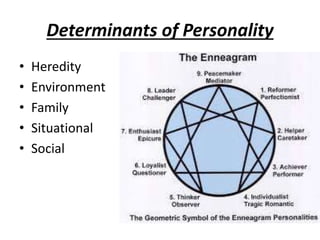
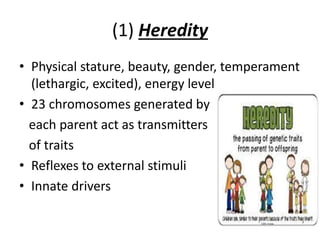
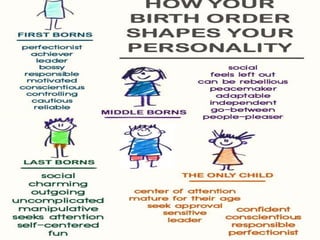
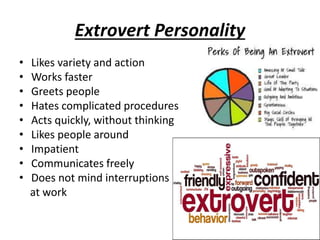
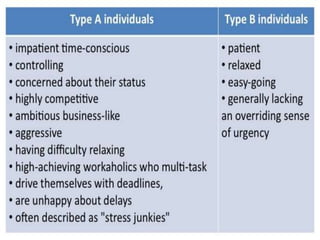
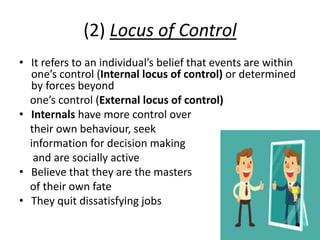
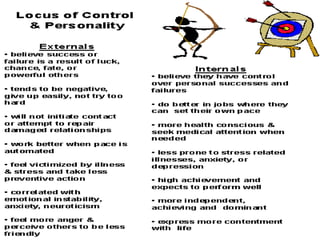
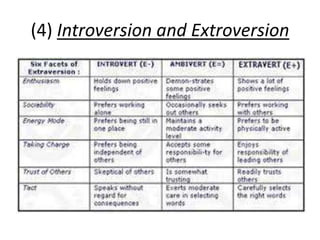
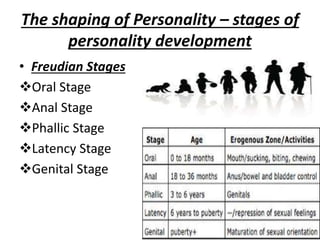
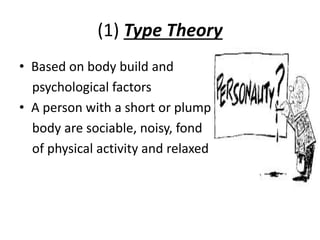
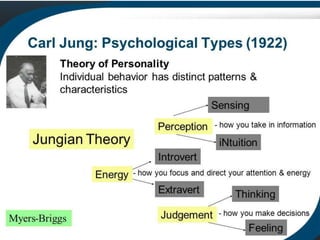
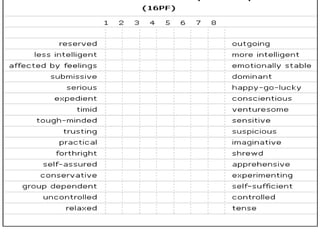
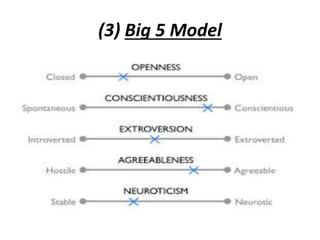
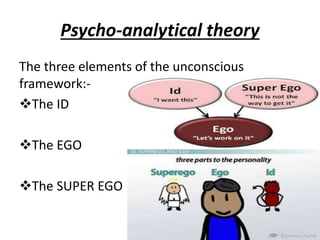
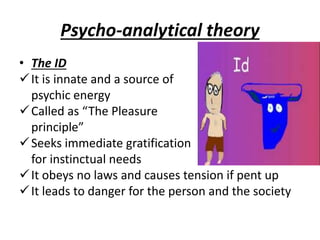
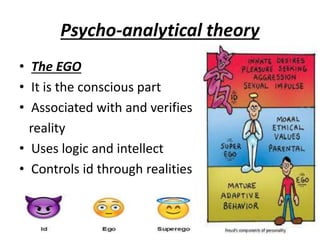
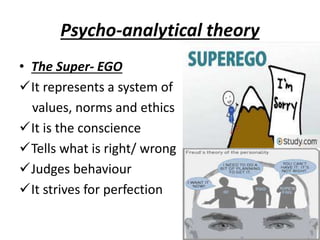
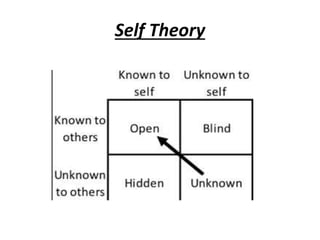
The document is a comprehensive study on personality by Dr. Malathi Selvakkumar, defining personality as the sum of an individual's psychophysical systems influencing behavior. It explores the determinants of personality, including heredity, environment, family, situational, and social factors, as well as various personality types and traits. Additionally, it discusses theories of personality development, including Freudian and Eriksonian stages, and various personality theories such as the Big Five, psychoanalytical theory, and social learning theory.