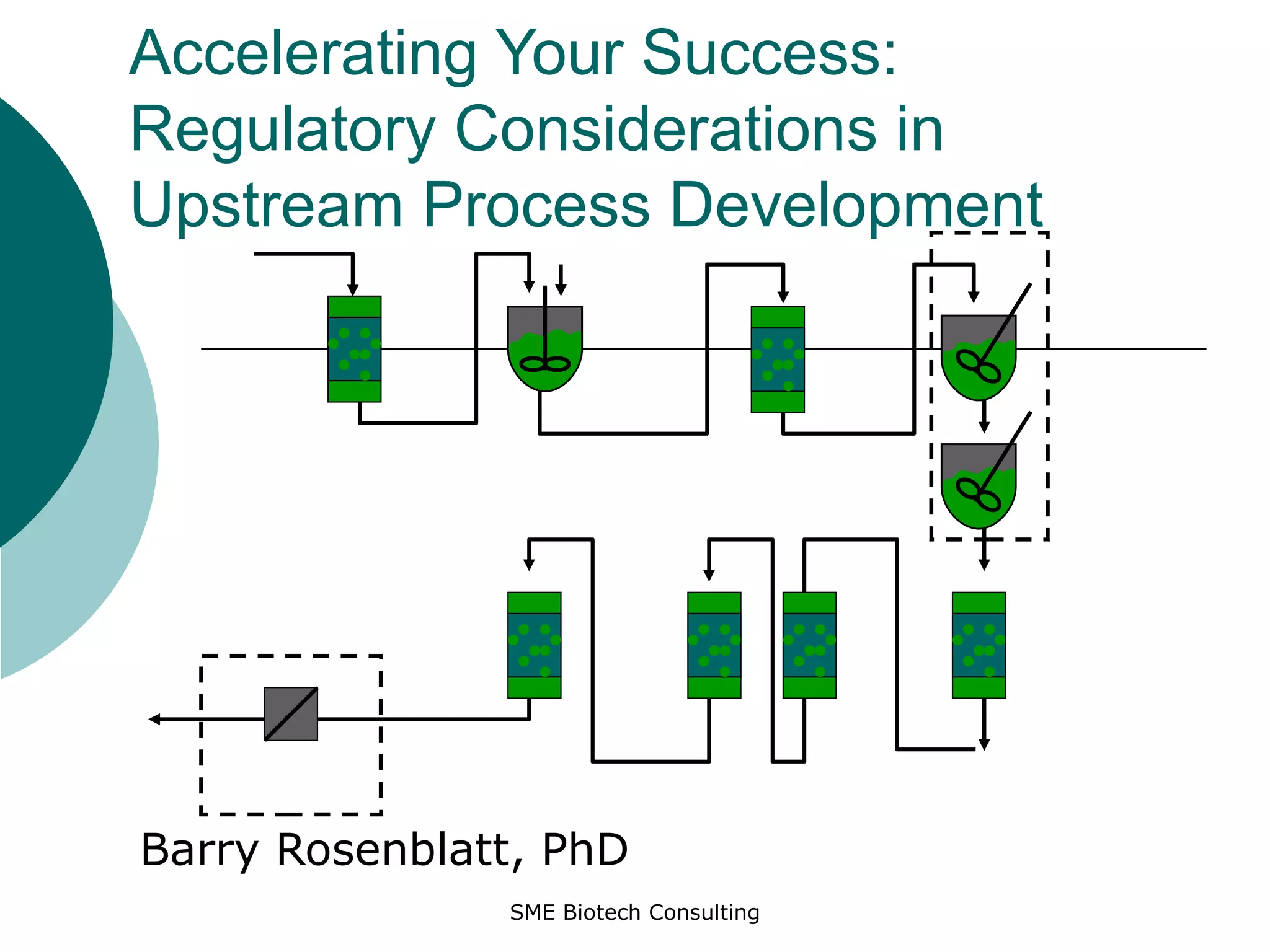
The document discusses regulatory guidelines for characterization of continuous cell lines used in bioprocessing. It outlines the key definitions, tests, and guidelines recommended by ICH, FDA, and EU for master cell banks, working cell banks, and end-of-production cells. These include testing for sterility, mycoplasma, adventitious agents, karyotyping, and more. The guidelines aim to ensure safety and consistency of cell lines used in biotherapeutic production.