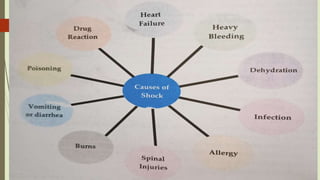
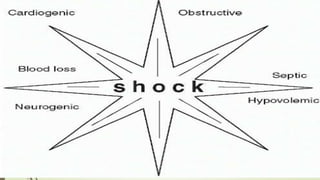
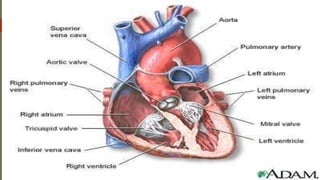
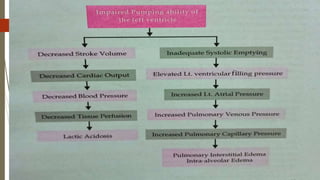
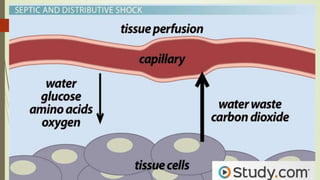
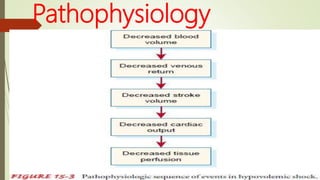
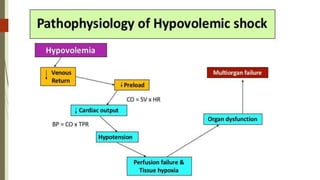
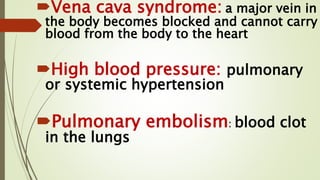
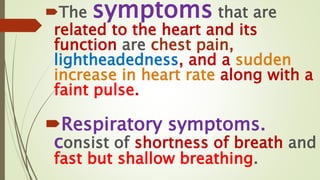
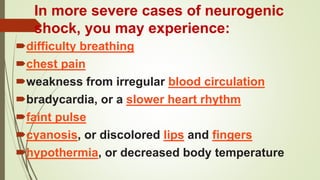
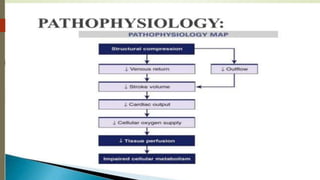
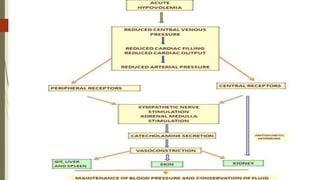
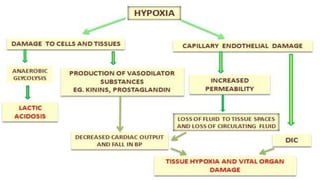
Shock is a life-threatening condition where the body's tissues do not receive enough blood flow and oxygen. There are several types of shock including cardiogenic, hypovolemic, obstructive, and distributive shock. Distributive shock includes anaphylactic, septic, and neurogenic shock. Shock progresses through initial, progressive, and irreversible stages characterized by worsening signs and symptoms as compensatory mechanisms fail. Treatment depends on the underlying cause but aims to restore adequate blood flow and oxygen delivery to tissues.