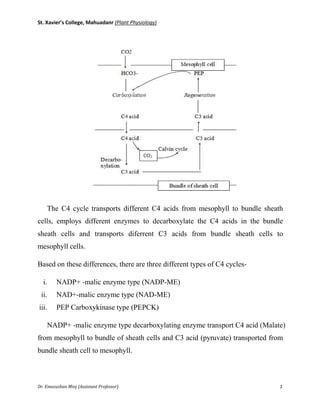
The document summarizes the Hatch-Slack or C4 pathway, an alternative to the Calvin cycle that fixes carbon and minimizes photorespiration. The pathway was discovered in 1966 and involves two cell types - mesophyll and bundle sheath cells. Carbon dioxide is initially fixed by the mesophyll cells into a four-carbon acid like malate or aspartate, which is then transported to the bundle sheath cells. There, the four-carbon acid is decarboxylated, releasing carbon dioxide to enter the Calvin cycle. The three-carbon acid byproduct is returned to the mesophyll cells, completing the five-stage cycle. The document further describes the three main types of C4 cycles that differ in the