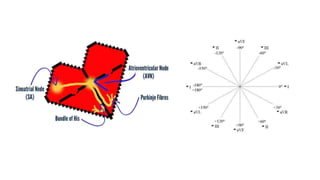
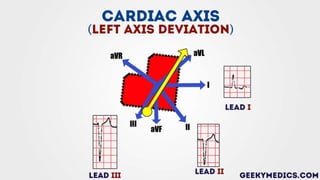
The document discusses the cardiac axis and methods for determining it from an electrocardiogram (ECG). The cardiac axis represents the overall direction of electrical conduction through the heart. It is normally between -30° and +90° but can deviate left or right. Left axis deviation occurs between -30° and -90° and may indicate conduction abnormalities, while right axis deviation is between +90° and +180° and can be caused by right ventricular hypertrophy. The hexaxial reference system and other methods are described for calculating the axis from the ECG readings.