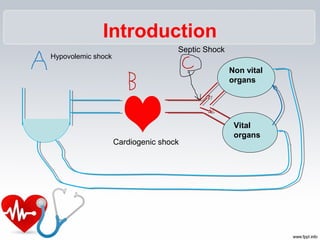
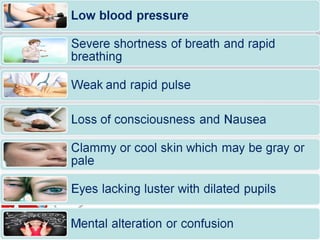
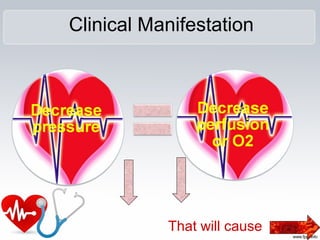
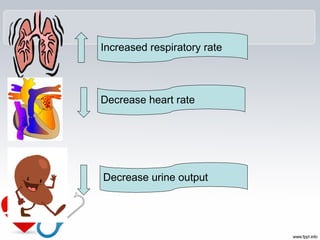
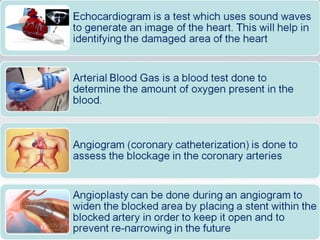
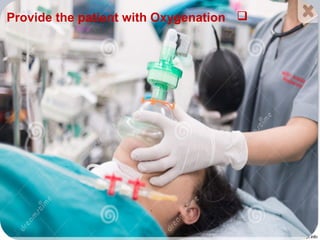
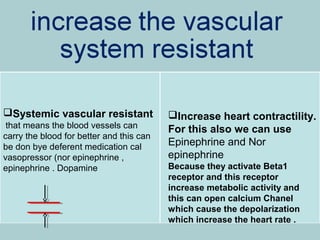
Cardiogenic shock is a life-threatening condition caused by the heart's inability to pump enough blood to meet the body's needs, usually due to a severe heart attack damaging the heart muscle. Symptoms include increased respiratory rate, decreased heart rate, decreased urine output, and decreased consciousness. Treatment focuses on oxygenation, increasing systemic vascular resistance through vasopressors like epinephrine and norepinephrine, and improving heart contractility with medications that activate beta-1 receptors. Preventing cardiogenic shock involves maintaining a healthy heart through lifestyle.