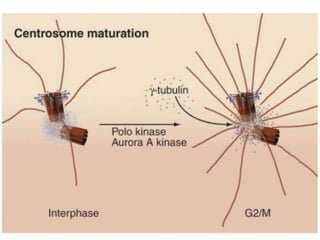
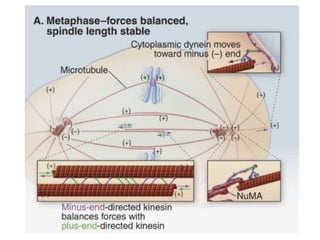
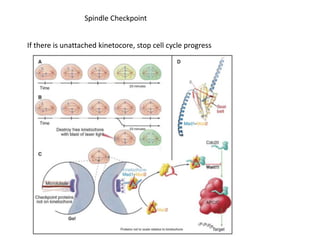
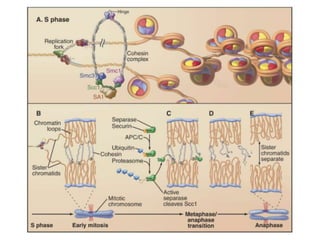
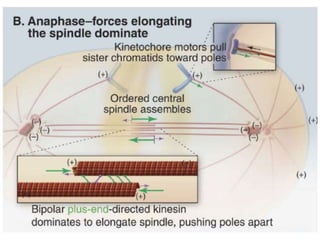
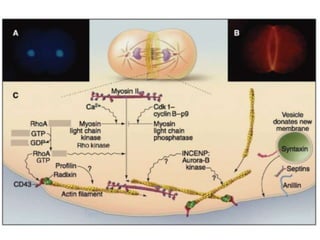
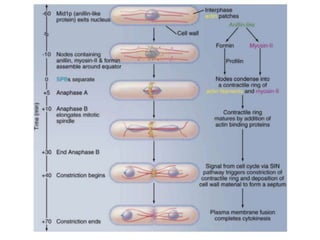
The document discusses the cell cycle and its regulation. It begins by outlining the four main phases: G1, S, G2, and M. Checkpoints exist to monitor DNA damage and proper chromosome attachment before transitions. Research led to the discovery of cyclins and cyclin-dependent kinases (CDKs) that control cell cycle progression. Specifically, maturation promoting factor (MPF), composed of cyclin B and CDK1, induces mitosis. Protein destruction via the anaphase promoting complex (APC) also regulates the cell cycle. Growth and DNA integrity checkpoints in G1 determine whether a cell divides.