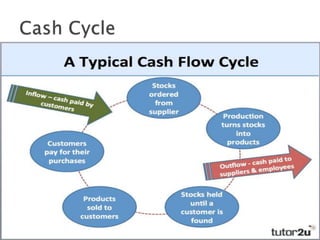
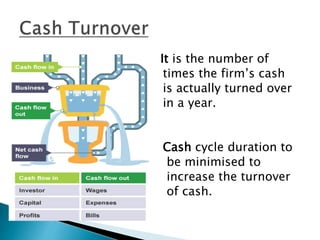
This document discusses cash management strategies for businesses. It describes cash as a medium of exchange that includes notes, coins, checks, and bank deposits. It then outlines strategies for managing cash flow, including:
1) Preparing cash budgets and using concentration banking to quickly collect and deposit receipts across collection centers.
2) Implementing lockbox collections where local banks directly deposit receipts to reduce clearance time.
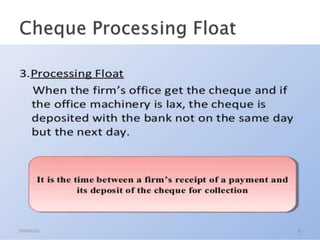
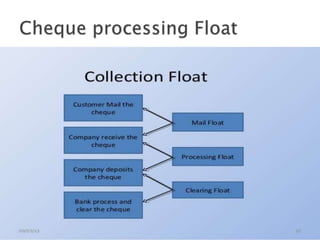
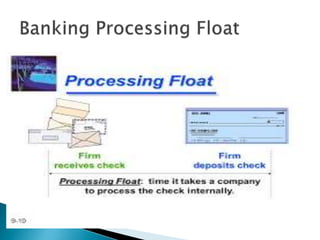
3) Accelerating collections, delaying payments to the due date, and using floats to the firm's advantage to maximize available cash.