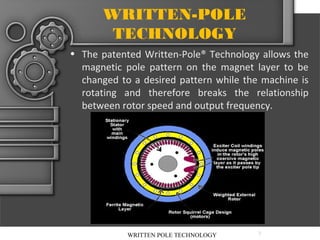
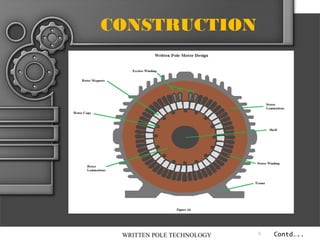
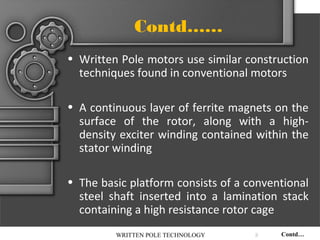
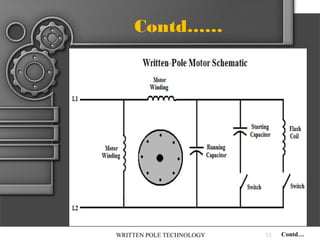
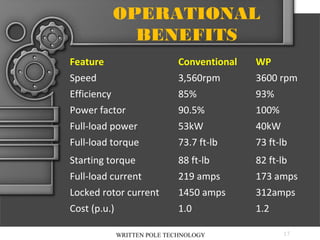
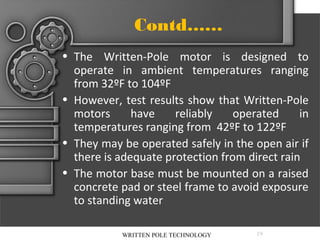
The document describes written-pole electric motor technology, which was developed in the 1990s as a new type of single-phase electric motor that dramatically reduces starting currents. It does this through an innovative approach of controlling the magnetic field in the motor to generate a rotating field. Written-pole motors have starting currents only twice as high as normal running currents, and efficiencies as high as 90% compared to 85% for conventional motors. The technology works by writing the magnetic pole pattern on the rotor magnet layer while it rotates, breaking the relationship between rotor speed and output frequency. This allows benefits like low starting current, high efficiency, and the ability to ride through brief power interruptions.