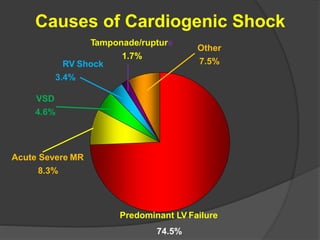
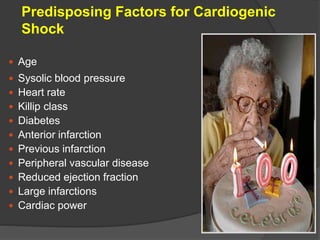
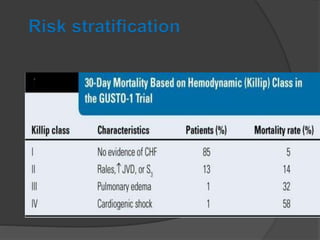
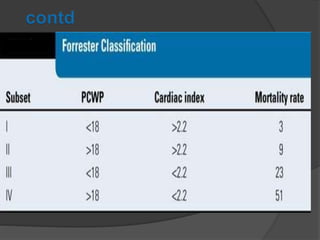
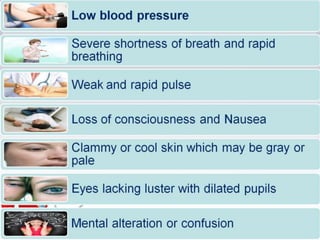
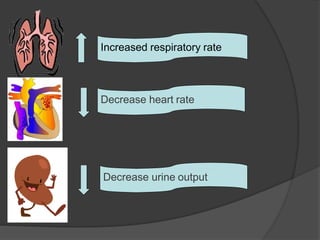
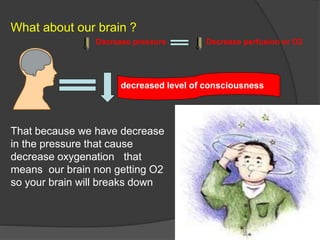
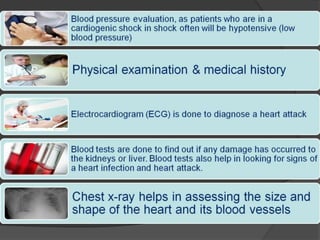
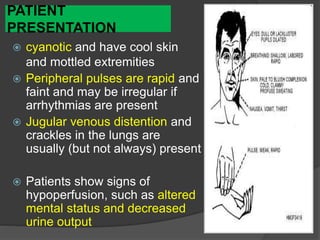
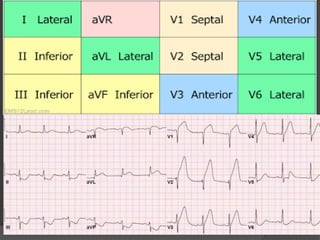
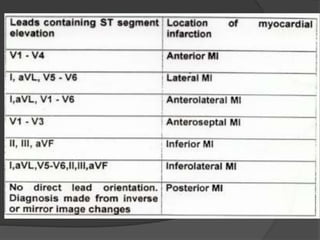
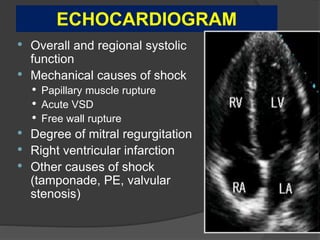
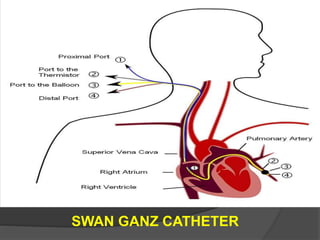
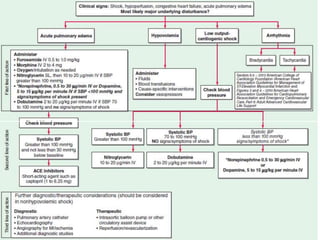
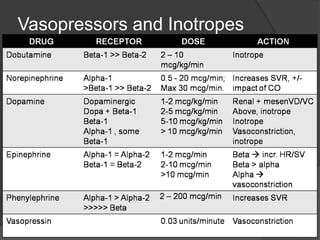
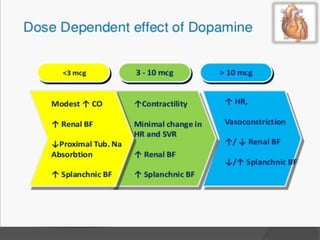
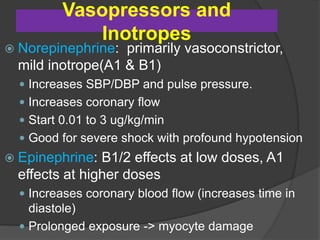
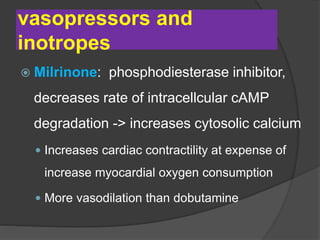
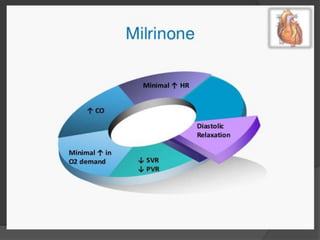
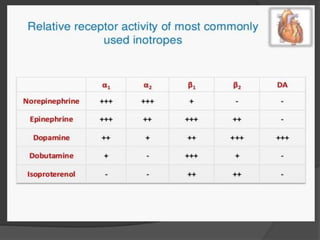
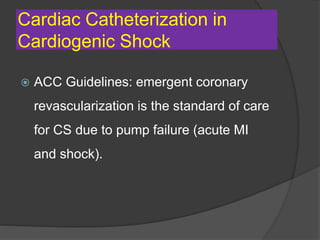
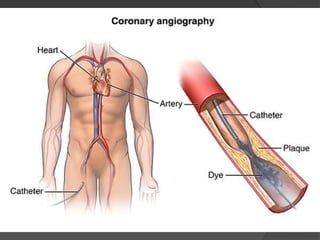
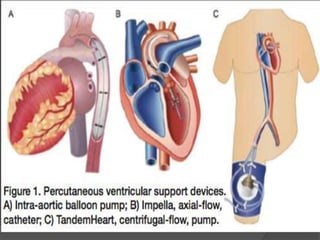
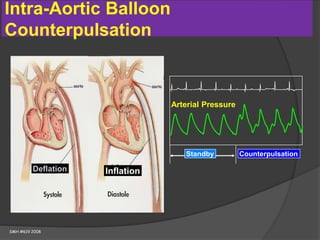
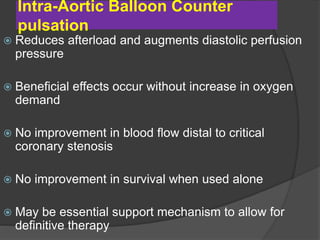
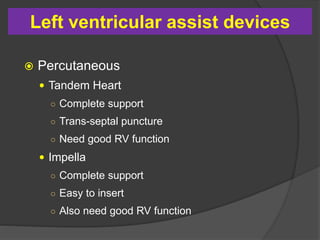
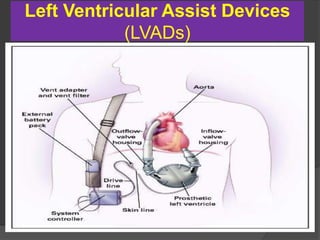
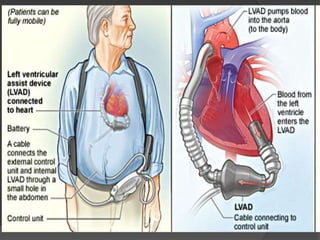
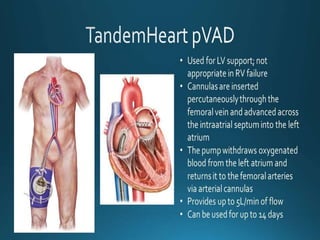
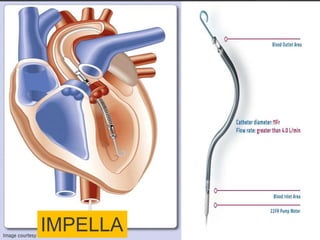
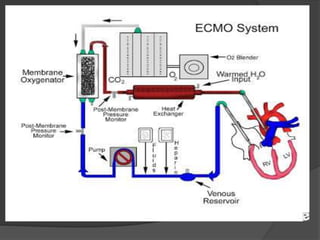
Cardiogenic shock is defined as inadequate tissue perfusion due to cardiac dysfunction or hypo-perfusion of end organs due to cardiac failure. It has a high mortality rate of 50-80% and is most commonly caused by extensive acute myocardial infarction. Symptoms include cyanosis, decreased consciousness, and low blood pressure. Diagnosis involves identifying hypotension, low cardiac index, and signs of hypoperfusion on physical exam along with supportive tests like EKG, echocardiogram, and Swan-Ganz catheter. Treatment focuses on optimizing prefusion with vasopressors or inotropes, diuretics, emergent revascularization through cardiac catheterization, and mechanical circulatory support like IABP,