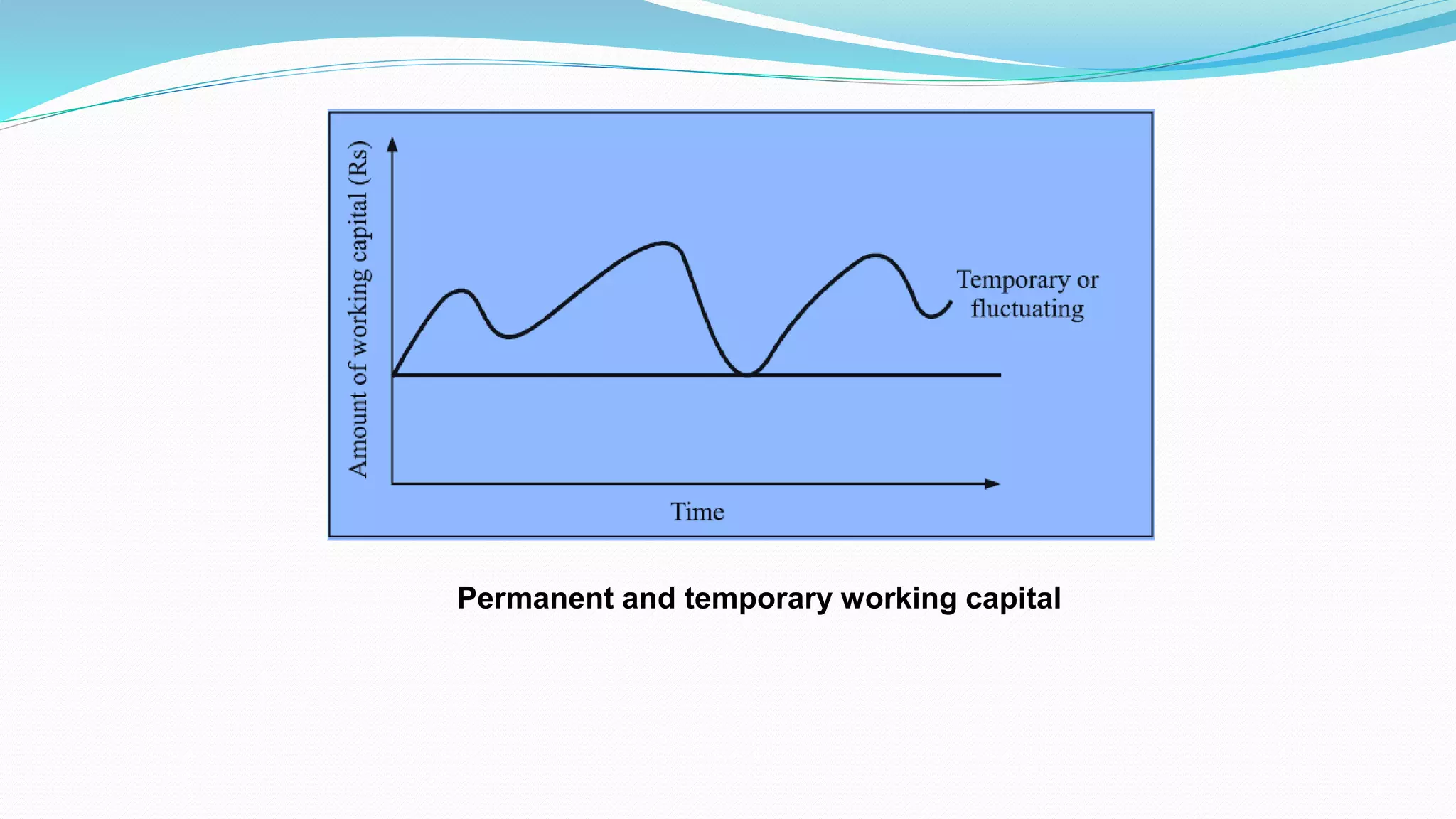
The document discusses working capital management, which involves managing a firm's current assets and liabilities. It explains the concepts of gross and net working capital, the operating cycle, and the importance of adequate working capital for business solvency and growth. Additionally, it covers the disadvantages of excessive or inadequate working capital and various methods of financing working capital.