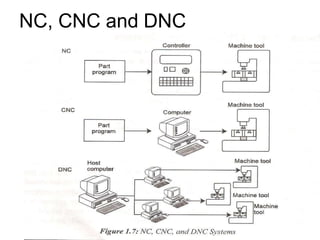
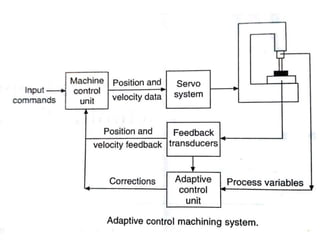
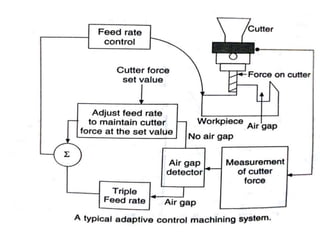
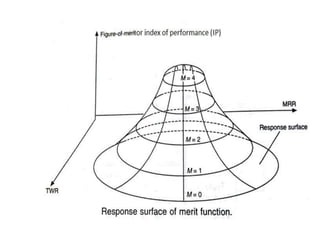
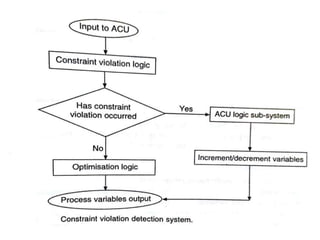
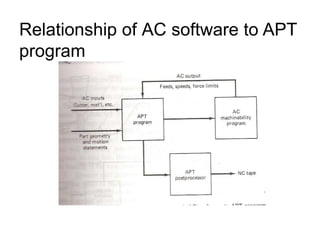
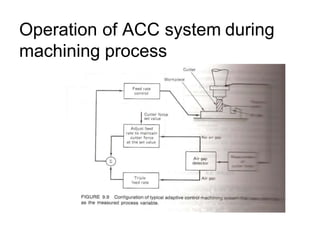
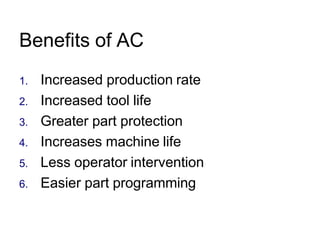
Adaptive control machining systems, including NC, CNC, and DNC, utilize feedback from various machining process variables to optimize operations and minimize non-productive time. The adaptive controller adjusts speed and feed based on factors such as spindle deflection, cutting temperature, and material properties, which enhances efficiency and reduces costs. Key applications include scenarios with significant in-process time variability, where improved tool life, production rates, and operator involvement are achieved.