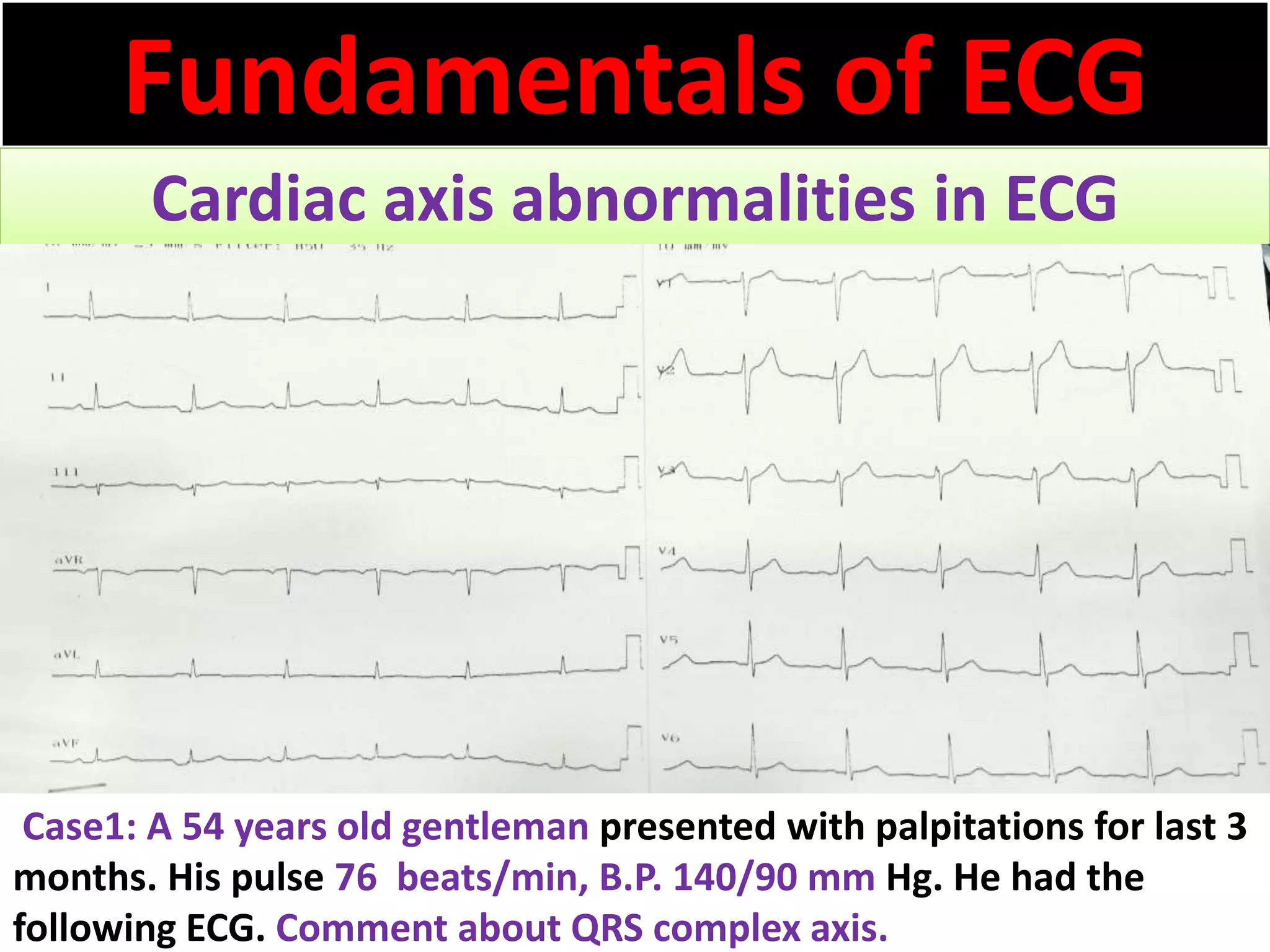
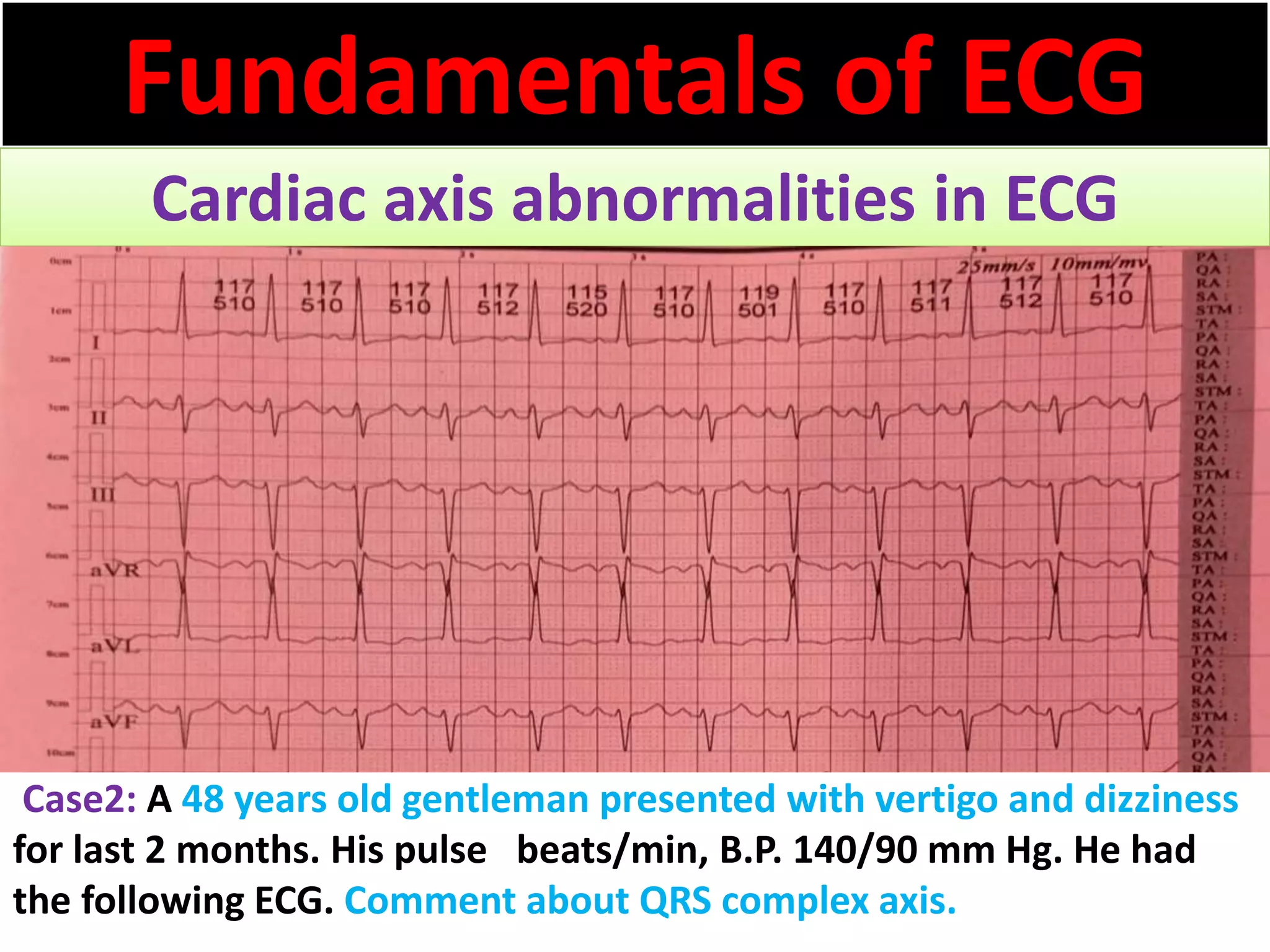
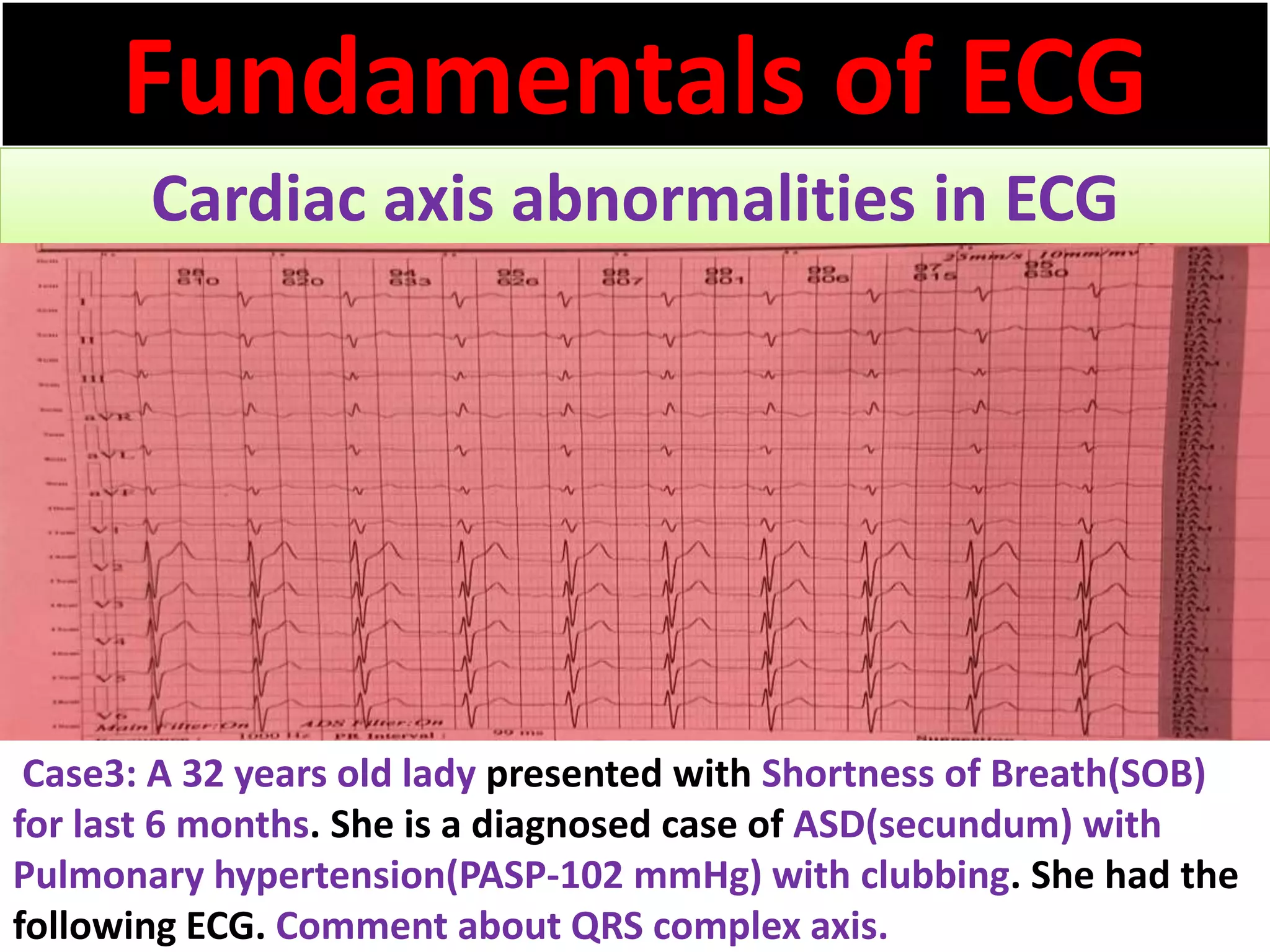
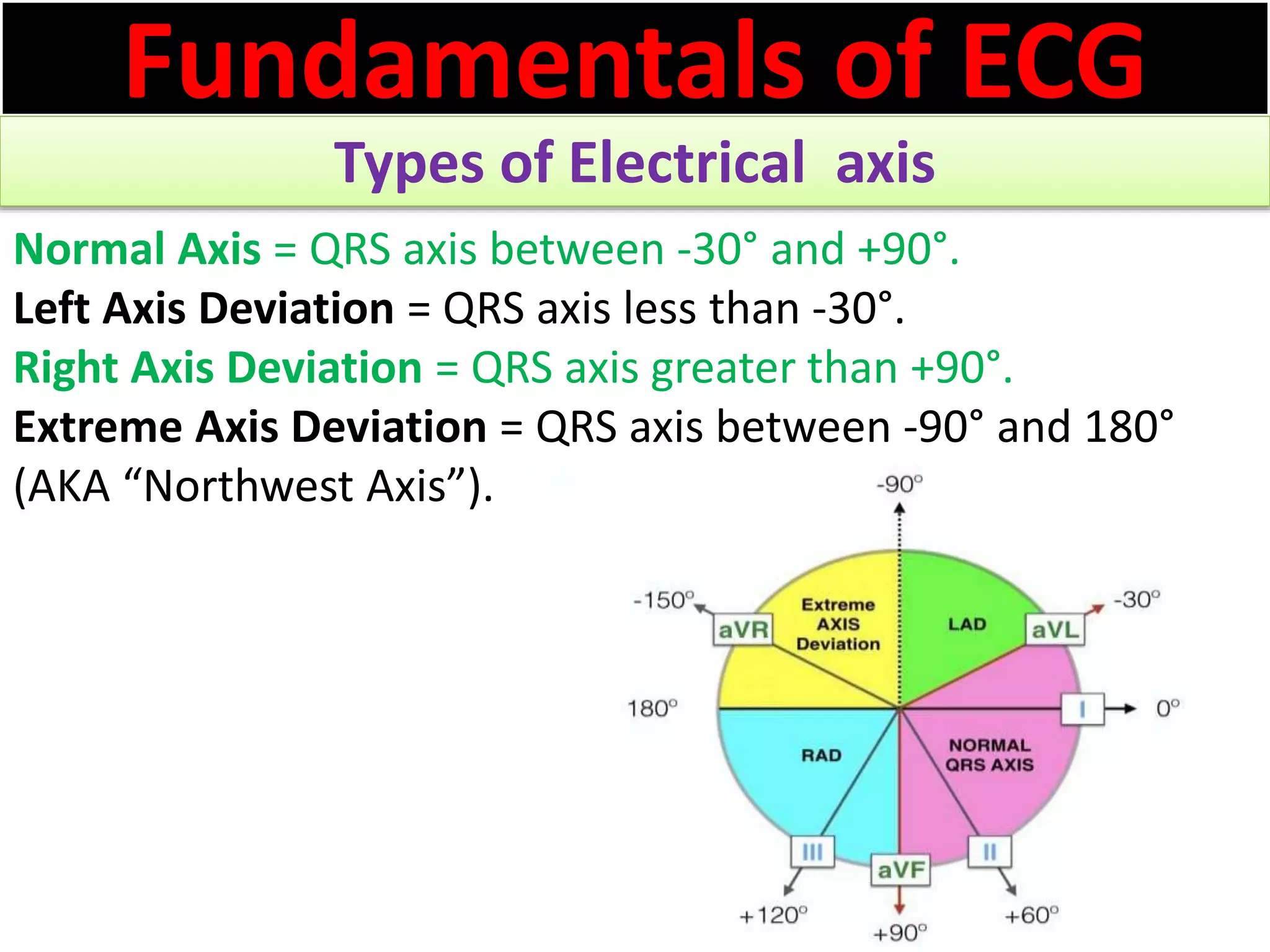
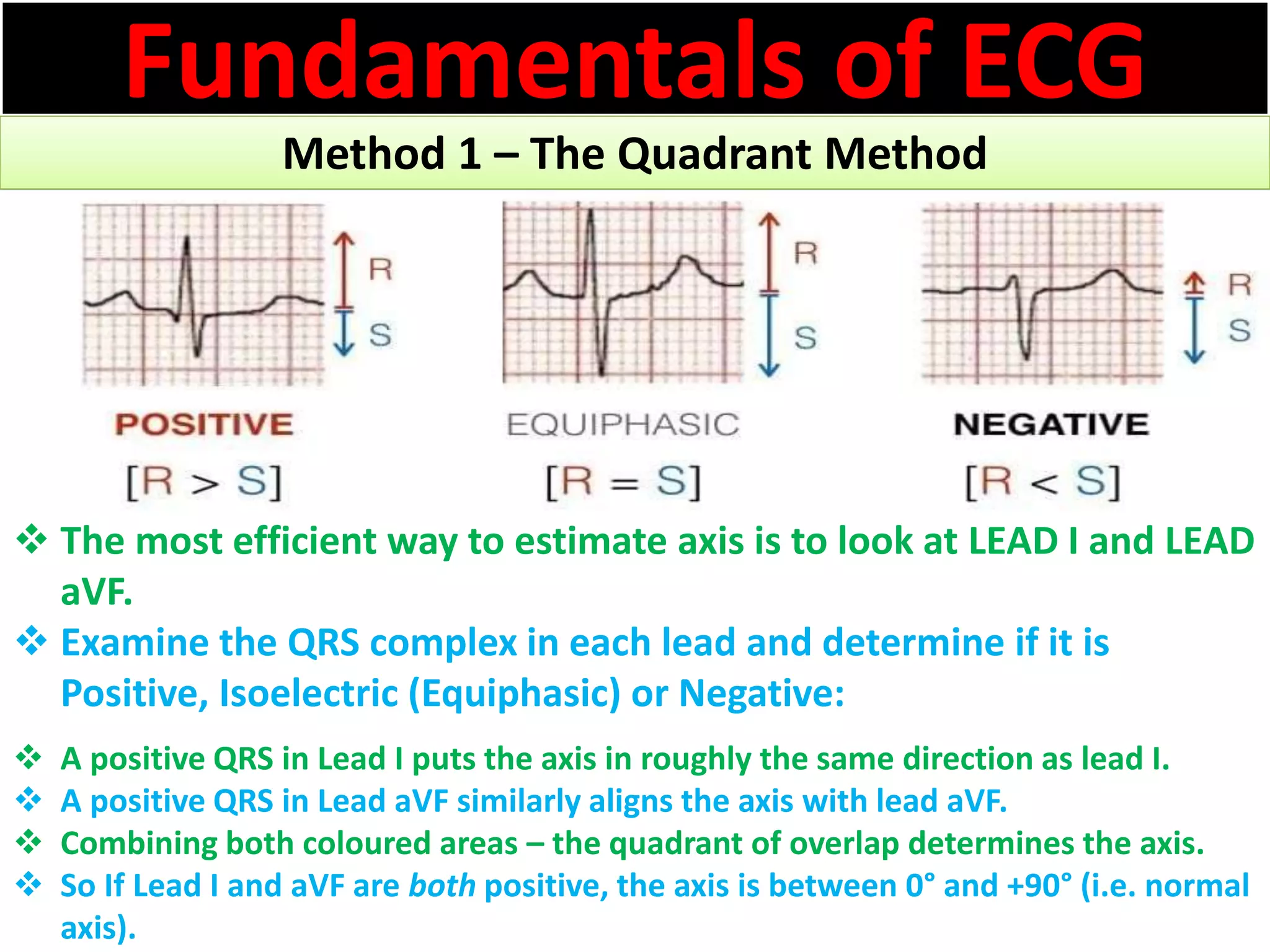
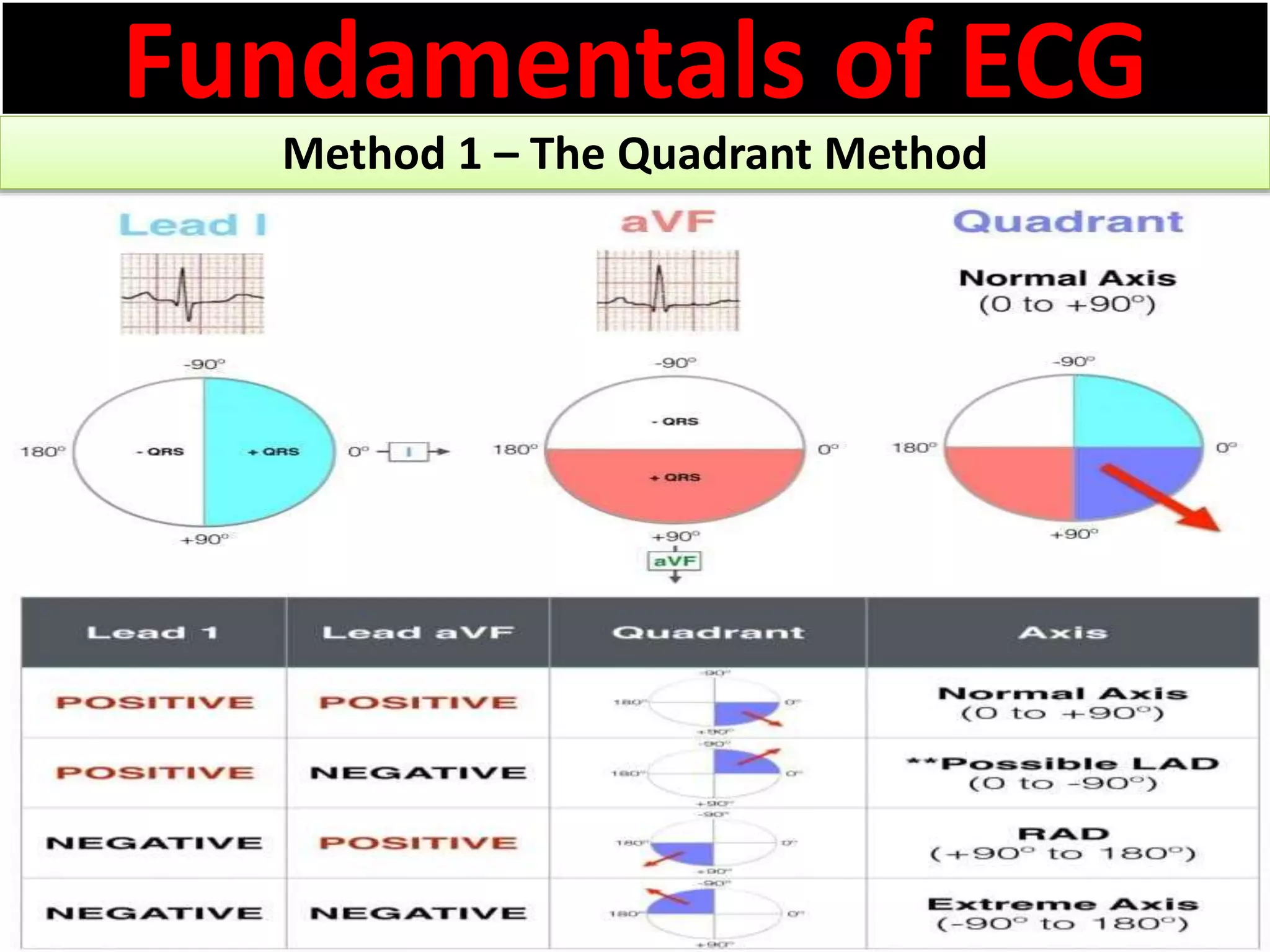
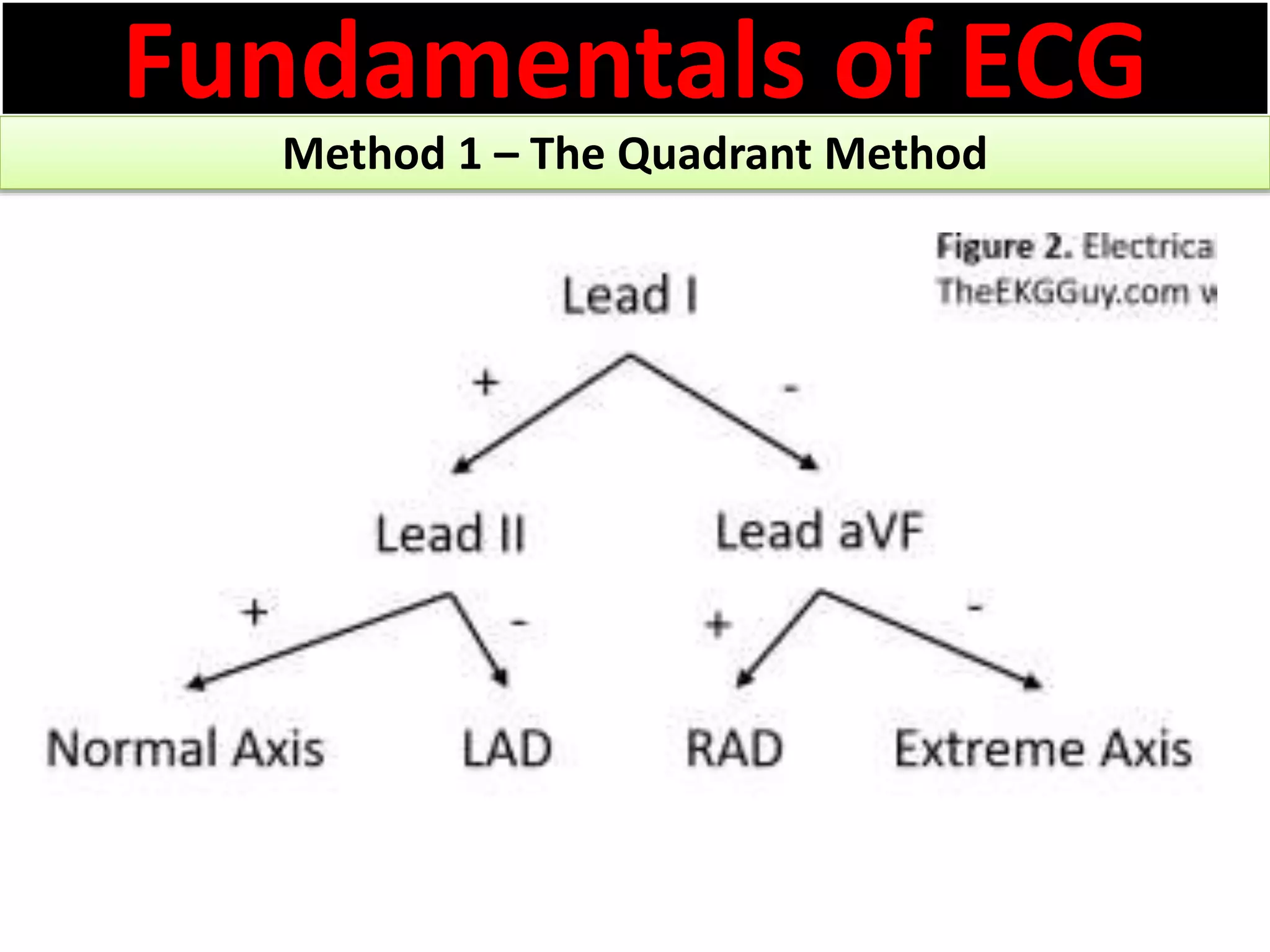
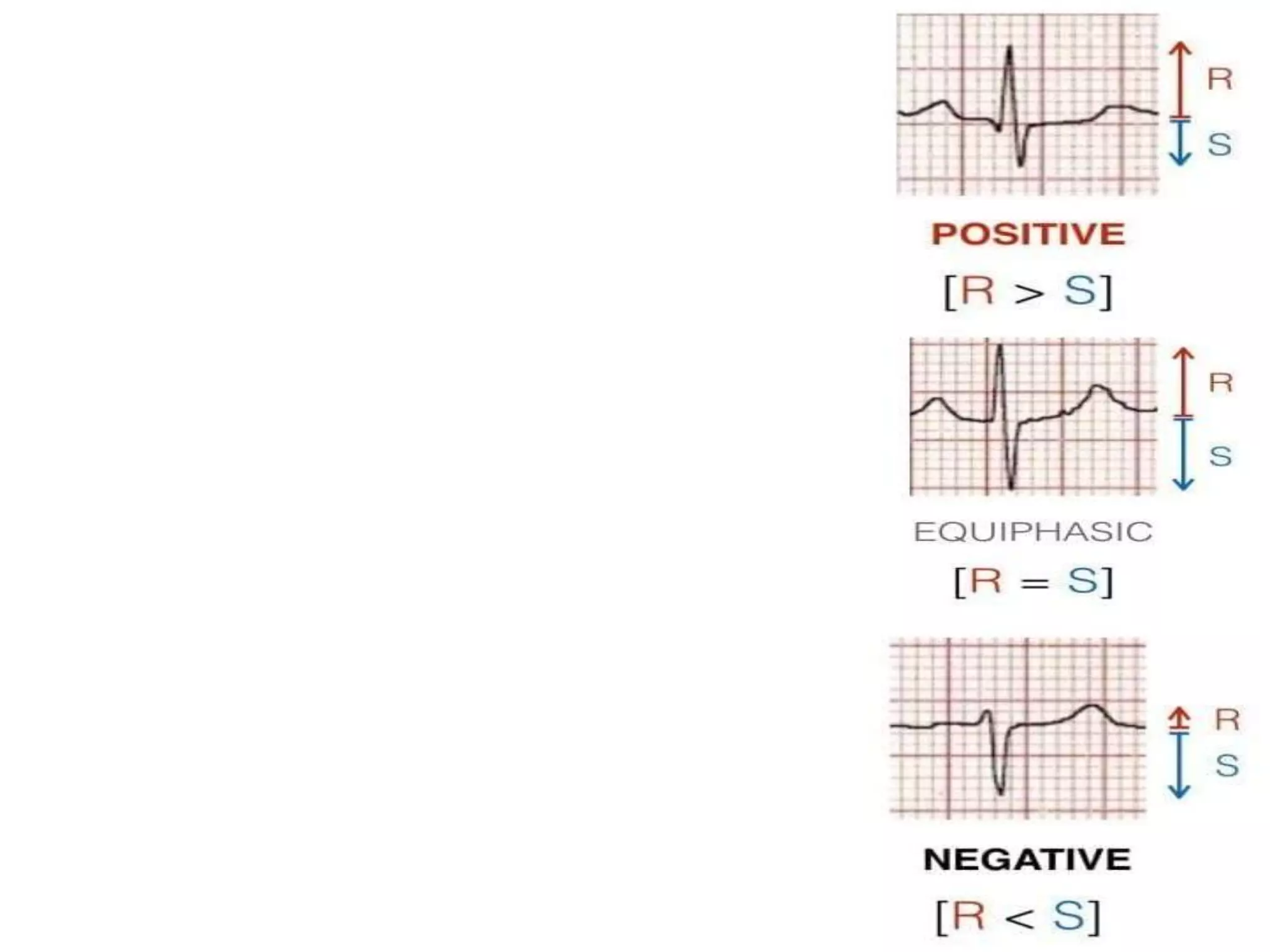
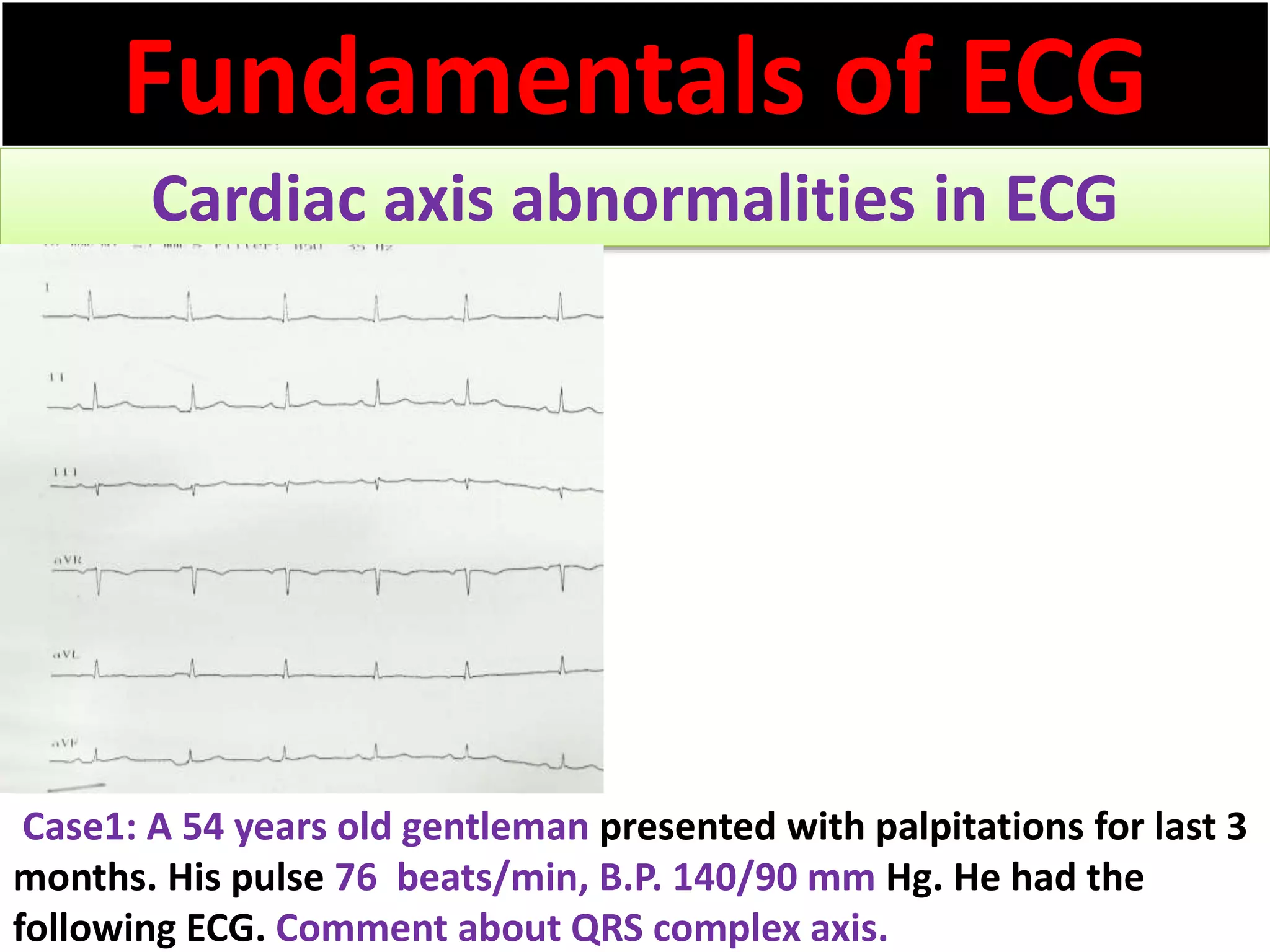
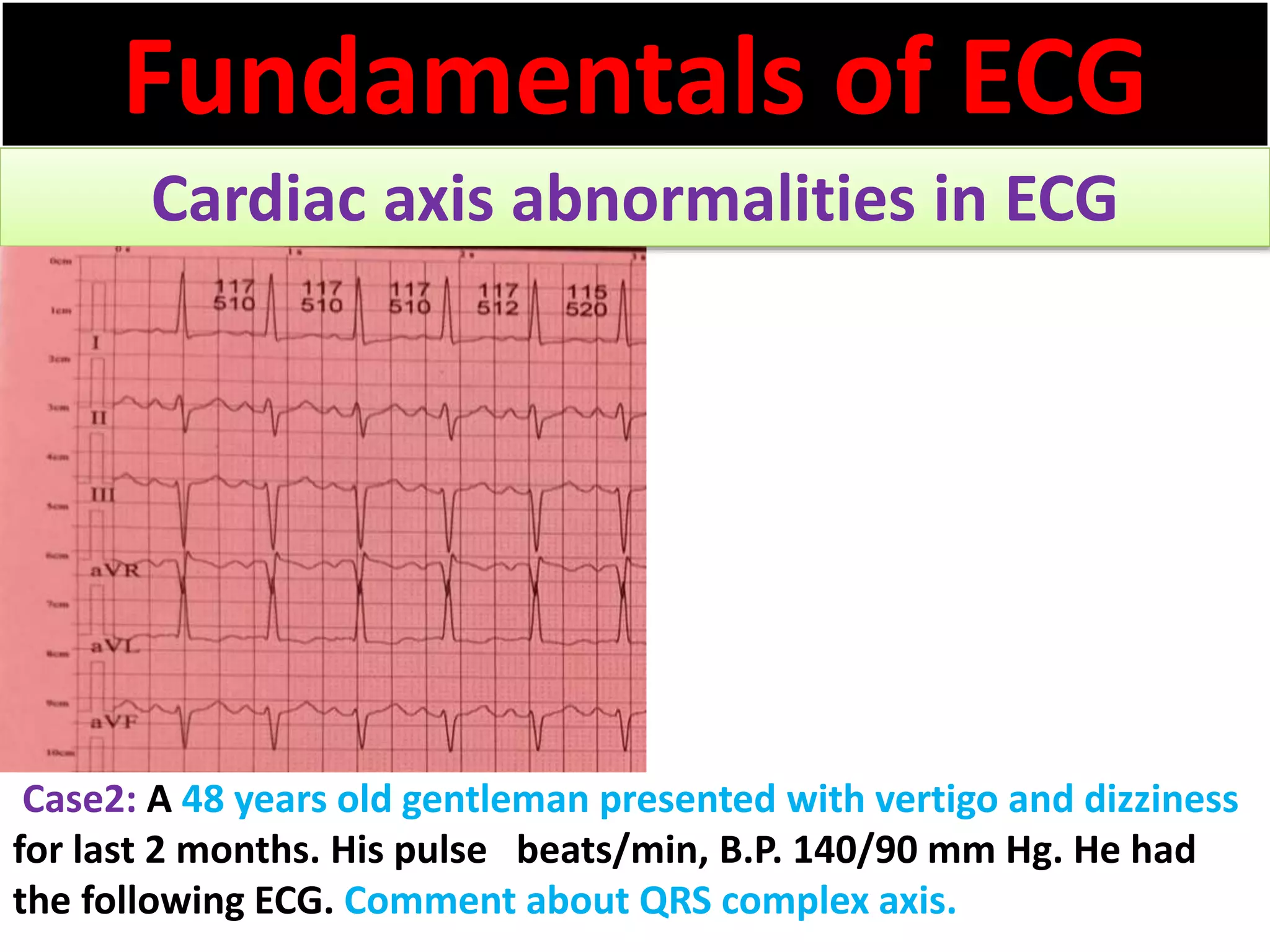
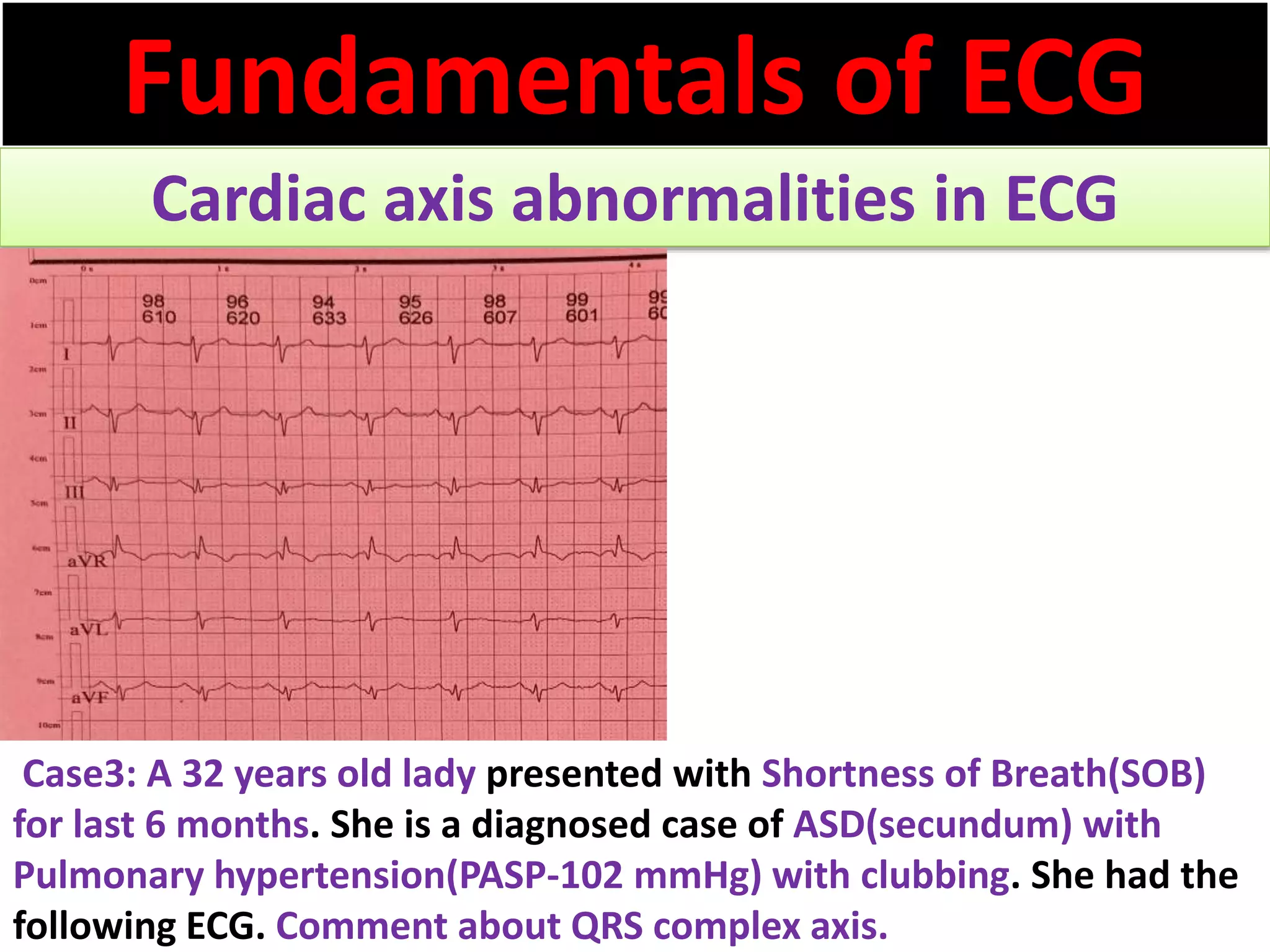
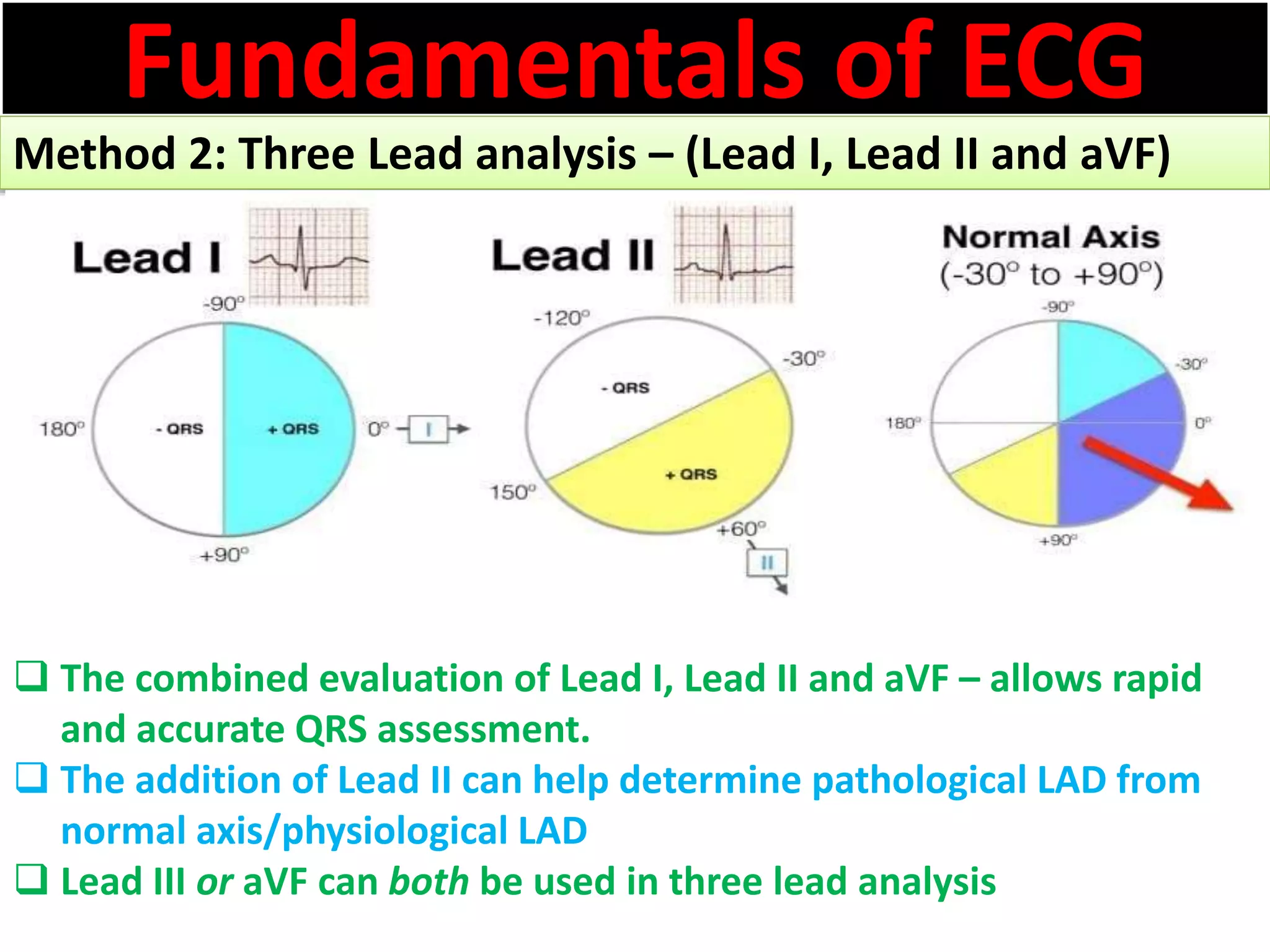
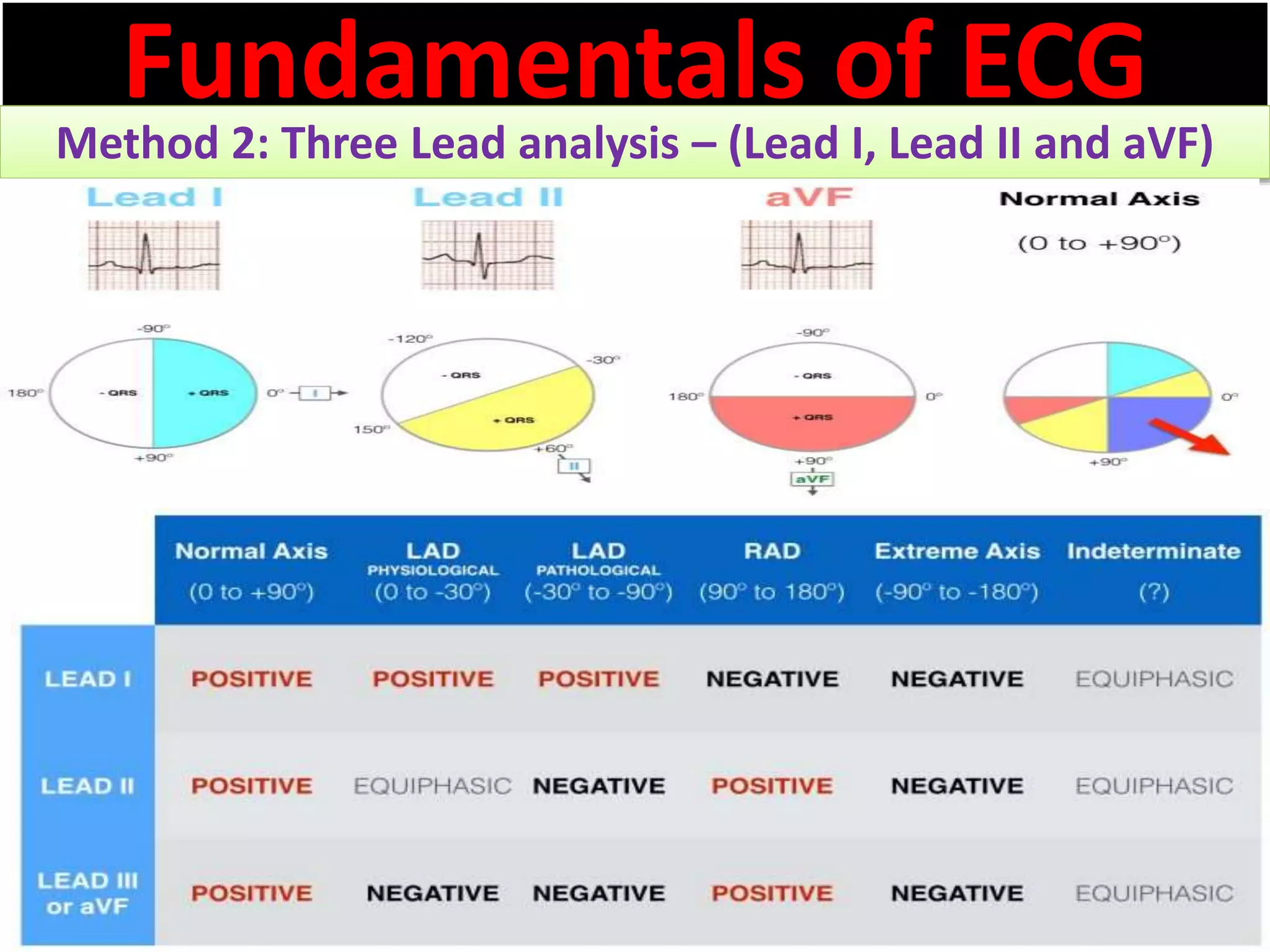
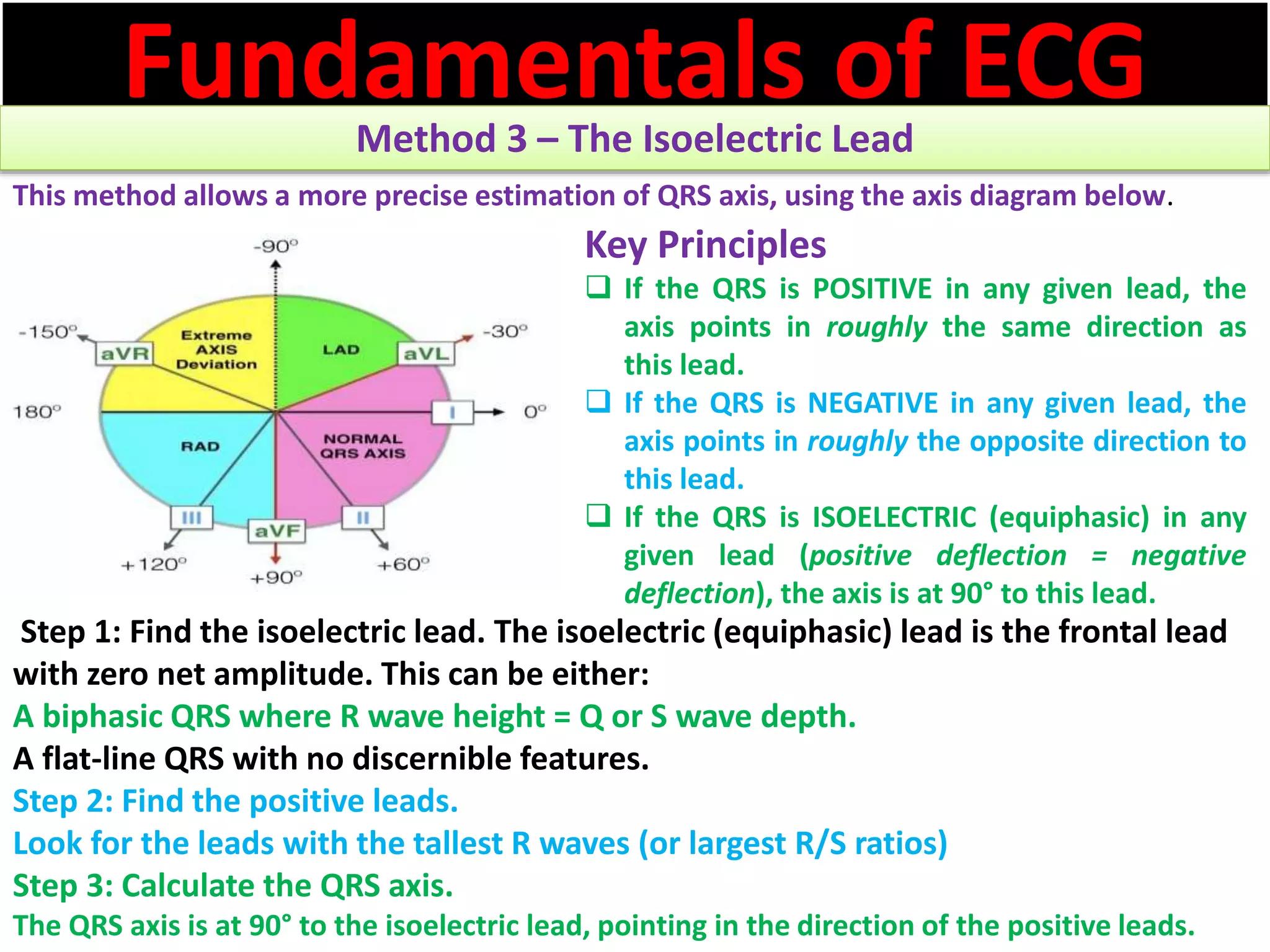
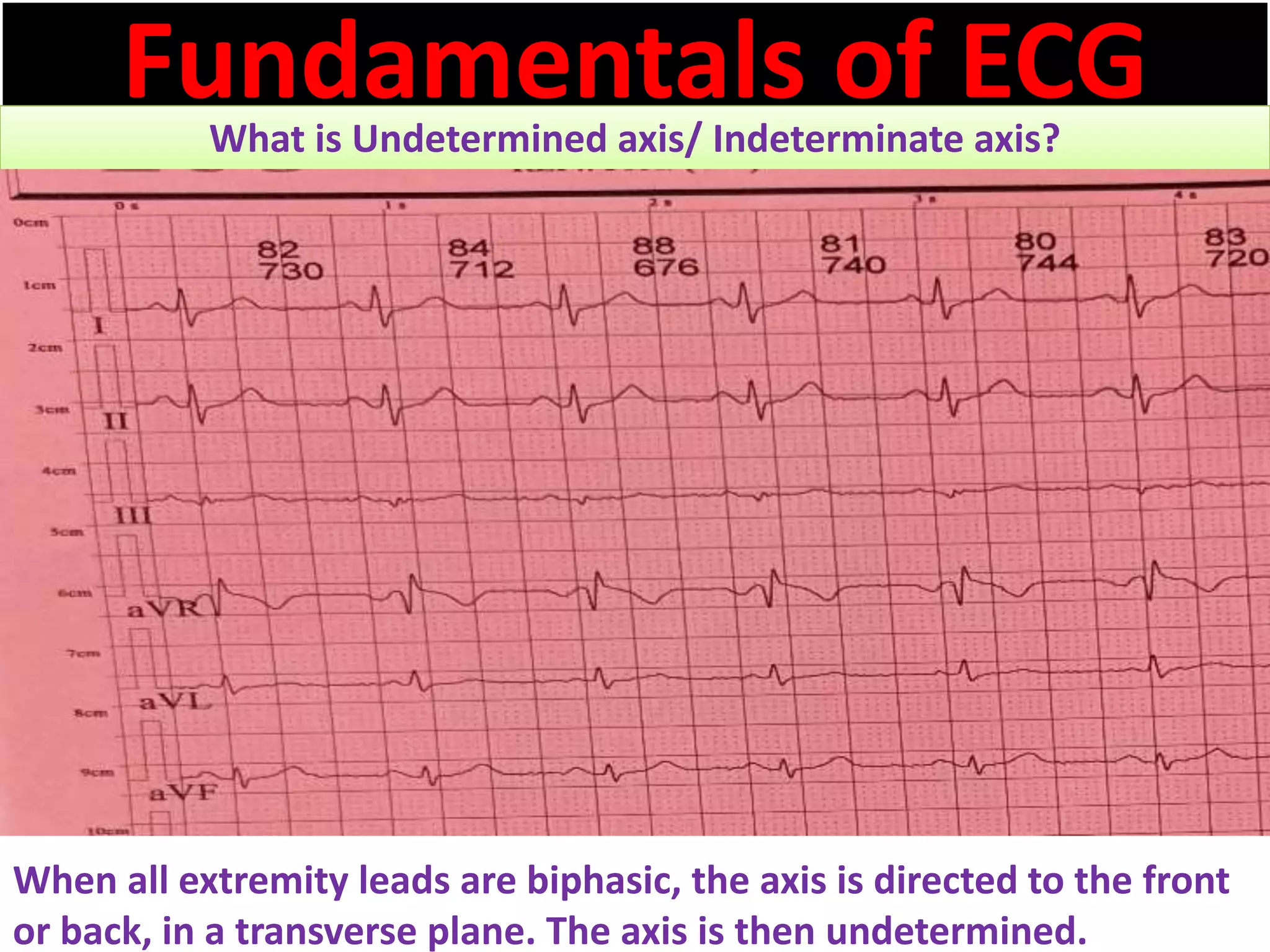
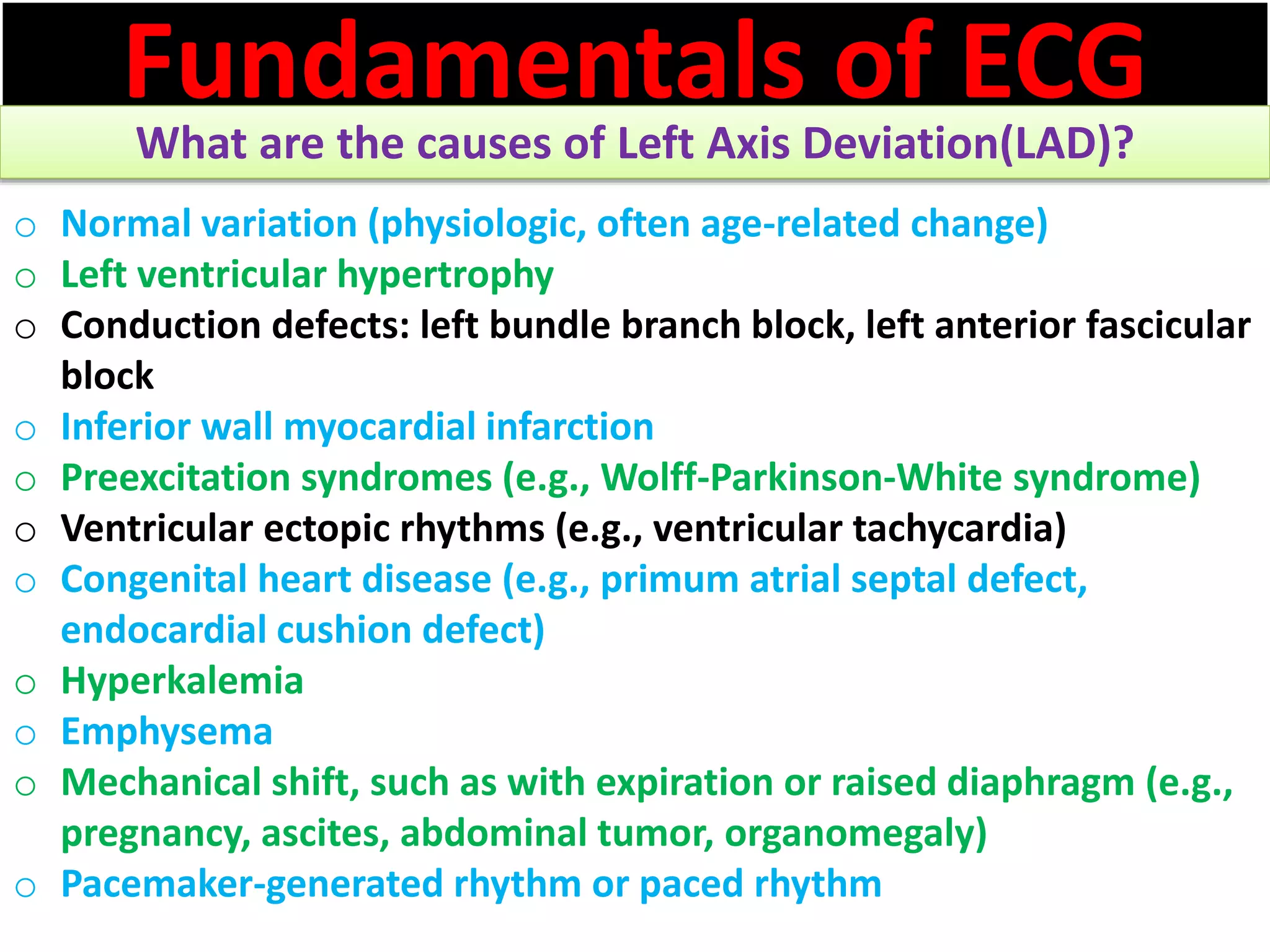
The document discusses the fundamentals of ECG cardiac axis abnormalities, detailing types such as normal, left axis deviation, right axis deviation, and extreme axis deviation. It outlines methods for ECG axis interpretation and clinical significance, providing case studies to illustrate different presentations and their QRS axis assessments. The document further explores causes of abnormal heart axis and associated conditions.