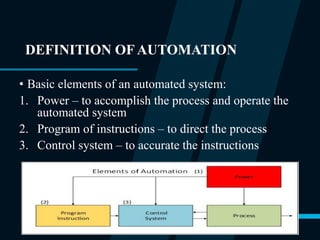
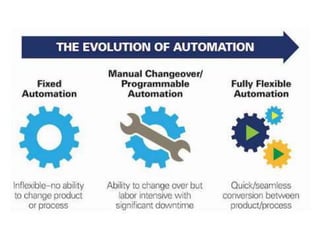
The document outlines the concept of manufacturing automation, detailing definitions, types, levels, and strategies for automation within manufacturing systems. It describes various automated manufacturing systems such as fixed, programmable, flexible, and integrated automation, alongside their advantages, reasons for automation, and a migration strategy for evolving automation processes. The document emphasizes the benefits of automation, including increased productivity, improved safety, and enhanced product quality.