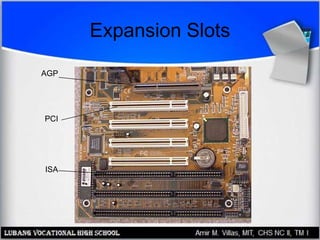
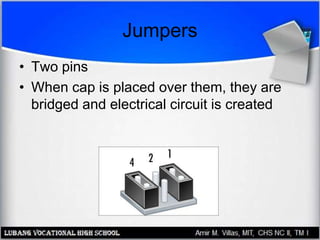
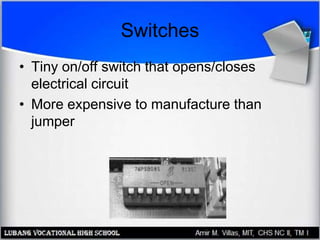
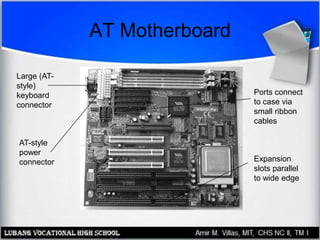
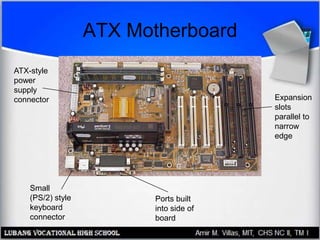
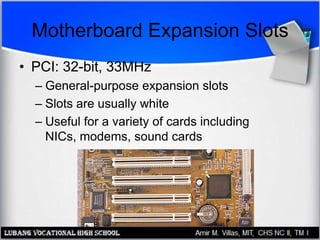
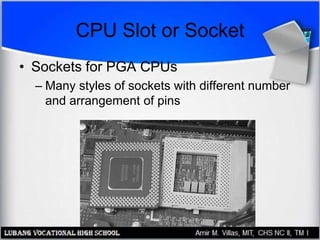
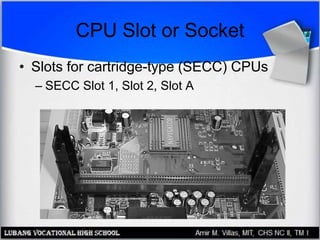
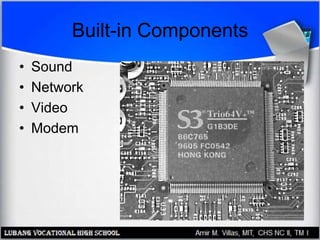
The motherboard contains the central processing unit (CPU), memory, and controls input/output functions and expansion capabilities. It connects various components via buses and slots. Key parts include the chipset, CPU, memory, and expansion slots like PCI, AGP, and ISA. Motherboards come in different form factors and feature varying ports, slots, and built-in components. Issues can be diagnosed through beep codes or by checking for loose connections, bent pins, or malfunctioning parts.