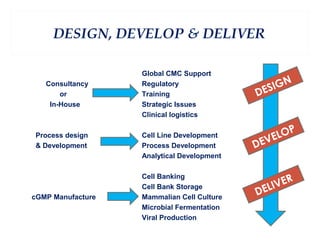
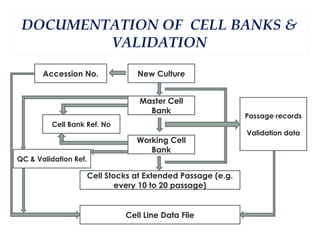
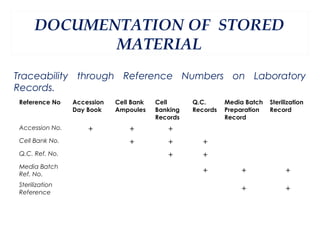
This document summarizes the key aspects of maintaining current good manufacturing practices (cGMP) for cell banks. It discusses the design, development, and delivery of cell banks. It defines cGMP and describes the cell banking system including master and working cell banks. It outlines the characterization, documentation, storage, and validation requirements for cell banks including testing for identity, purity, and stability. The goals are to ensure consistent production of safe, pure, and potent biotherapeutic products through well-characterized and validated cell banks.