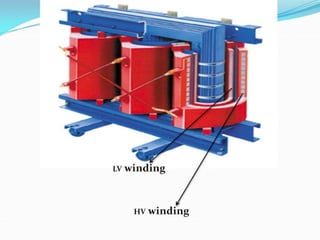
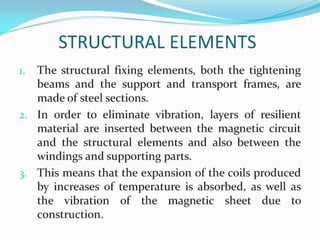
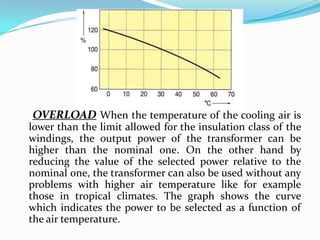
Cast resin transformers provide several advantages over oil-filled transformers including being non-flammable, fire safe, and maintenance free as they do not use liquids. They also have high overload capability and can operate using only air cooling. While cast resin transformers have a larger physical size and initially higher purchase cost than oil transformers, they are increasingly used where safety, environmental protection, space, and overall life cycle costs are primary concerns.