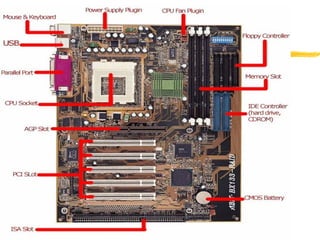
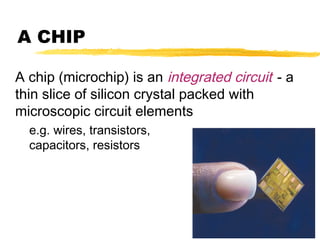
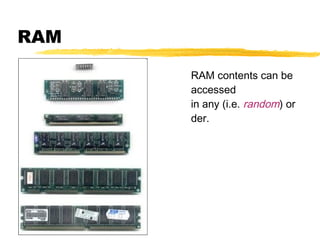
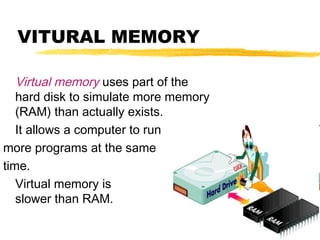
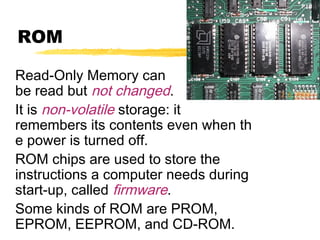
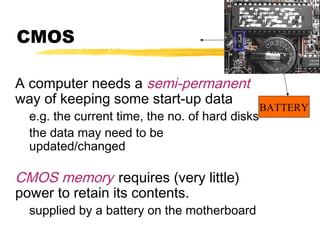
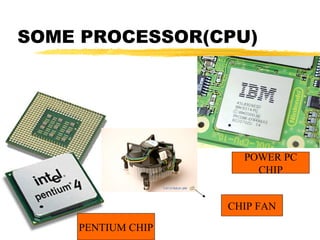
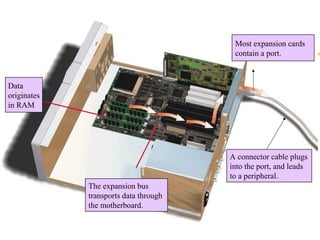
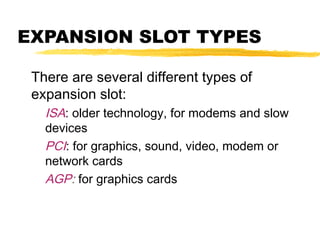
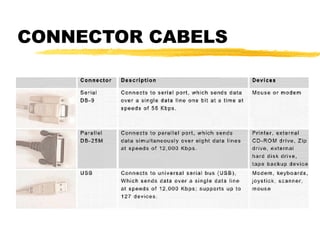
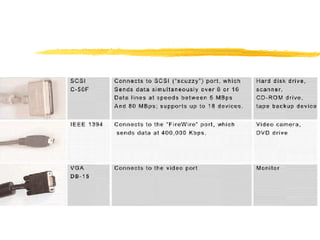
The motherboard is the main circuit board inside a PC that contains and controls the components responsible for processing data. It holds the processor, memory chips, I/O chips, and expansion slots. The motherboard determines the type of CPU, memory, ports, and compatibility standards. It connects all parts of the PC either directly or indirectly and allows them to communicate via buses on the board.