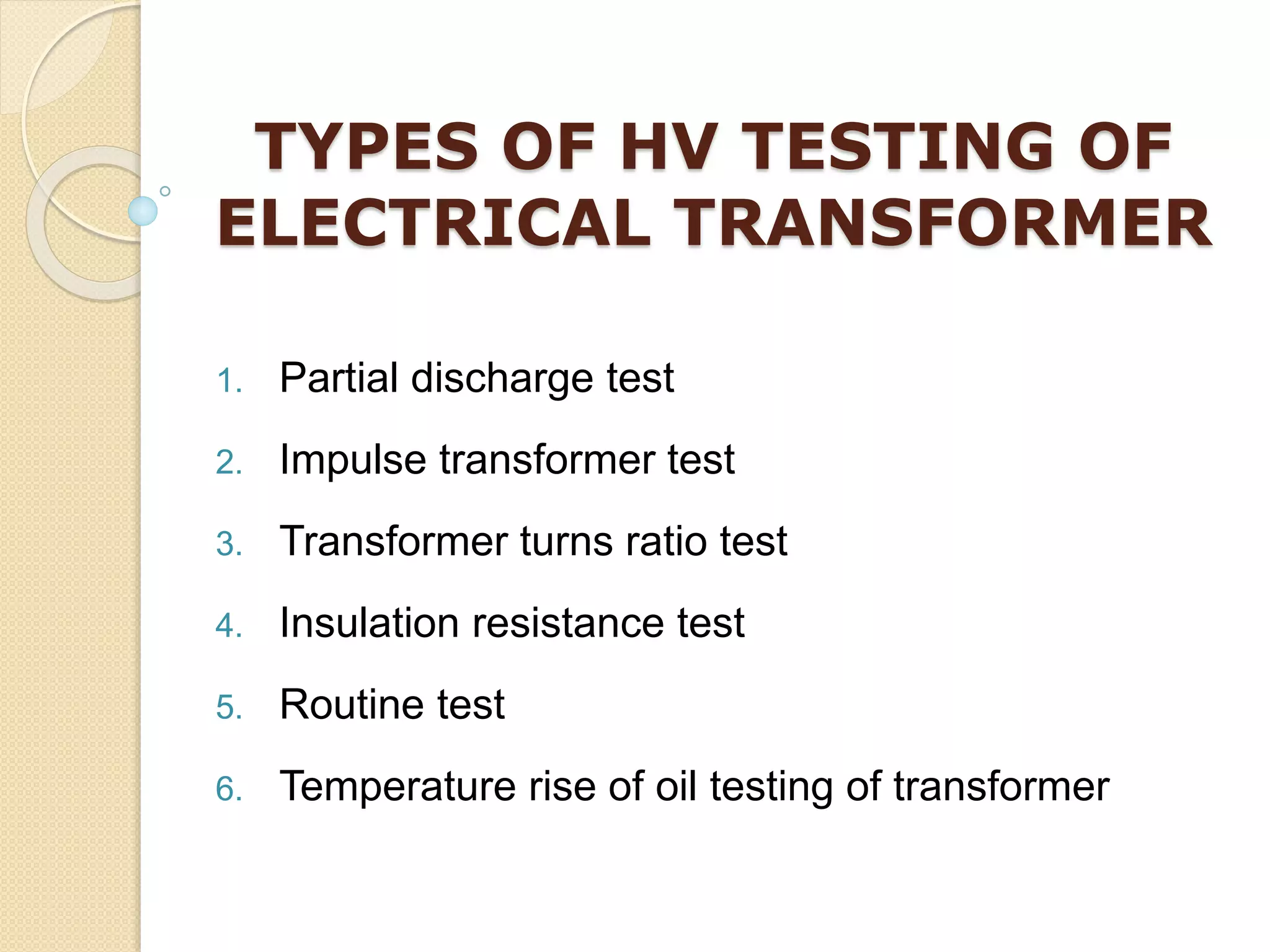
1. The document discusses high voltage testing of electrical transformers, including various types of tests like partial discharge testing, impulse testing, turns ratio testing, and insulation resistance testing.
2. These tests help check the insulation quality, detect defects, verify voltage ratios, and ensure transformers can withstand high voltage surges to prevent failures.
3. High voltage testing provides advantages like improved safety, energy efficiency, lower costs, and failure detection; but can also have disadvantages like not removing the root causes of failures.