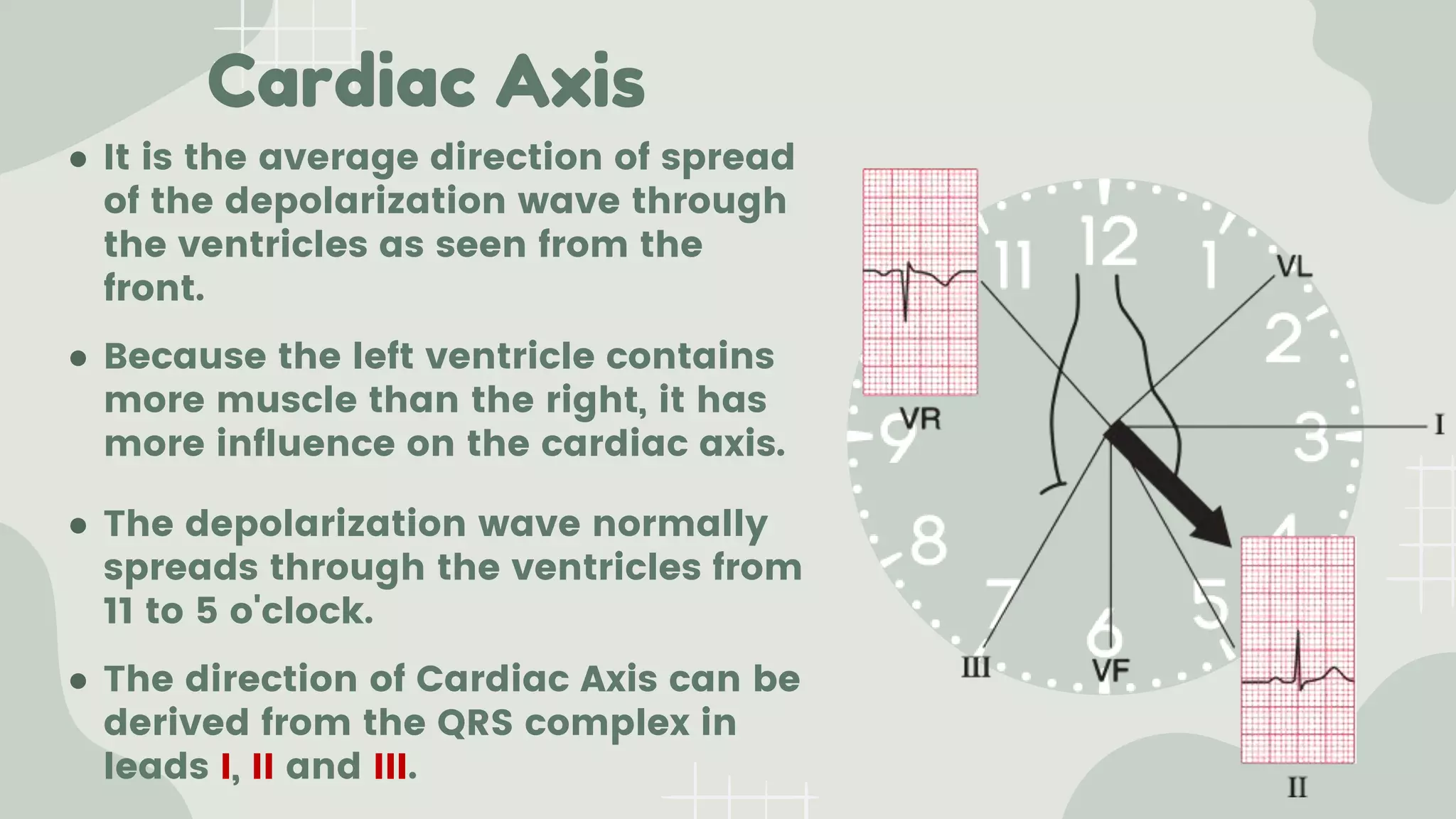
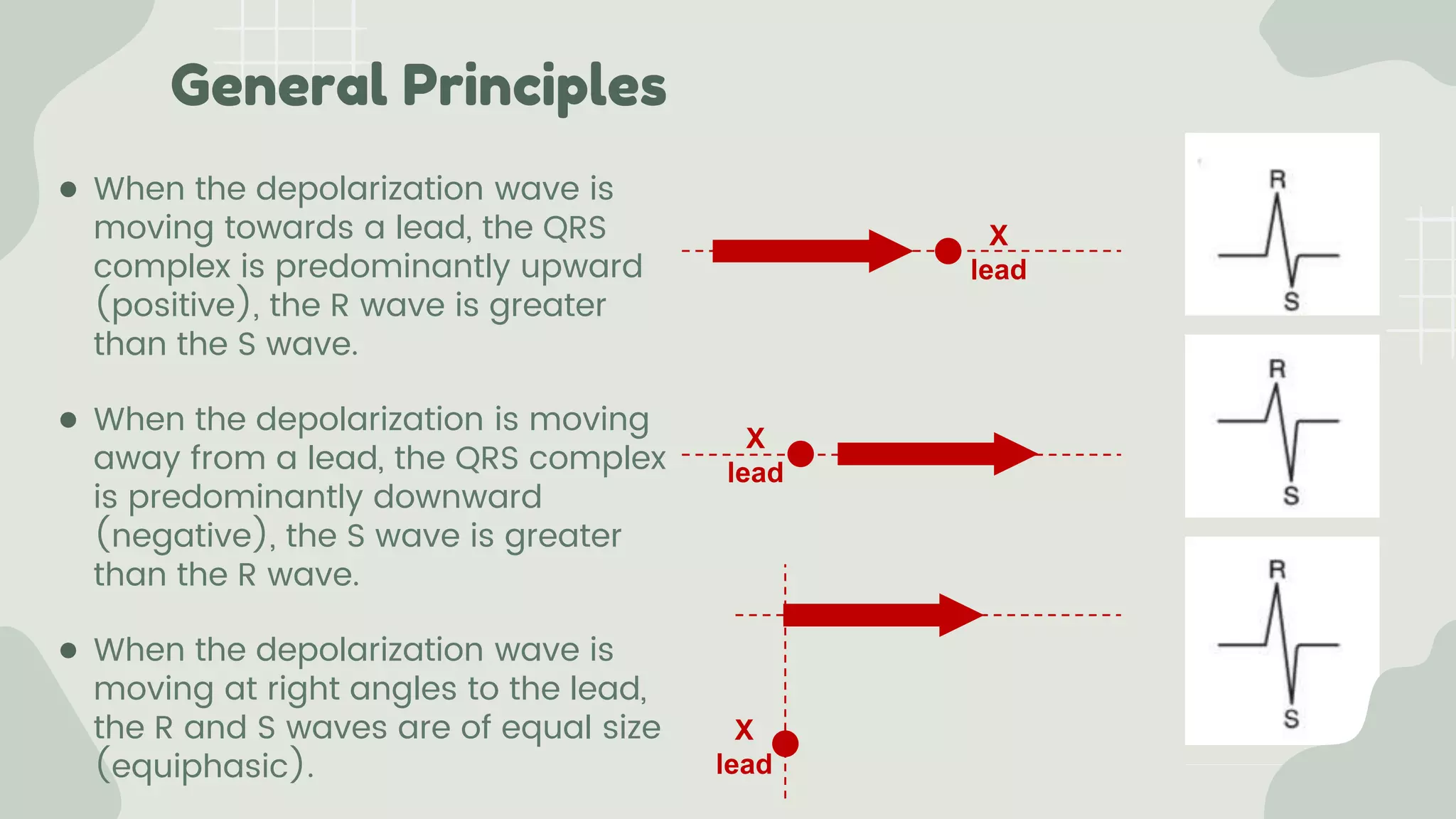
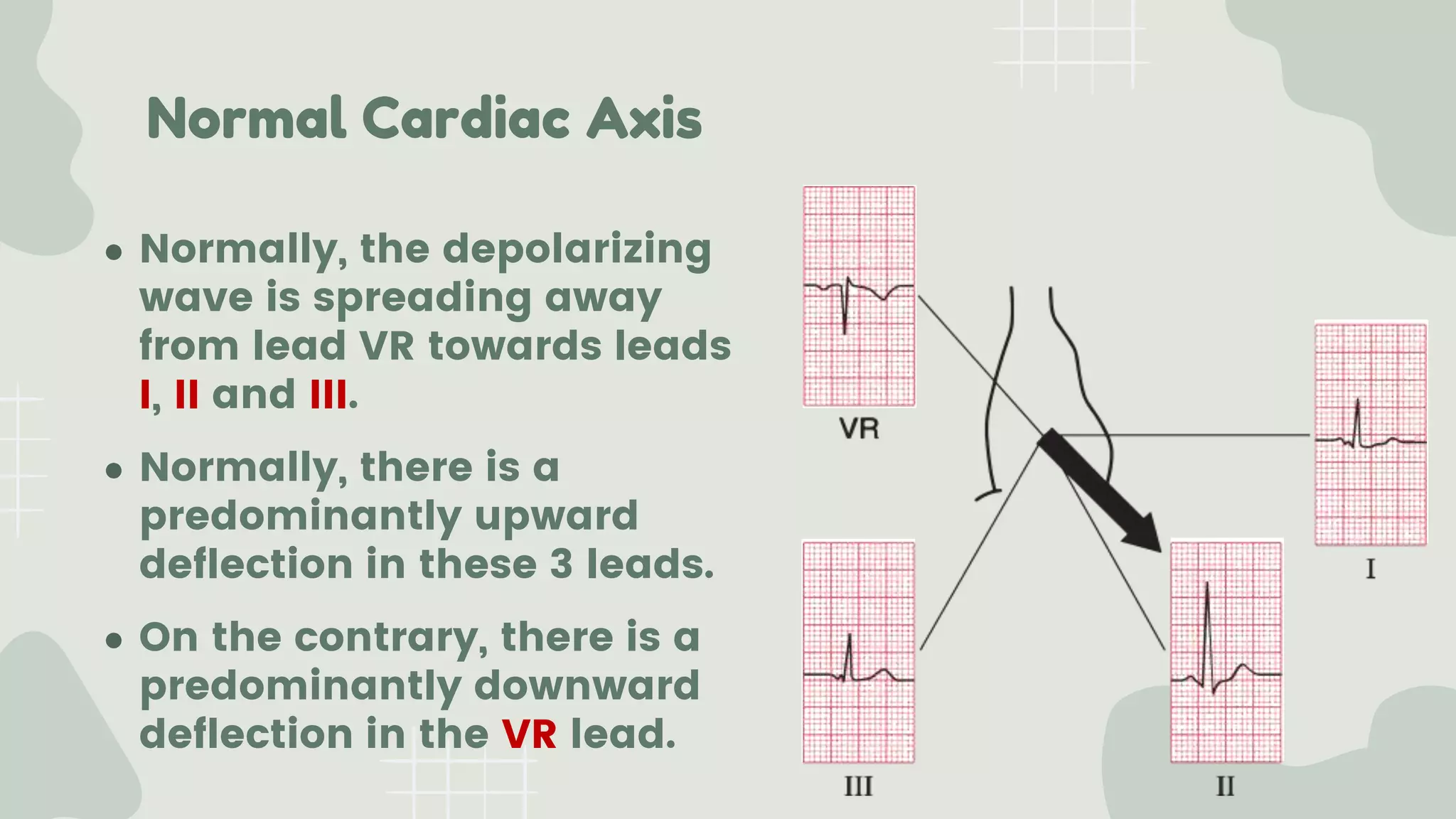
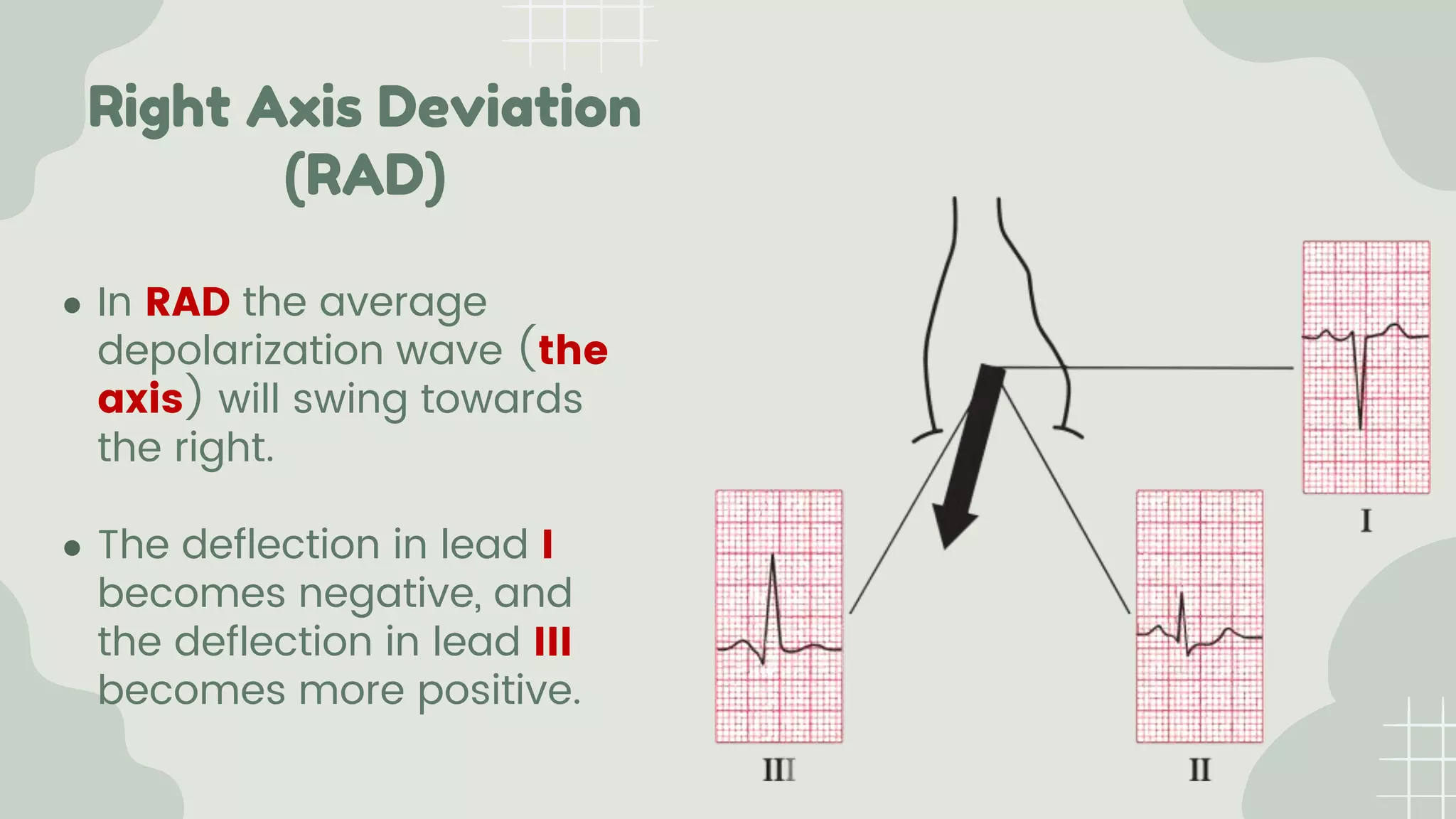
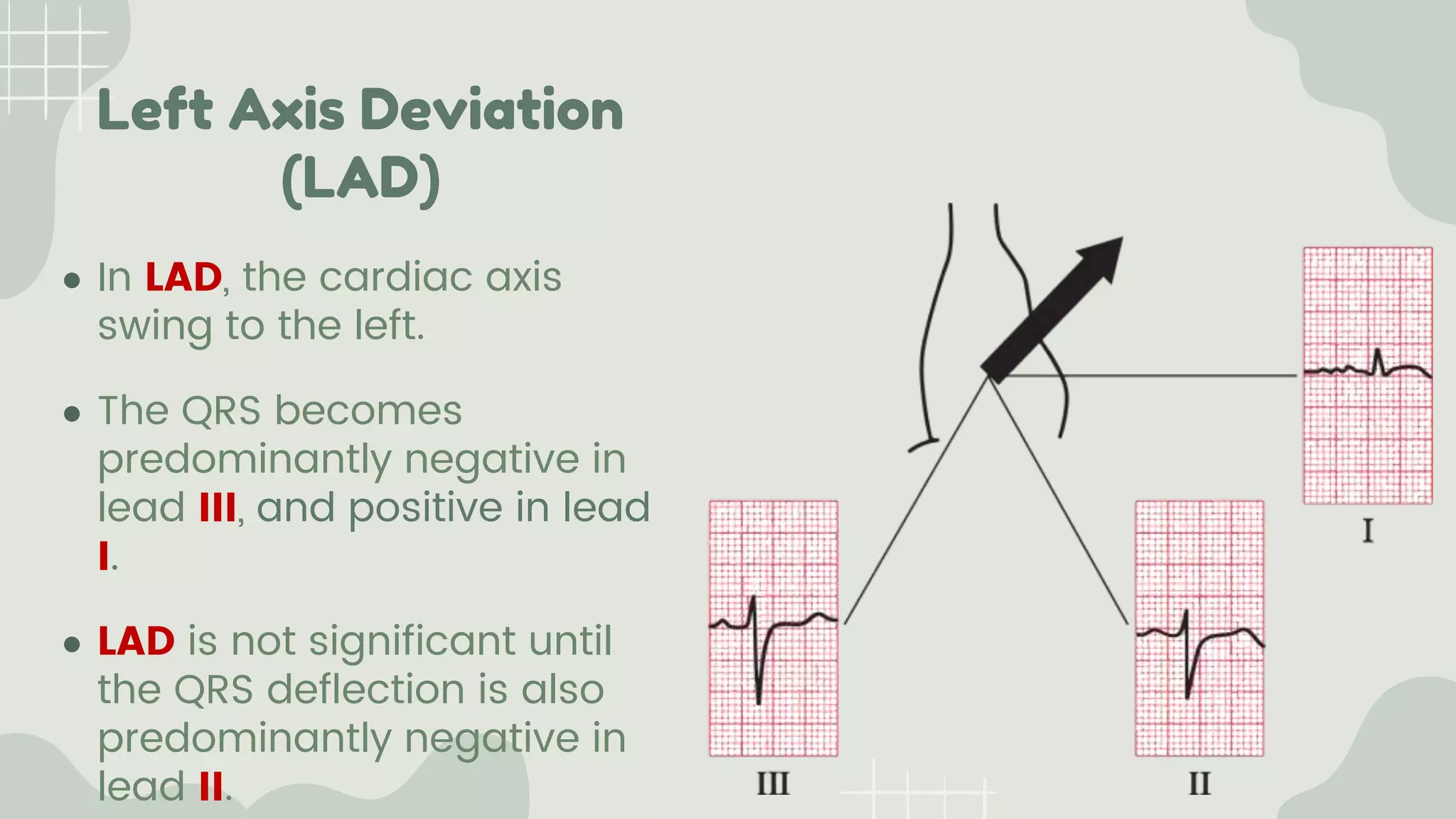
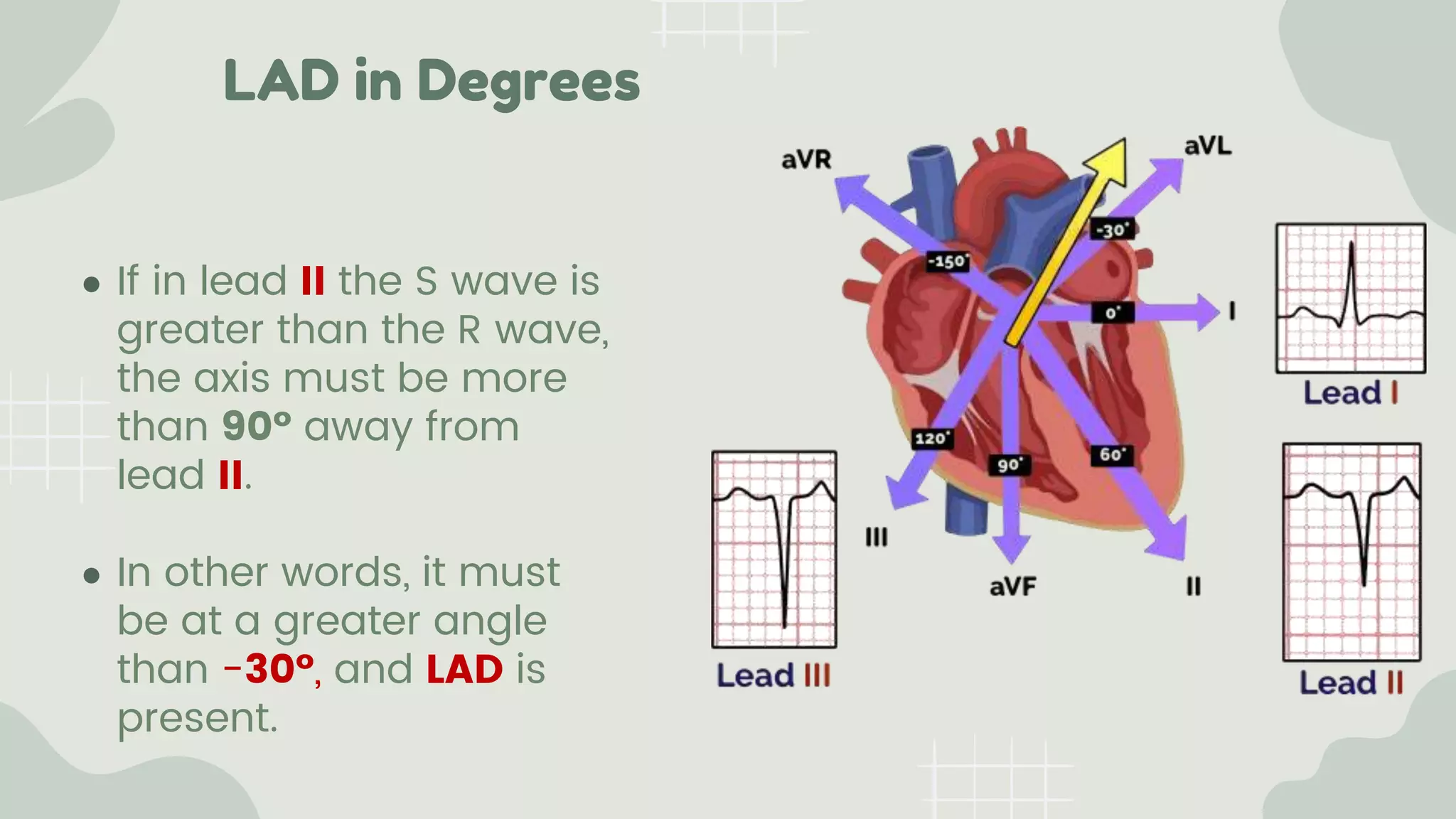
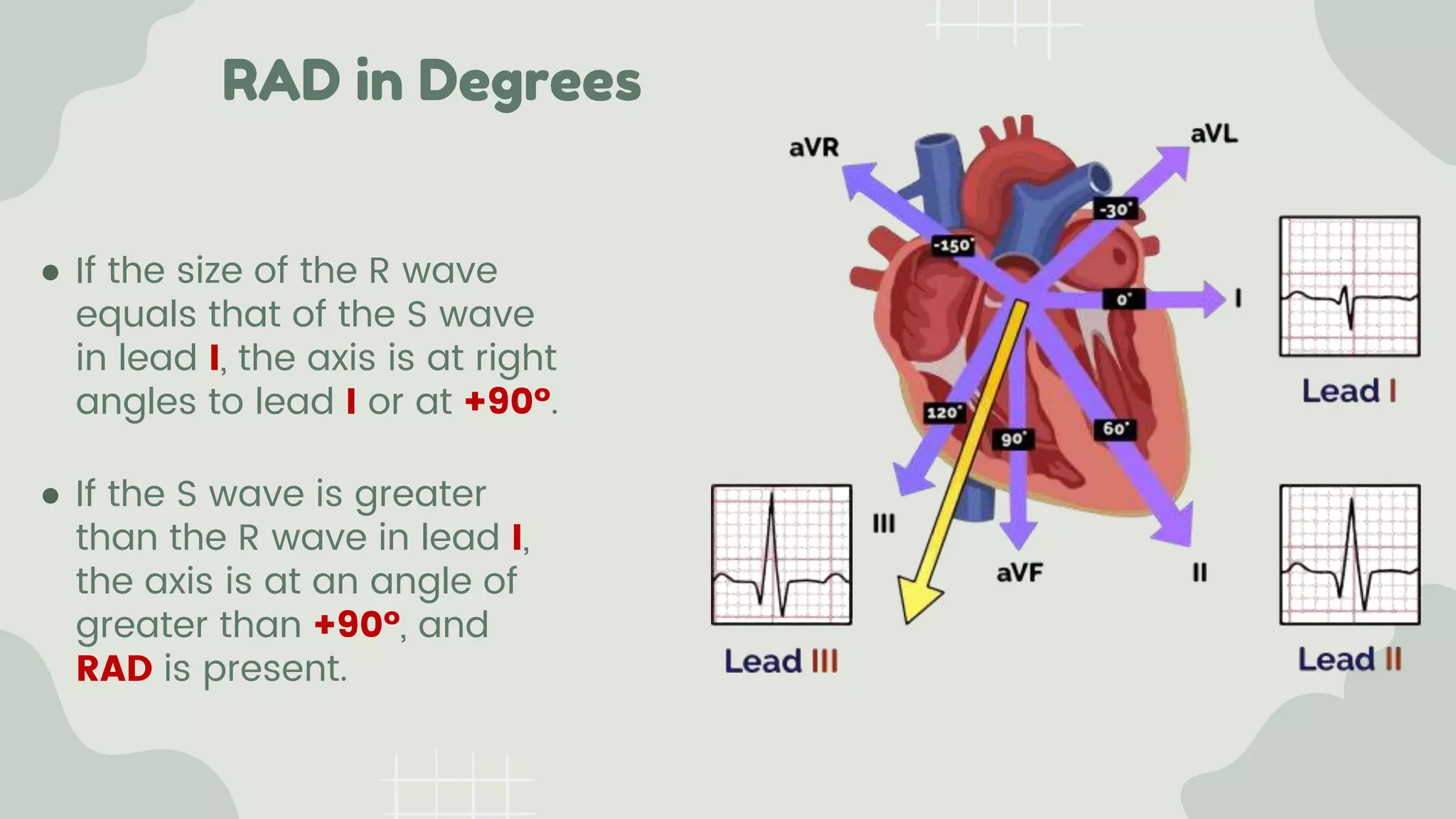
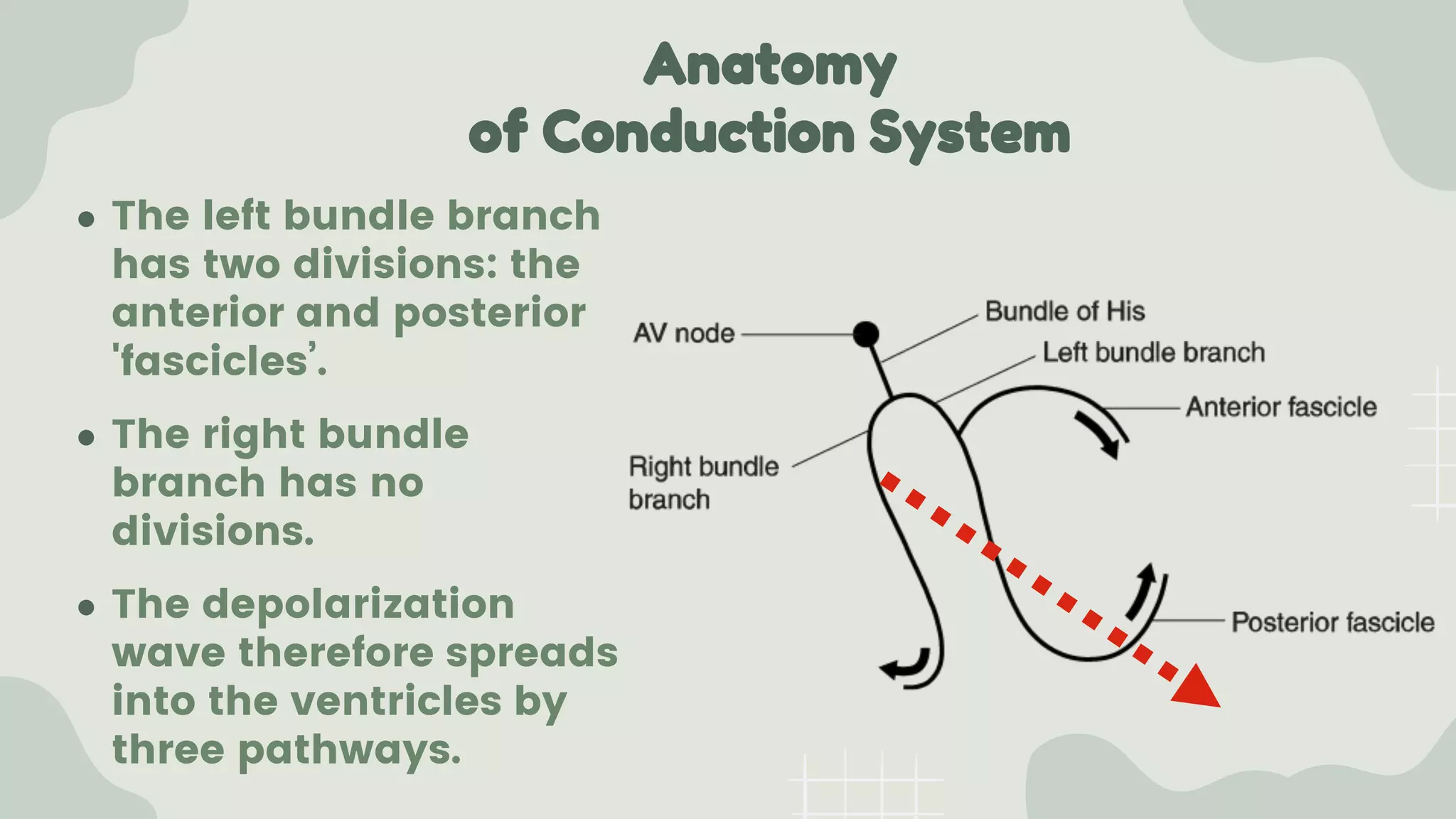
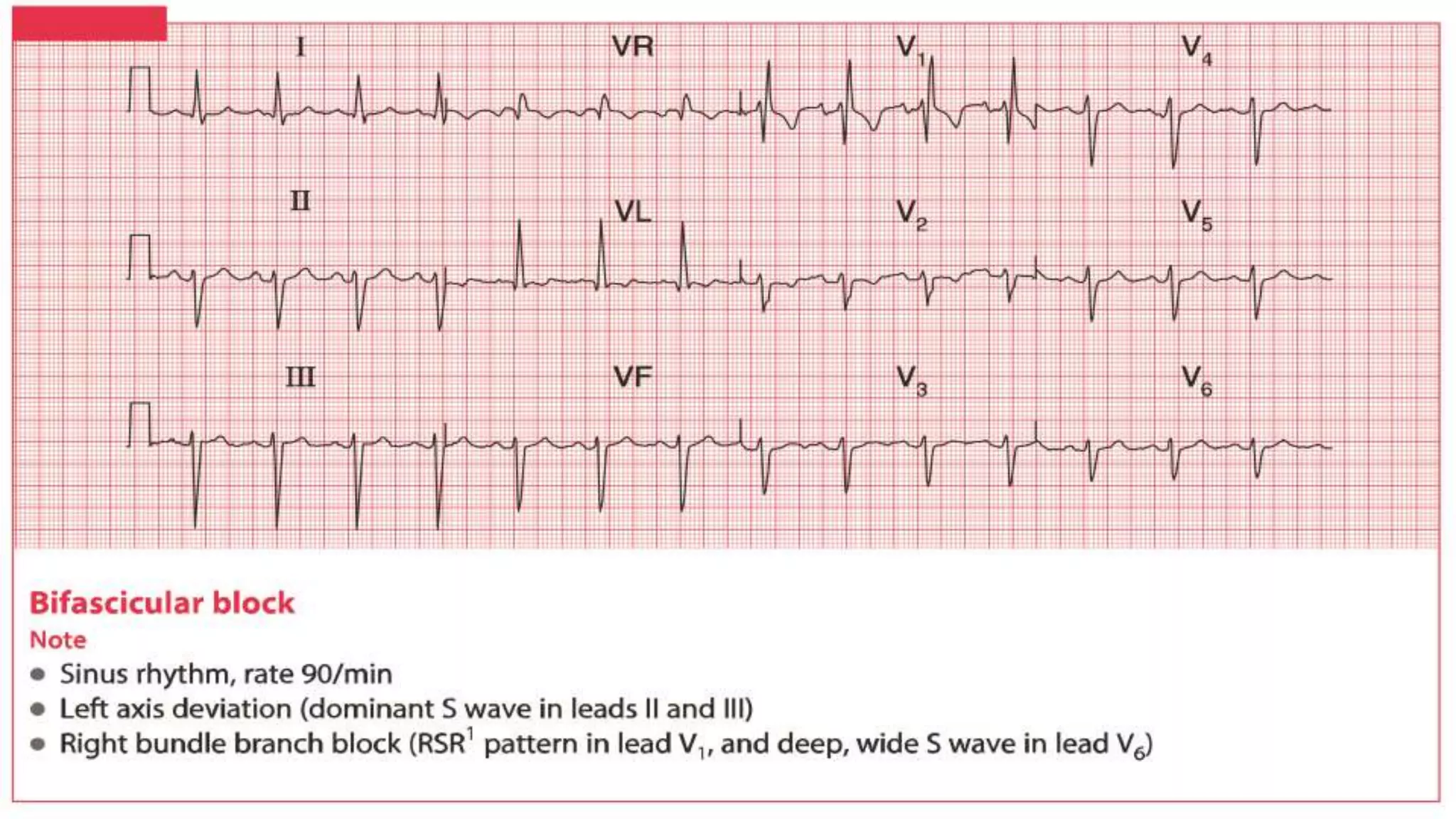
The cardiac axis represents the average direction of electrical depolarization through the ventricles. It is normally between -30 and 90 degrees but can deviate right or left. Right axis deviation occurs when the axis swings right of normal, seen as a negative deflection in lead I. Left axis deviation occurs when the axis swings left of normal, seen as a negative deflection in lead II. Specific conduction defects or conditions can cause axis deviation by altering the pathways of ventricular depolarization.