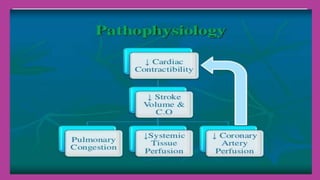
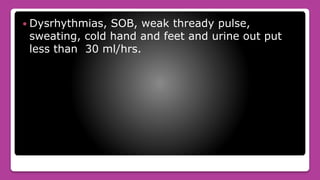
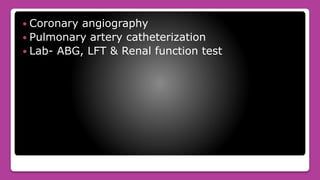
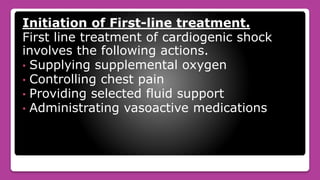
Cardiogenic shock is the failure of the heart to pump enough blood to meet the body's needs due to loss of contractile function. It most commonly occurs after a myocardial infarction which damages a significant portion of the left ventricle. Symptoms include low blood pressure, rapid breathing, decreased urine output, and confusion. Treatment involves oxygen, medications to improve contractility and reduce workload, and mechanical devices like IABP if needed. Nursing care focuses on monitoring circulation and tissue perfusion, managing devices, and addressing patient anxiety.