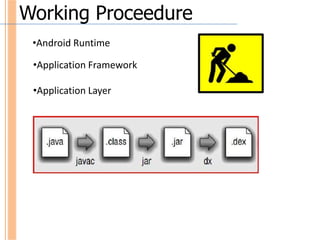
Google acquired Android Inc. in 2005 and launched the Android mobile operating system in 2007 with the Open Handset Alliance, including companies like Qualcomm. Android uses the Linux kernel for core functions and relies on Java for application development. It has an open source model and uses components like SQLite for data storage, Dalvik virtual machine, and integrated browser. While popular for its openness and customization, Android faces security and compatibility challenges. Overall it has become very successful with the mobile market.