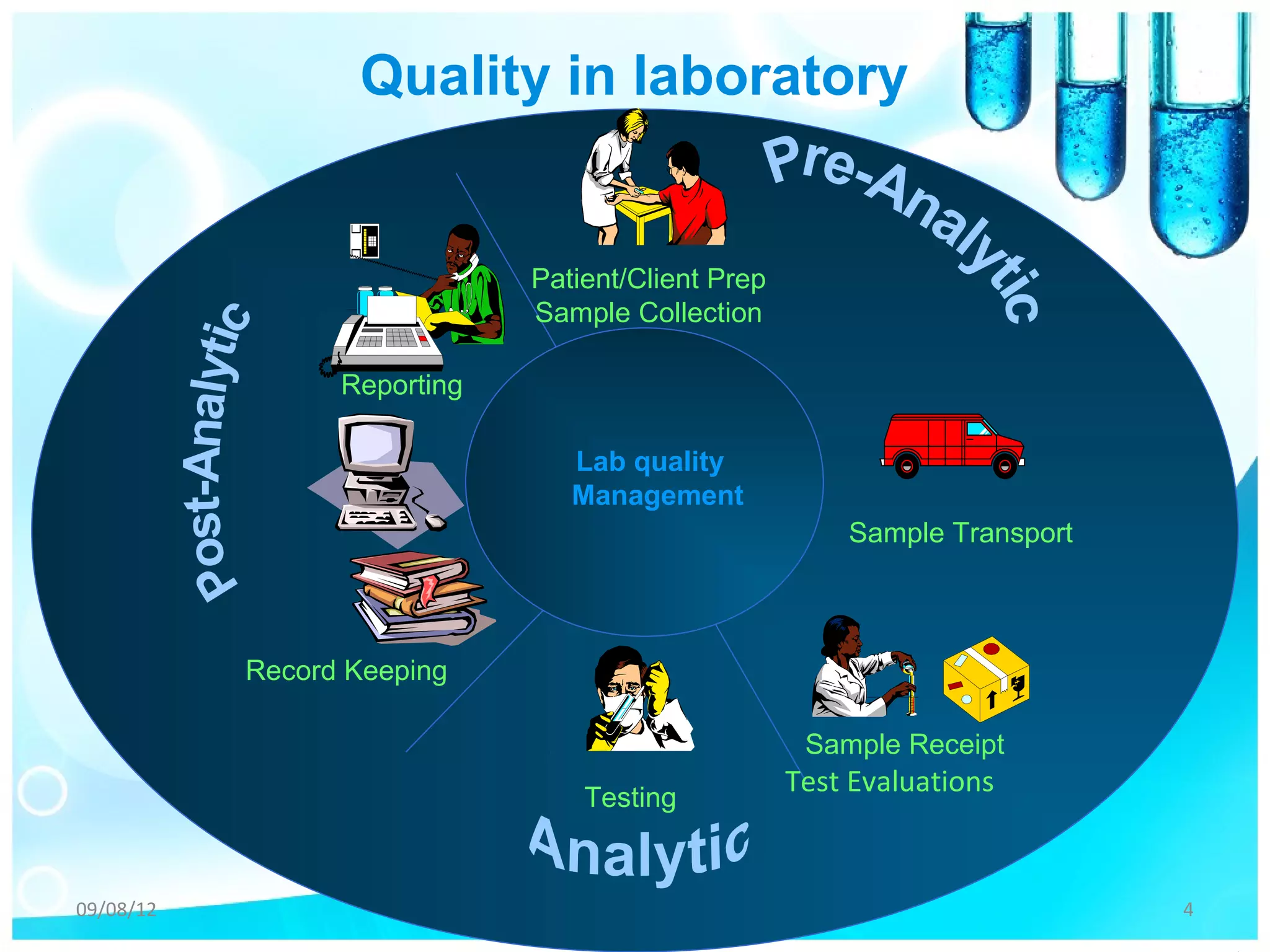
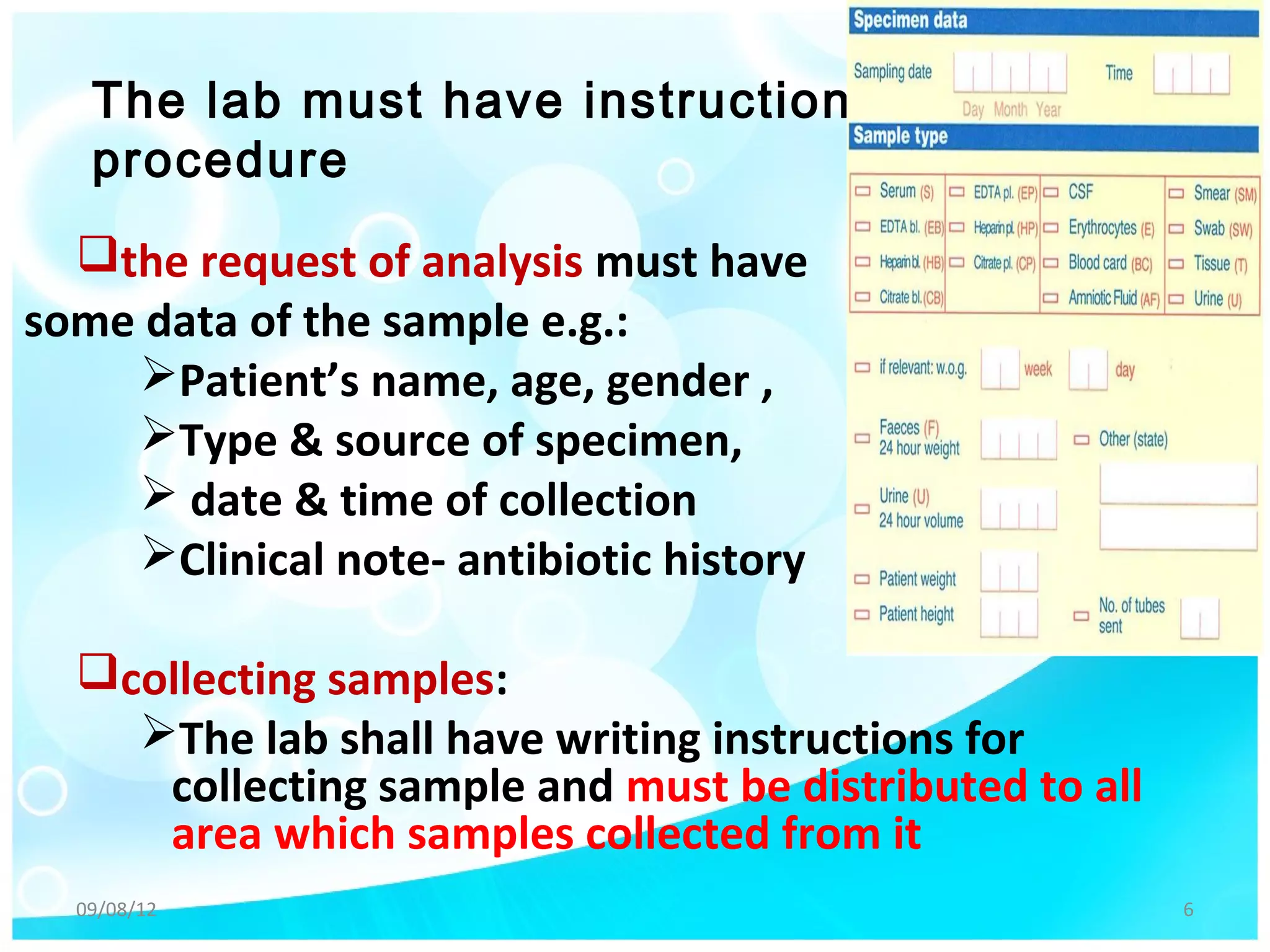
The document outlines the principles of quality management in microbiological laboratories, emphasizing the importance of pre-analytical, analytical, and post-analytical factors for ensuring accurate results. It details procedures for specimen collection, transportation, equipment calibration, and quality control measures for stains, reagents, and media. Documentation practices are also highlighted to maintain proper records and ensure compliance with standards.