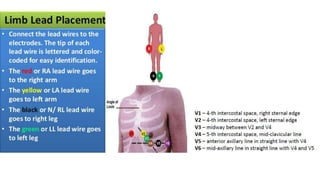
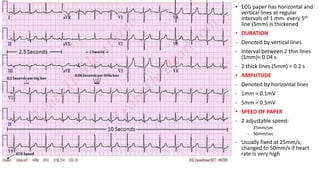
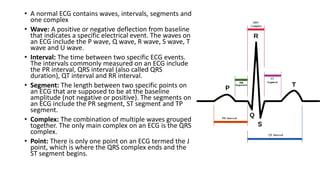
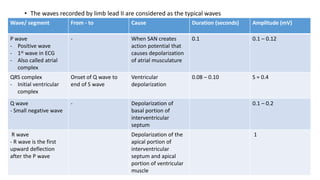
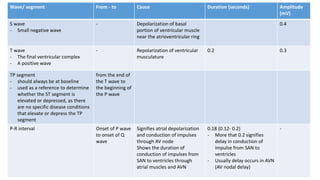
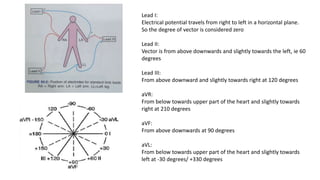
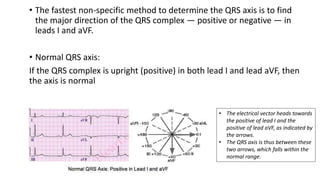
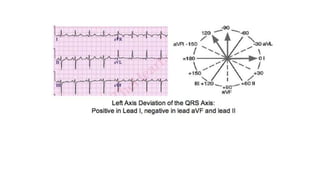
An ECG provides a picture of the electrical activity of the heart. It involves recording electrical signals via electrodes placed on the body. A normal ECG contains waves, intervals, segments and complexes that represent different electrical events in the heart during each heartbeat. Key aspects of an ECG include examining the rate, rhythm, axis, intervals and segments to identify normal patterns or abnormalities that may indicate cardiac disease. The standard ECG has 12 leads that measure the heart's electrical activity from different angles.