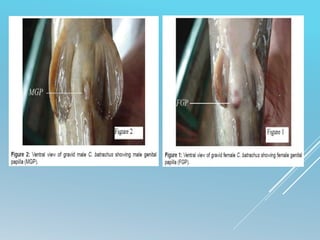
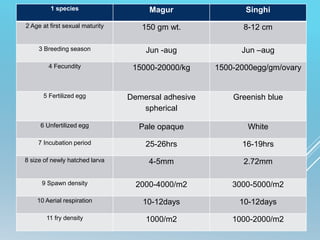
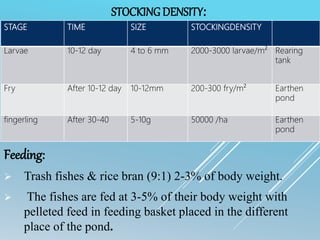
The document is a seminar submission on the breeding and culture of catfishes, specifically magur (Clarias batrachus) and singhi (Heteropneustes fossilis), detailing their classification, reproductive biology, brood stock maintenance, and induced breeding techniques. It covers aspects like hormone administration, incubation, and larval rearing, along with advantages and methods for successful aquaculture of these species in various environments. The document emphasizes the economic significance and market demand for catfishes in India.