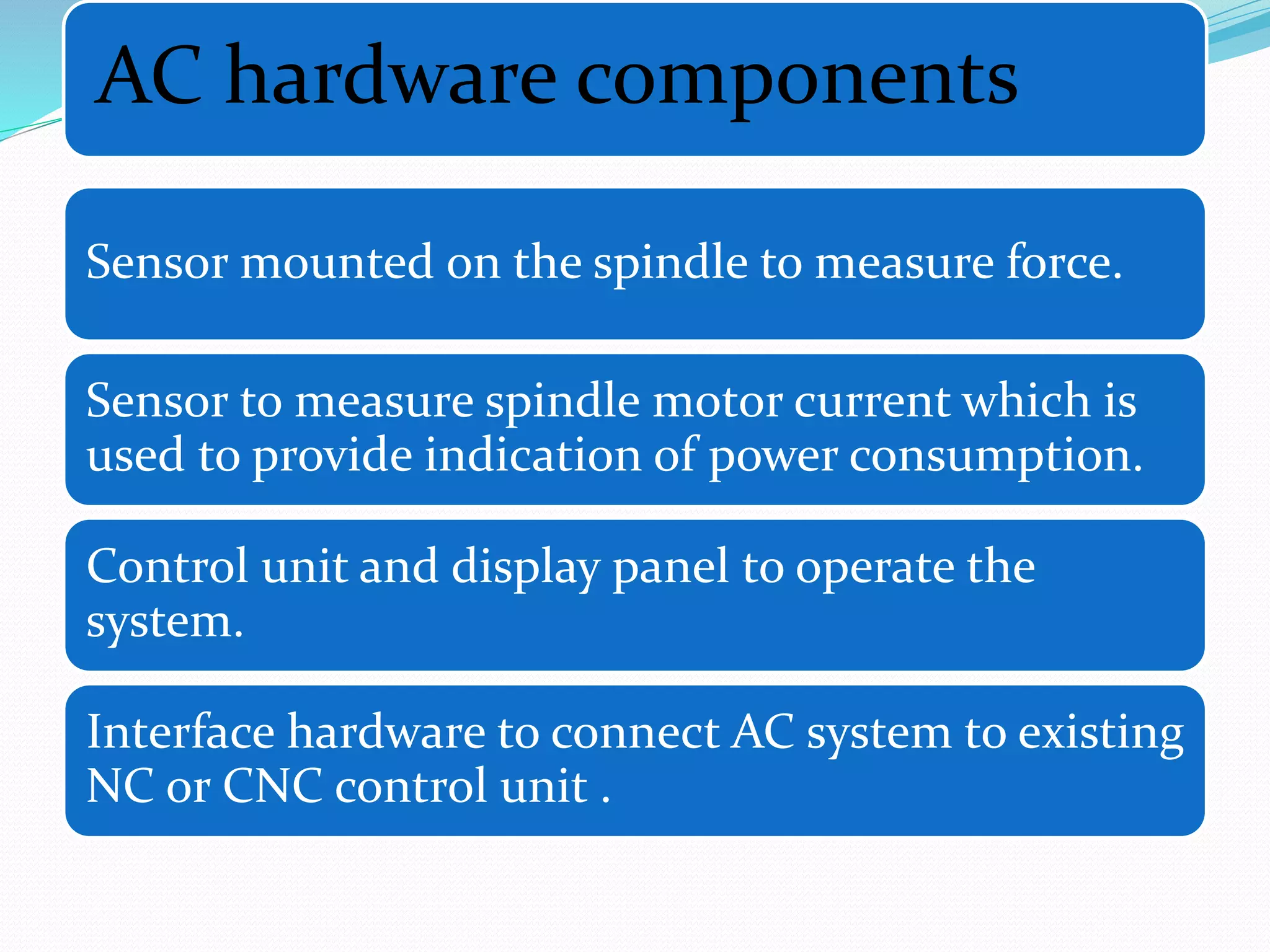
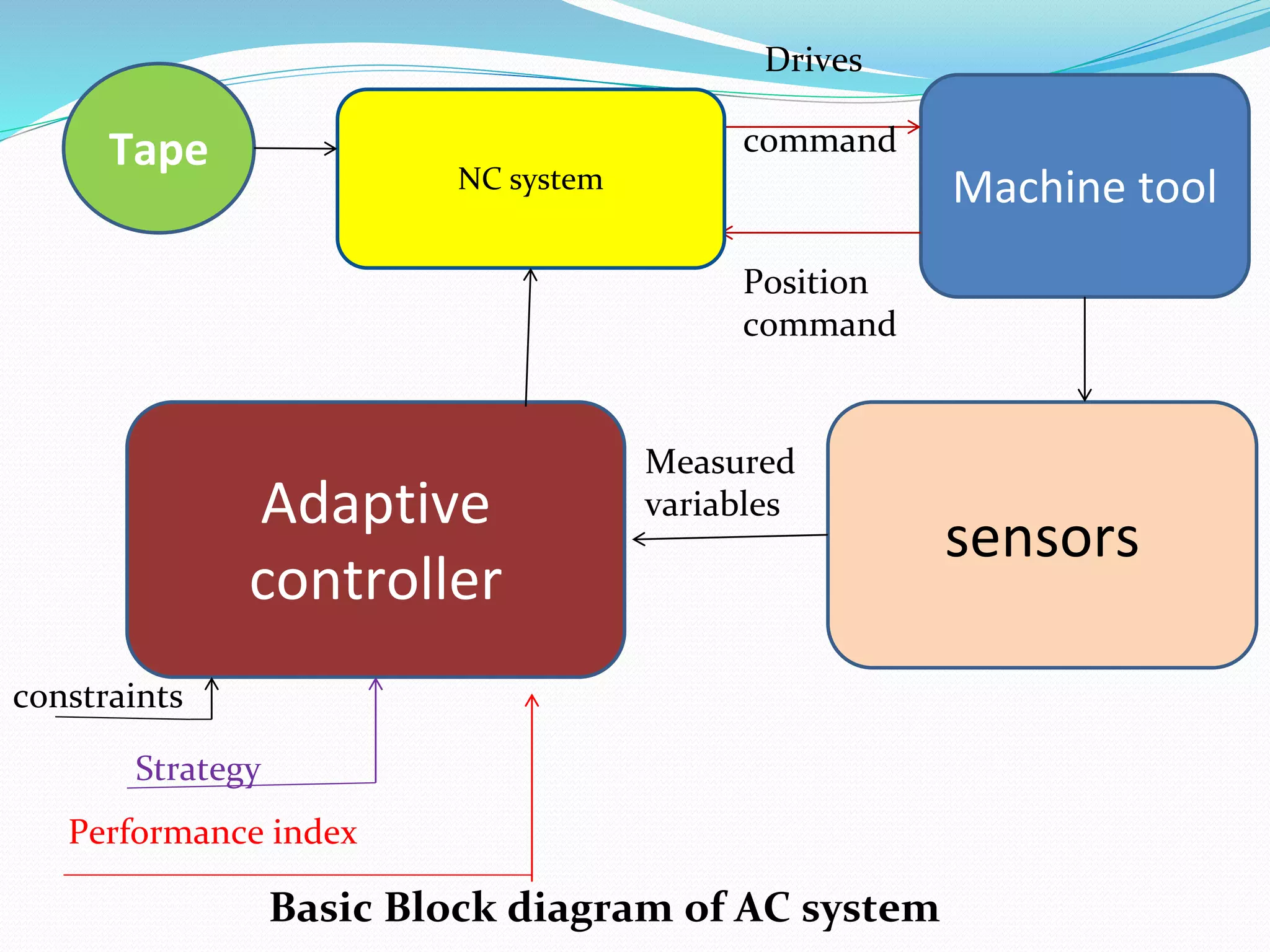
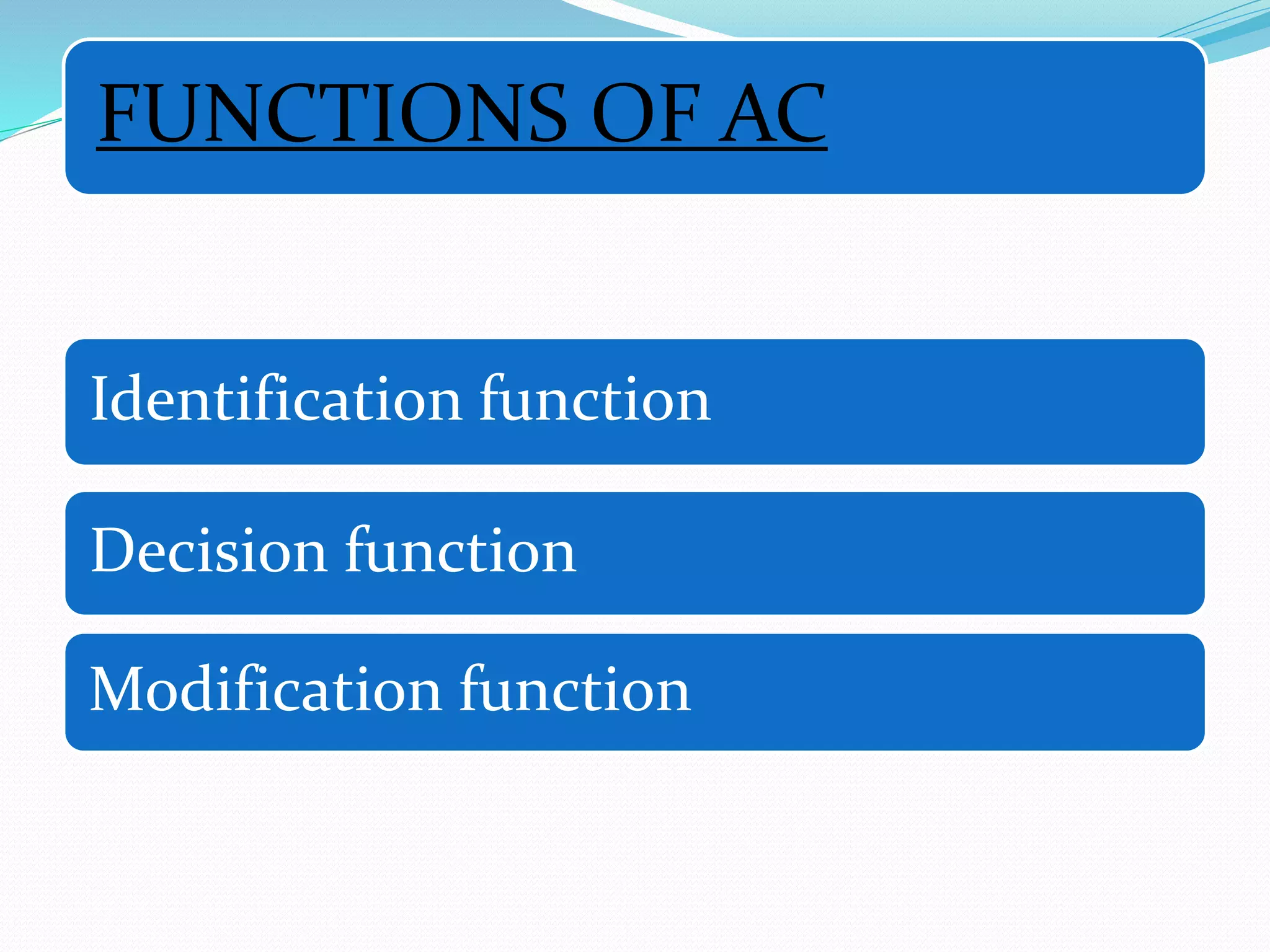
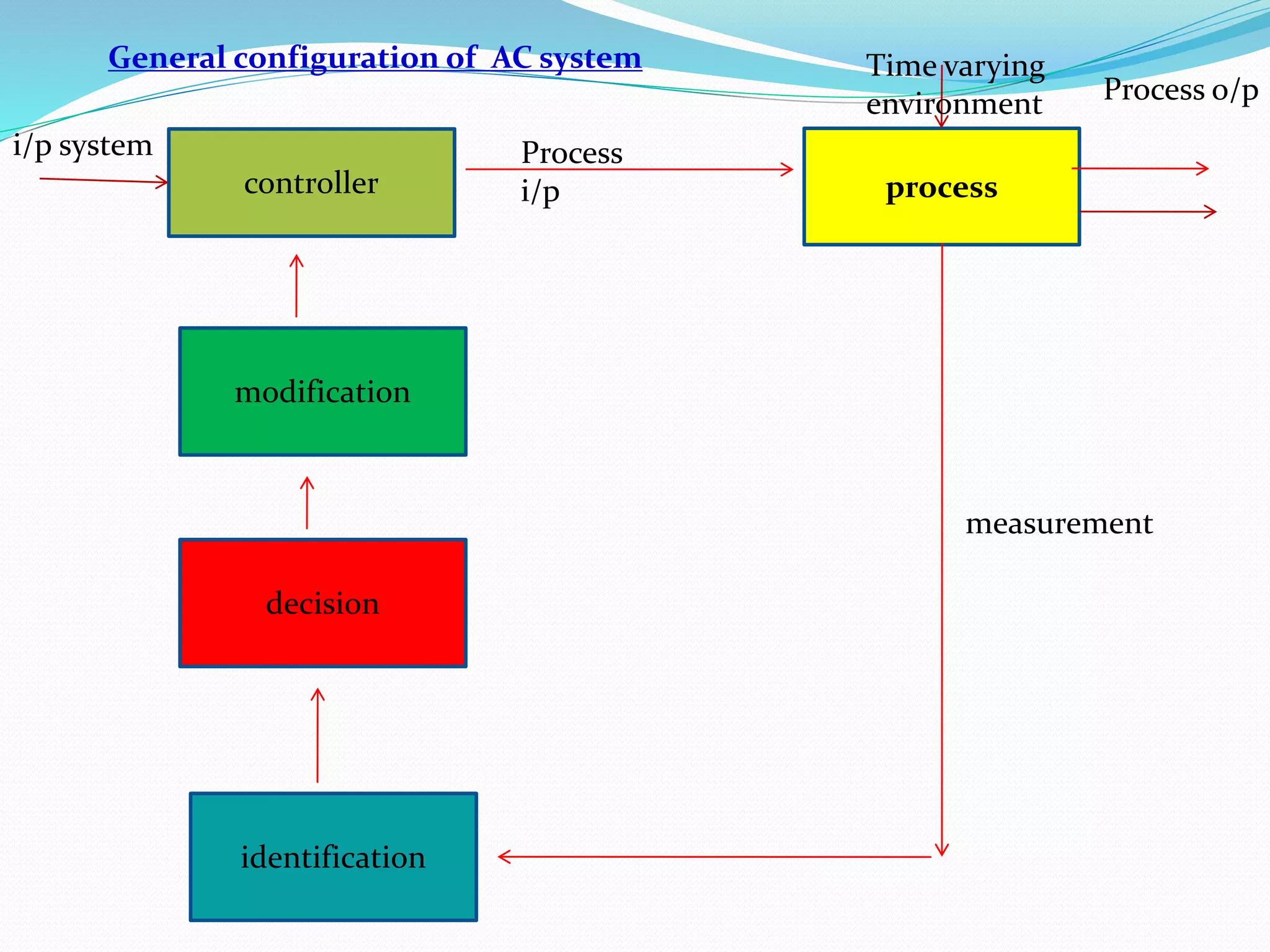
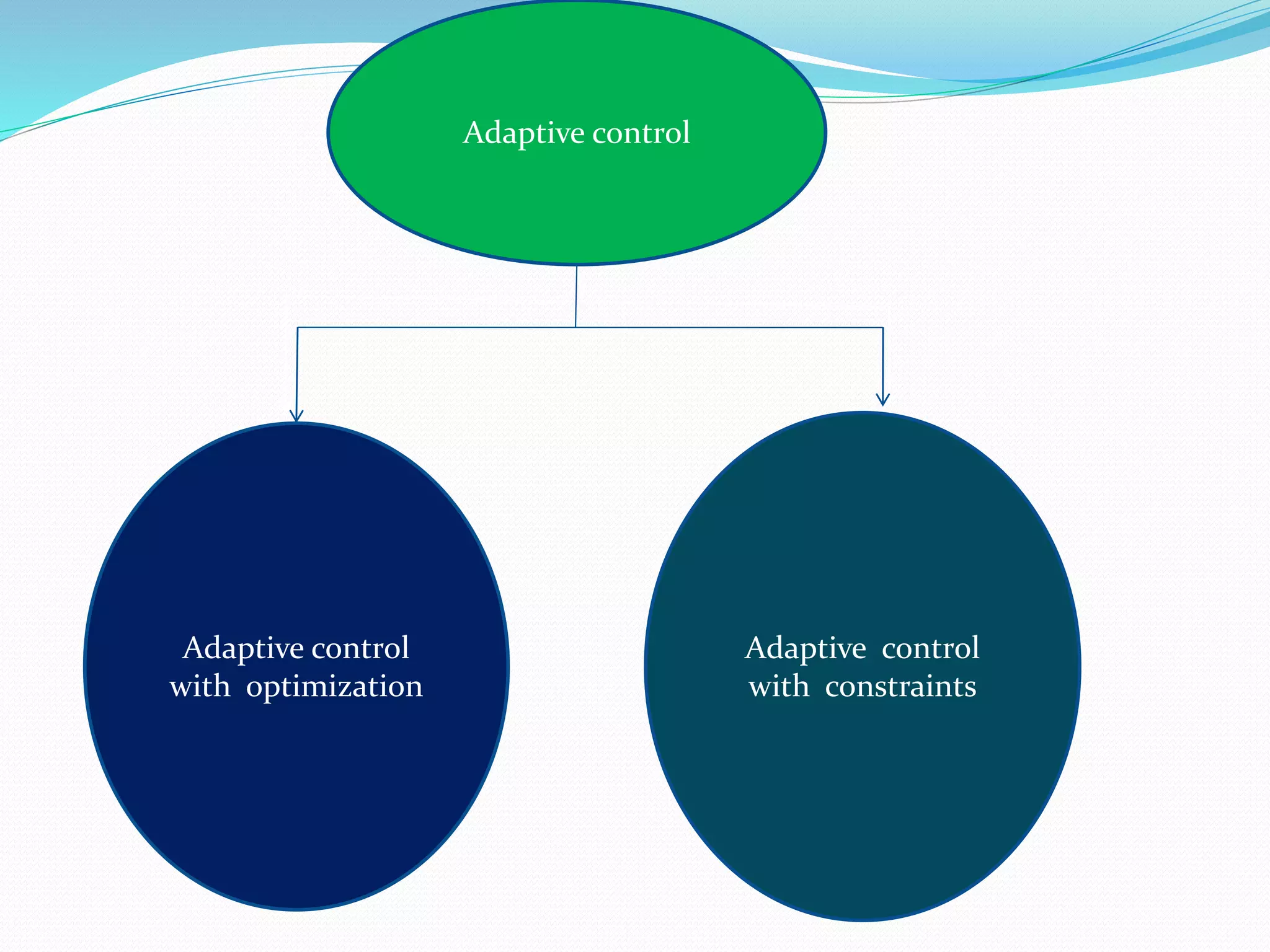
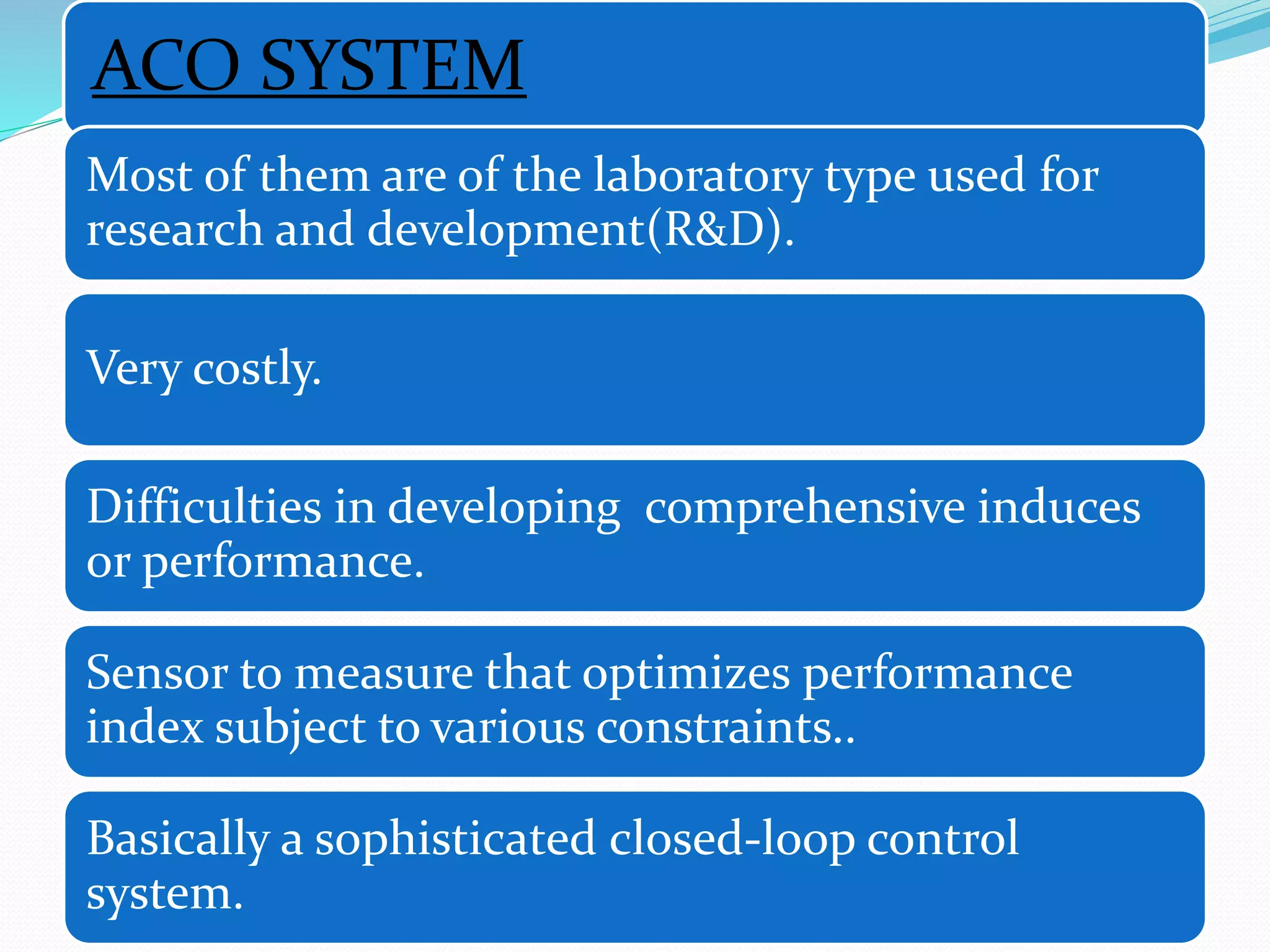
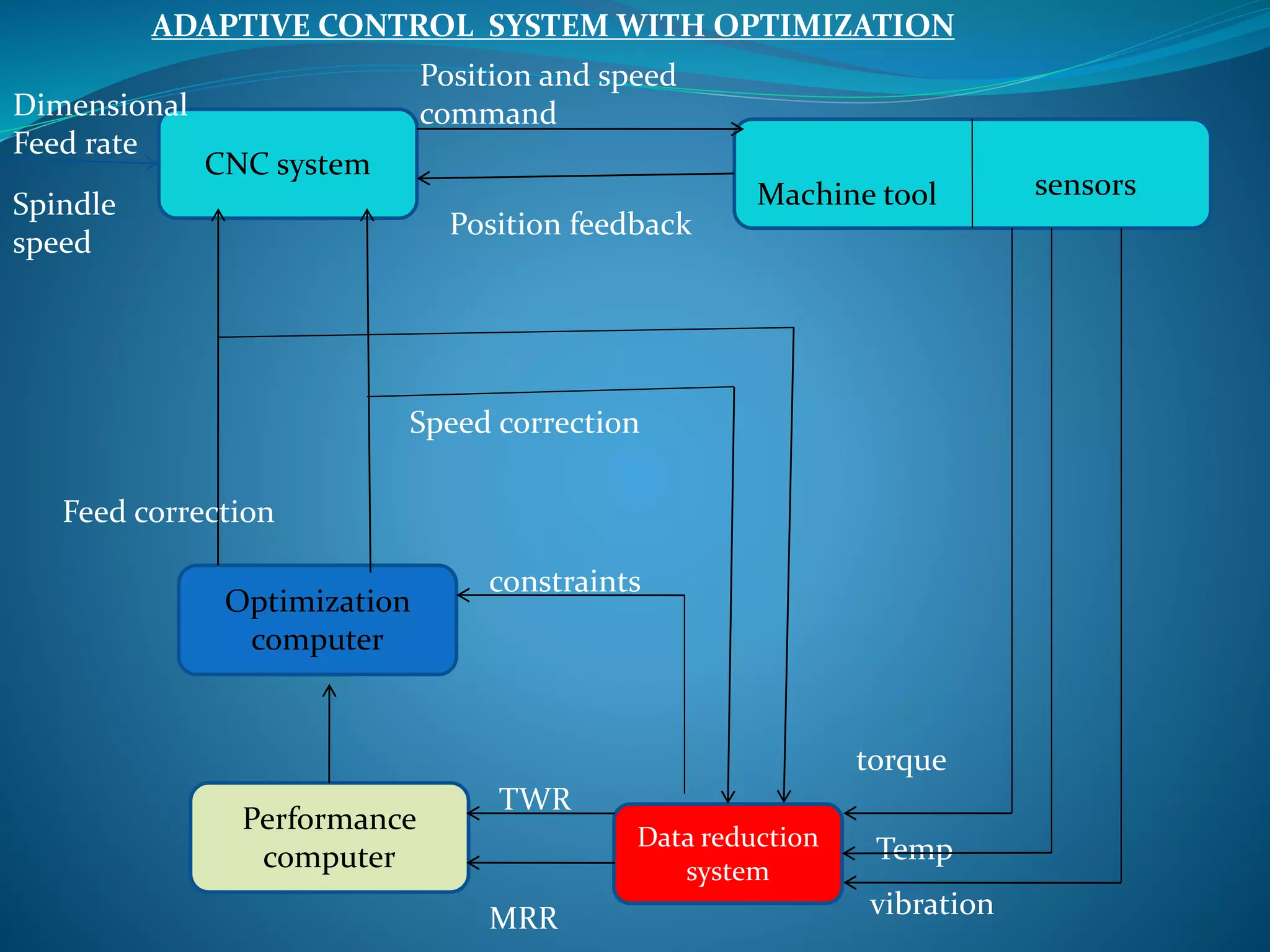
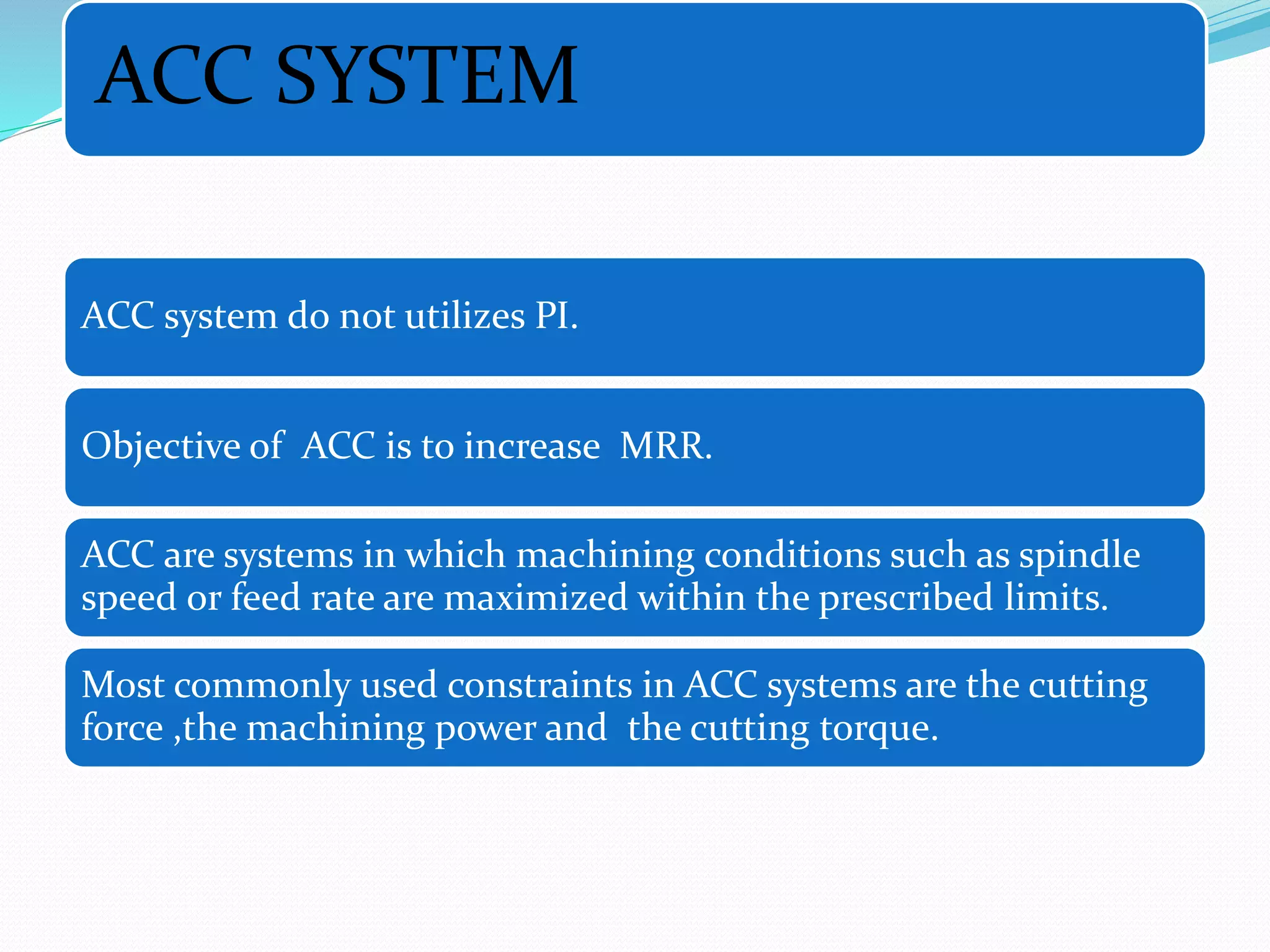
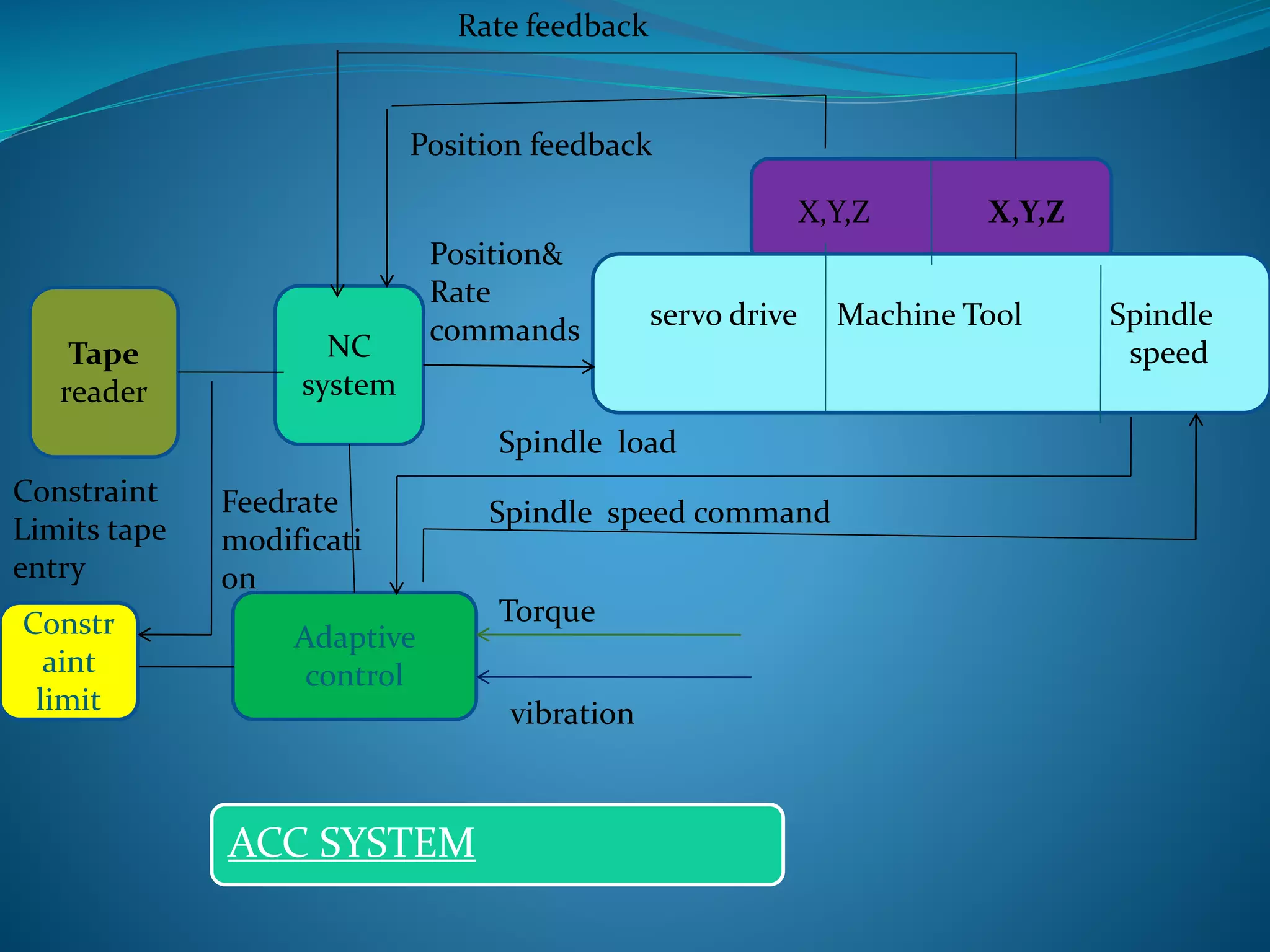
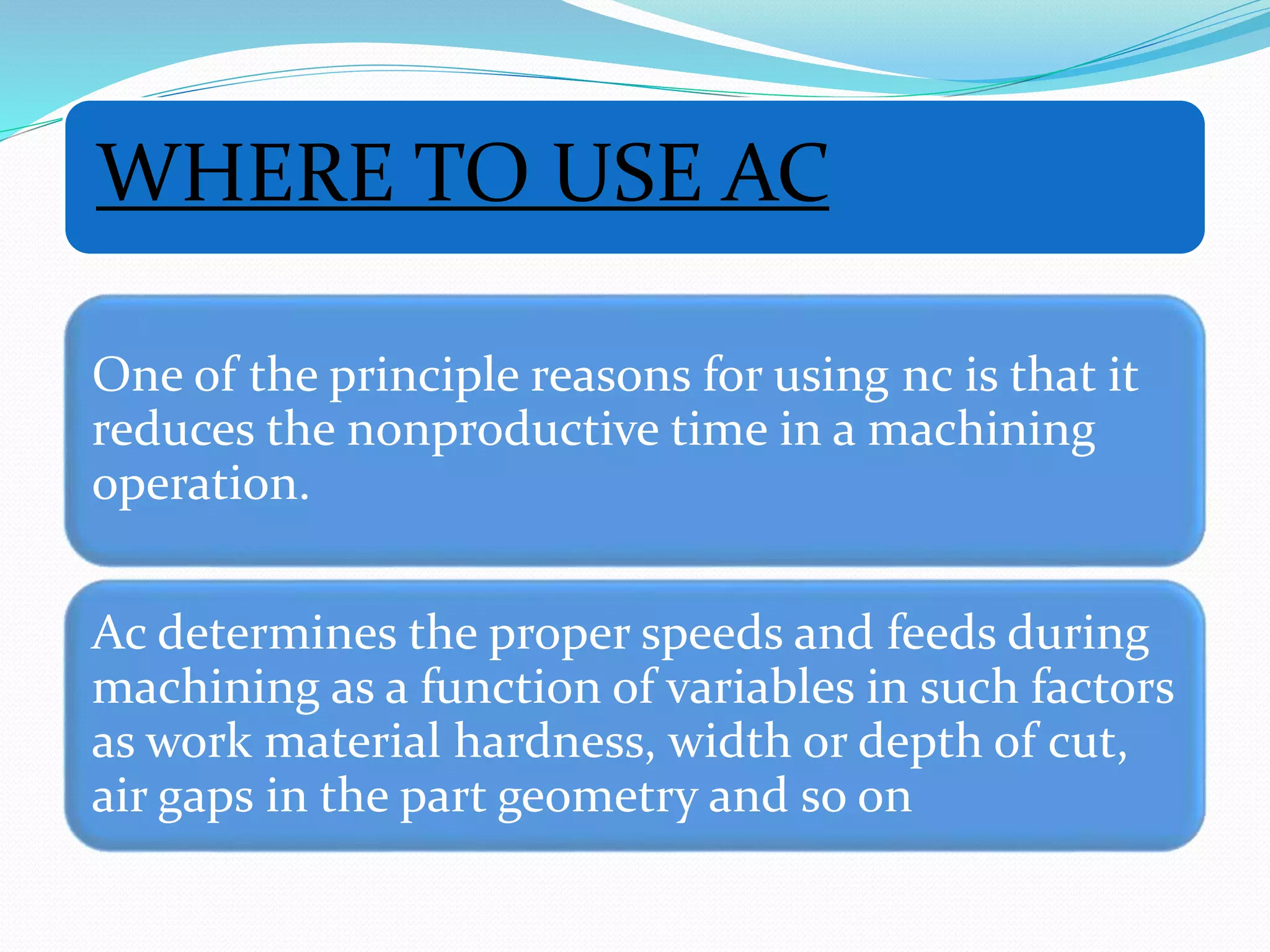
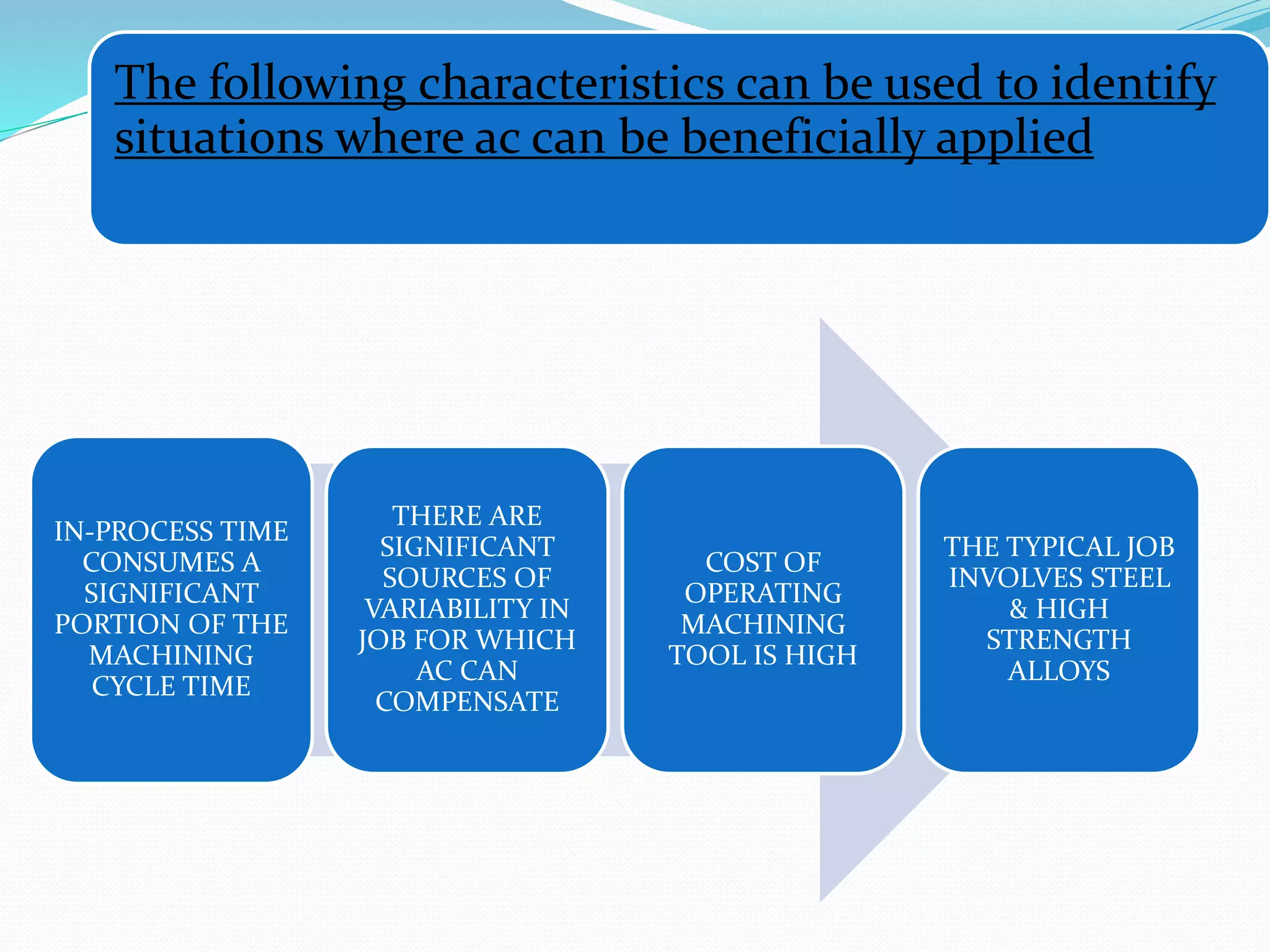
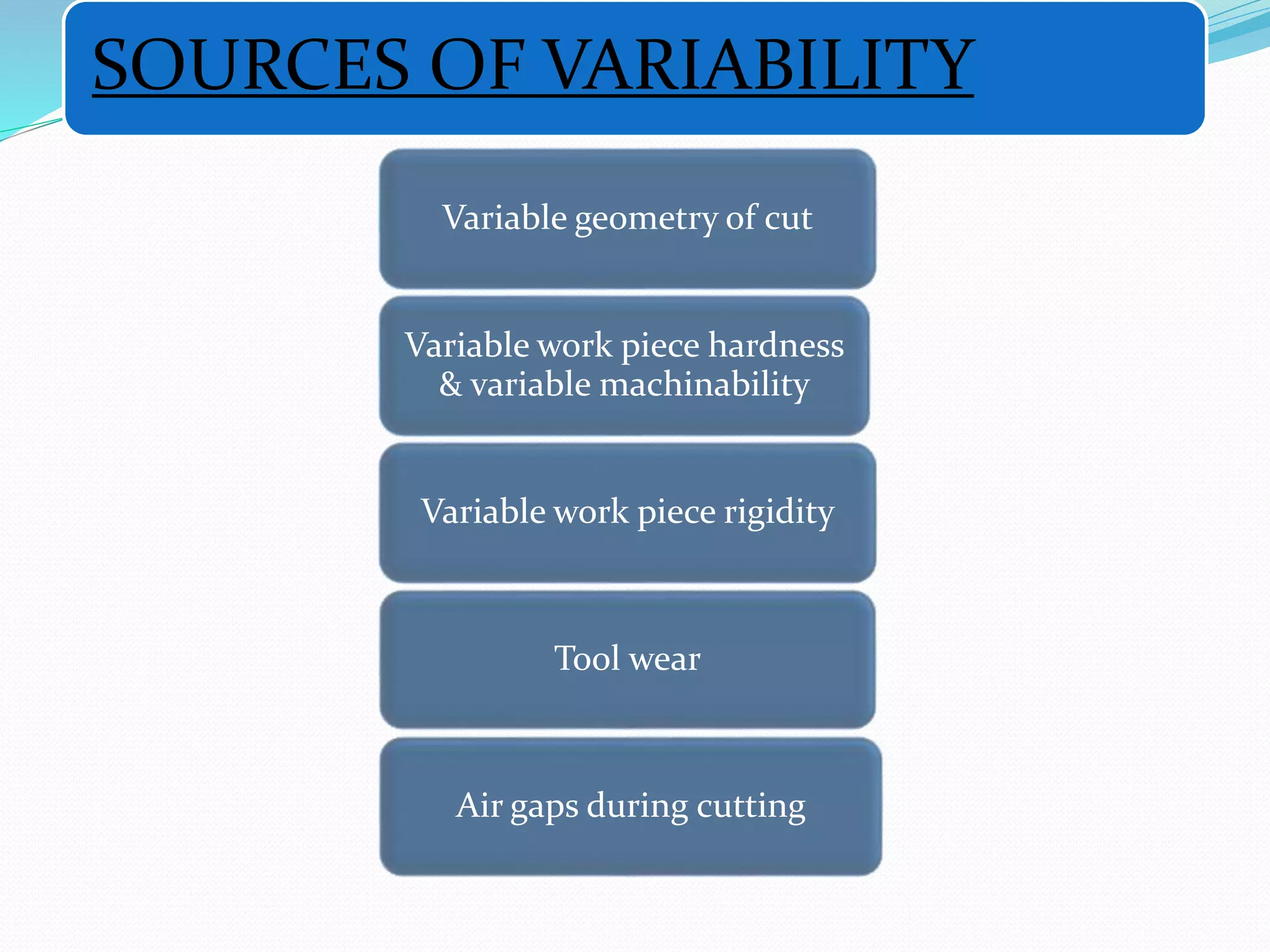
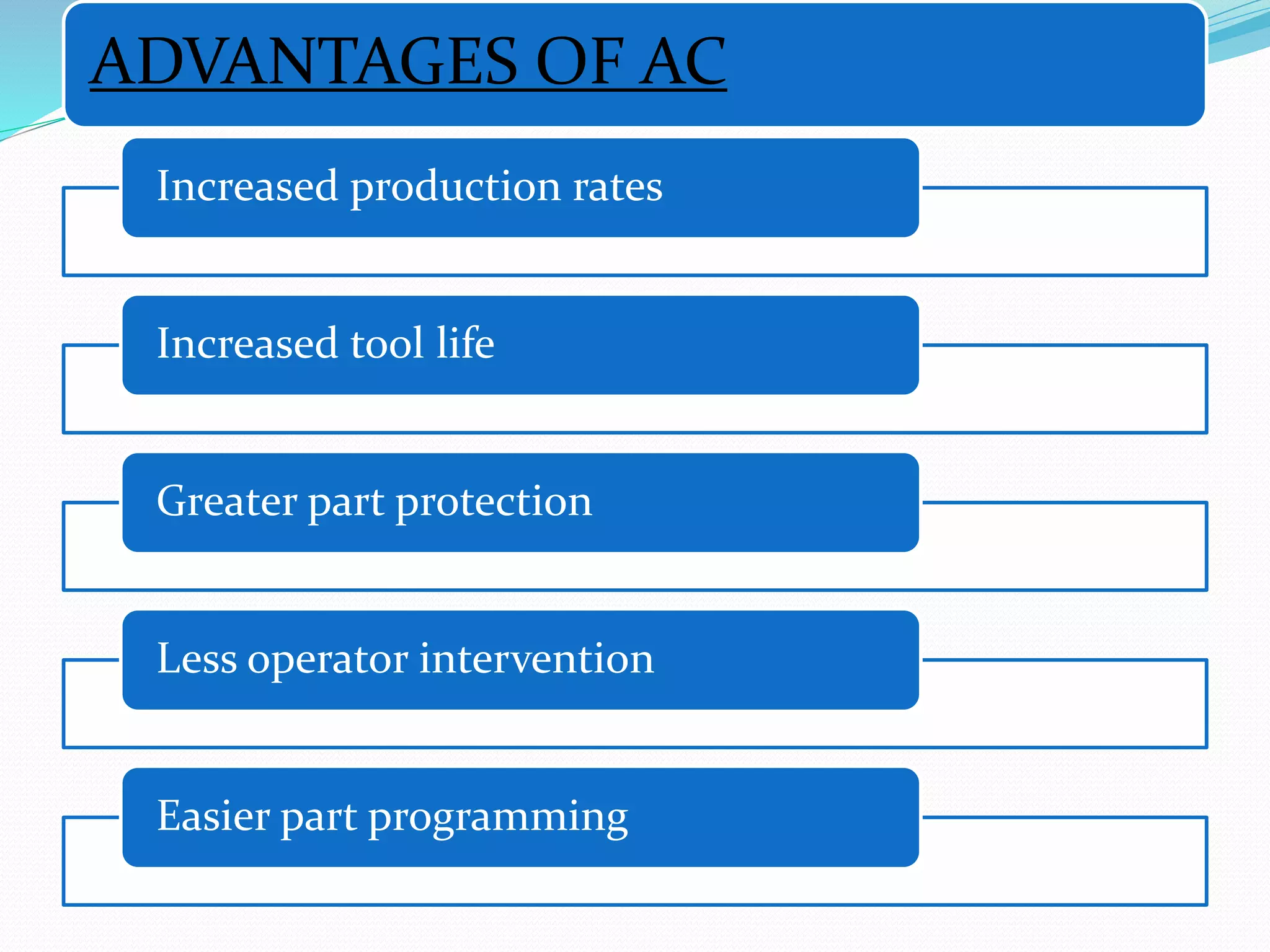
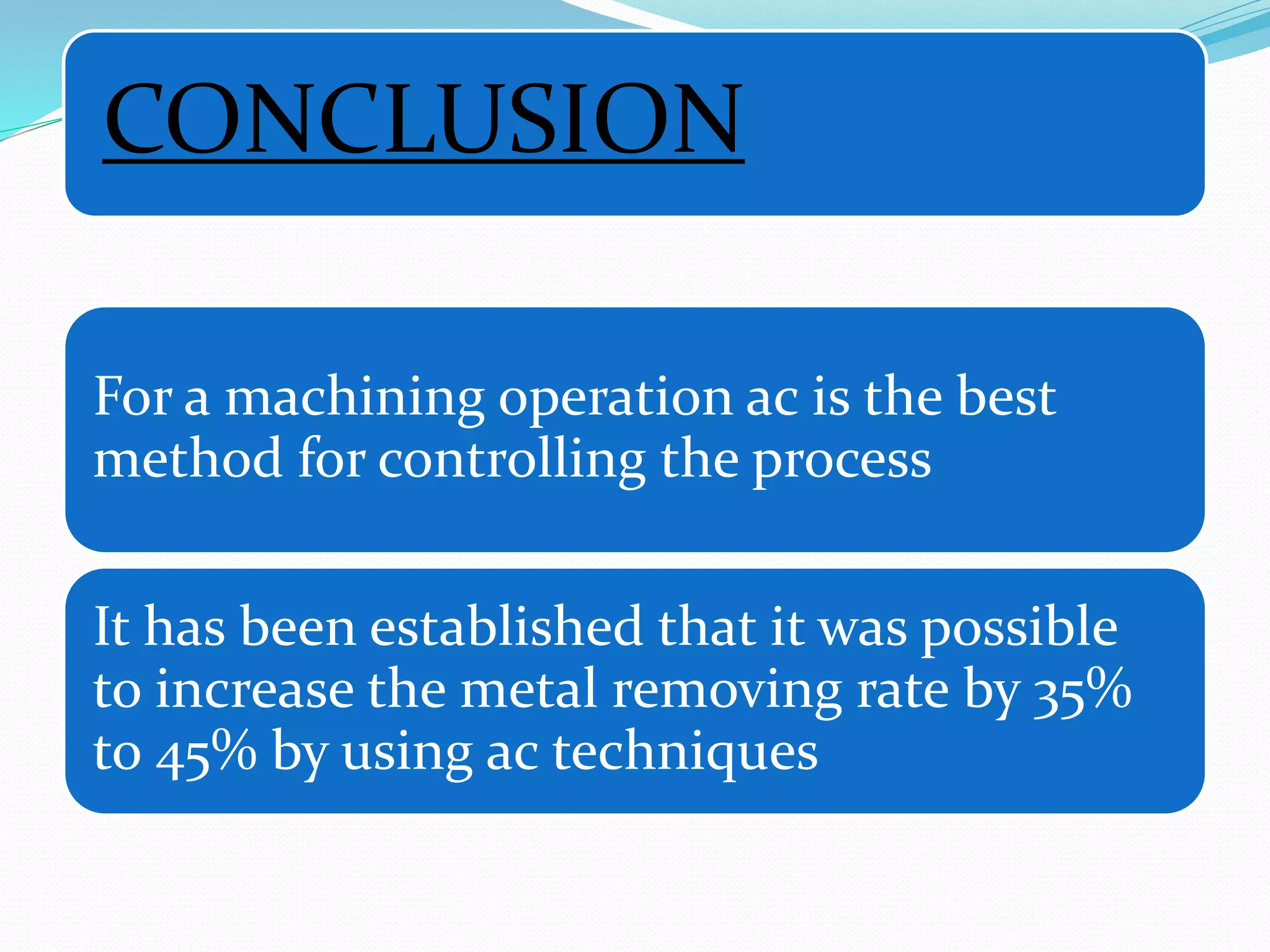
Adaptive control (AC) machining originated in the 1960s from U.S. Air Force research. It uses sensors to measure output variables during machining and automatically adjusts cutting speed and feed rate to improve performance. The goal is to optimize a performance index like material removal rate while meeting constraints like safe cutting forces and power limits. AC systems work by identifying process characteristics, deciding optimal speeds/feeds, and modifying the machining program in real-time for process improvement.