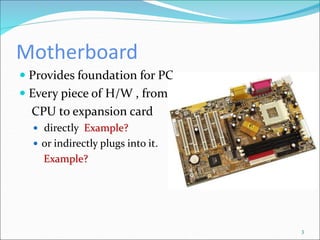
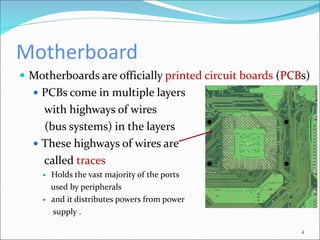
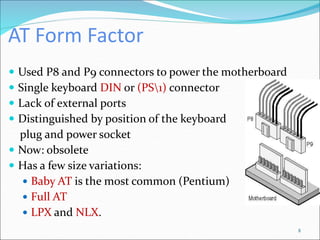
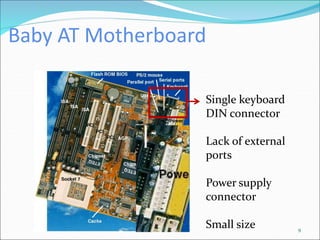
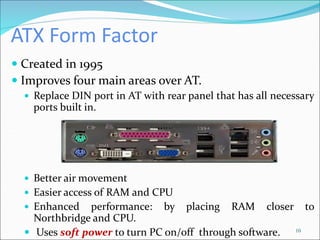
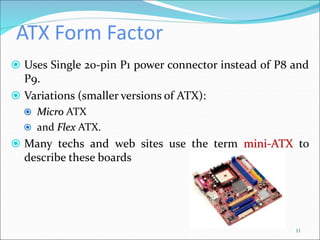
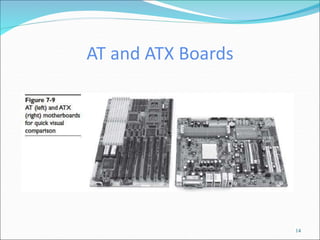
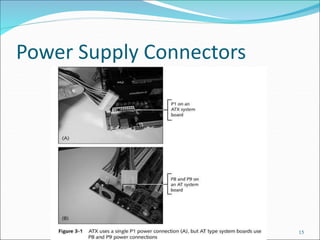
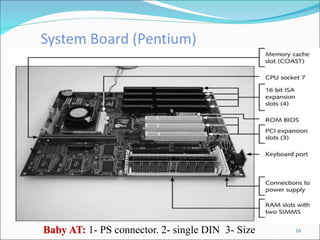
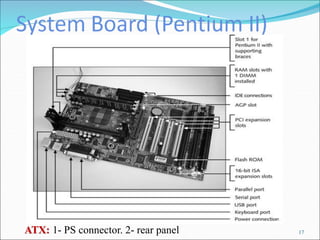
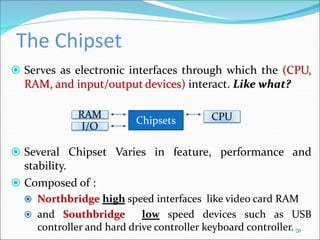
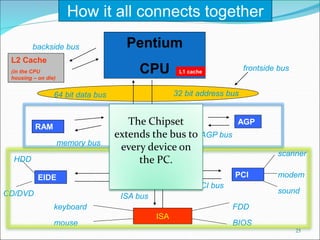
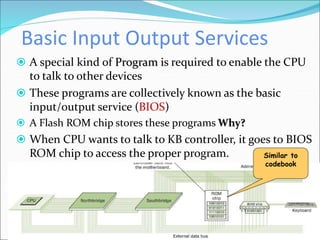
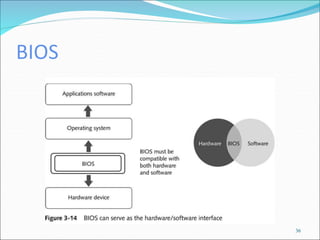
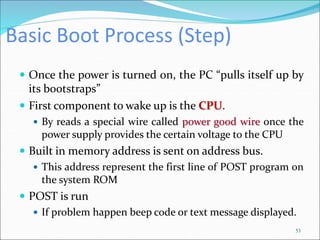
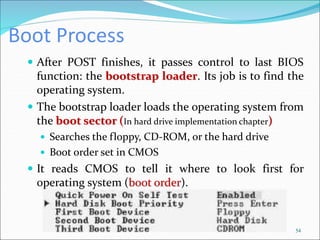
The document discusses motherboards and BIOS. It explains that the motherboard provides the foundation for the PC and acts as the central connecting point. The BIOS stored in ROM allows the CPU to communicate with devices. It discusses chipsets, form factors, boot processes, and how the CMOS stores configurable settings to customize a system.