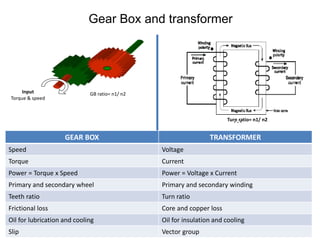
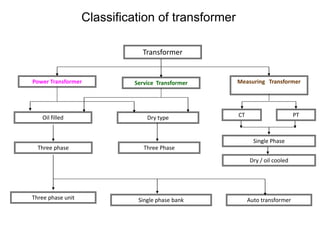
1. The document discusses different types of transformers used in power plants including power transformers, service transformers, and measuring transformers.
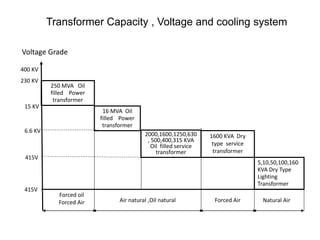
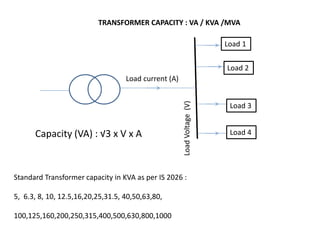
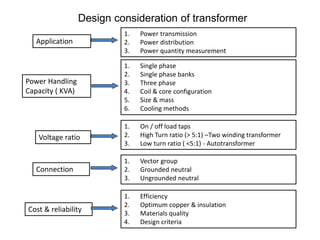
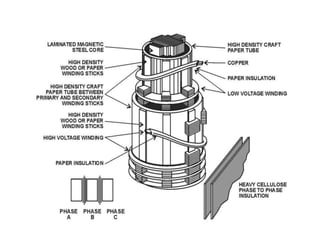
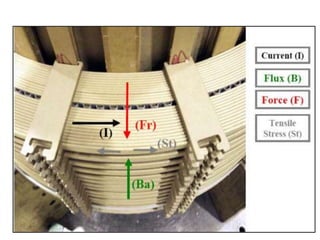
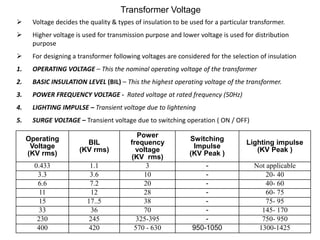
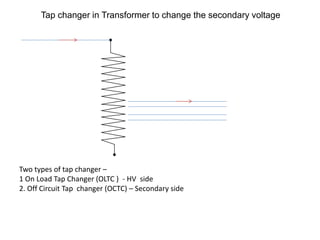
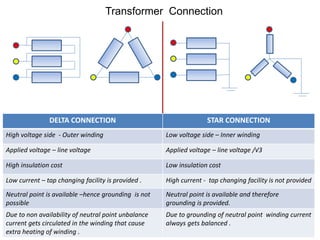
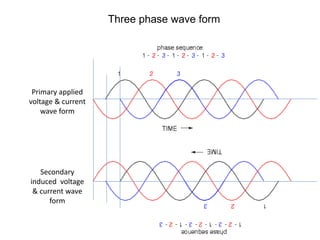
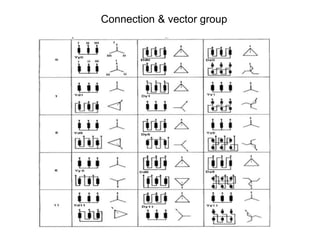
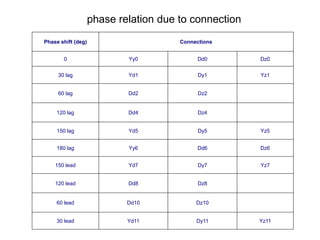
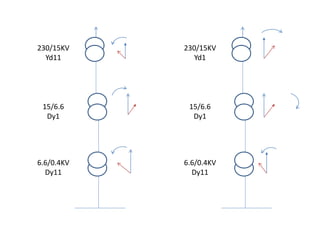
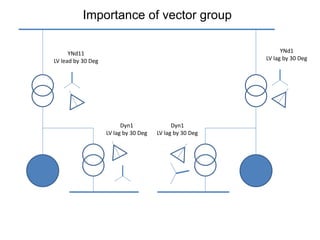
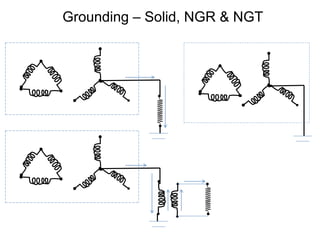
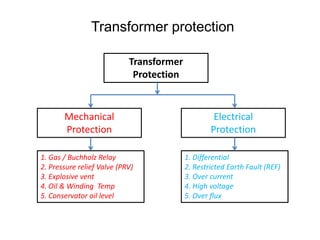
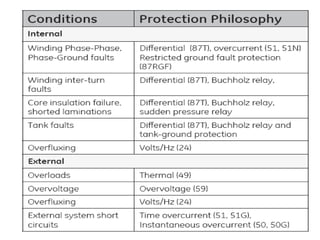
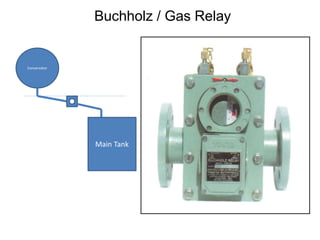
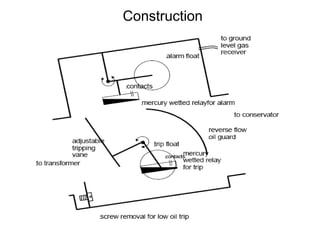
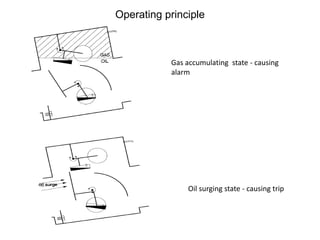
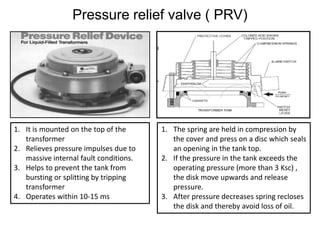
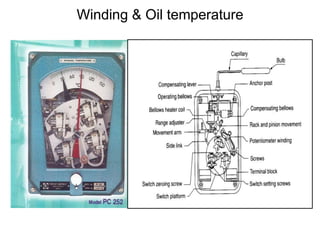
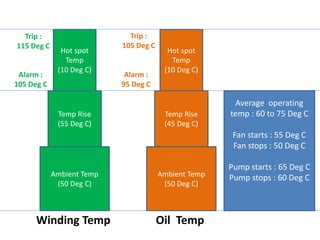
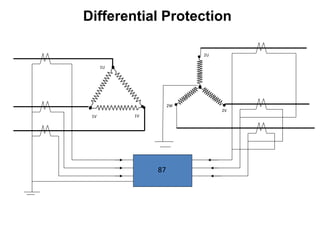
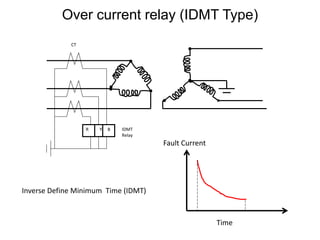
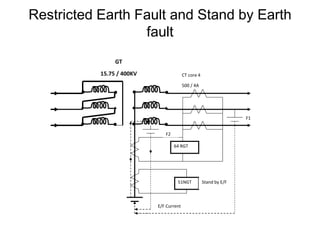
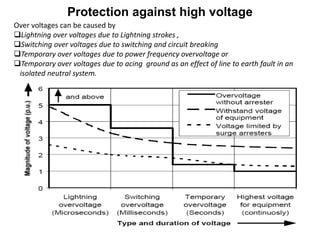
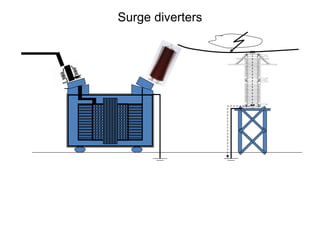
2. It describes key components of transformers like the core, windings, cooling systems, and protections devices. Transformer connections, vector groups, and voltage classifications are also covered.
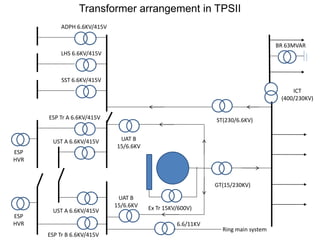
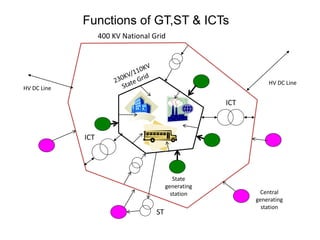
3. Various transformers used in thermal power plants are discussed including generator transformers, station transformers, unit auxiliary transformers, and those used for distribution within the plant.