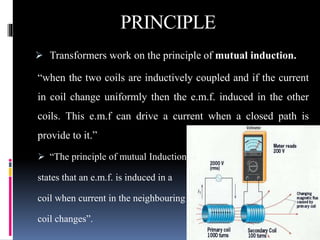
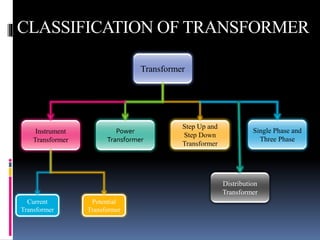
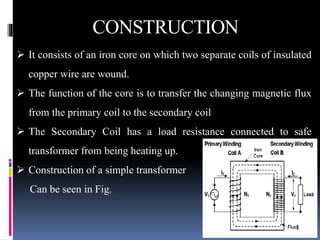
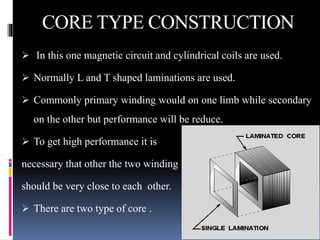
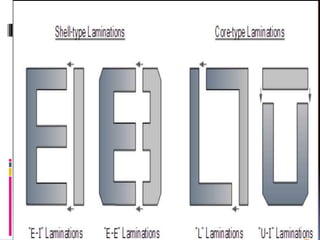
This document presents a summer training presentation on transformers, detailing their function, construction, and testing processes. It includes an introduction to the company 'Danish Private Limited' and covers various aspects such as transformer classification, working principle, and application. Additionally, the presentation outlines the advantages and disadvantages of transformers in the electrical engineering field.