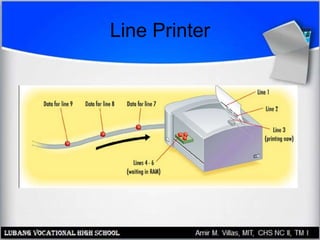
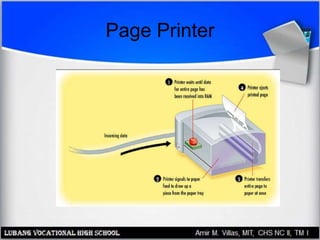
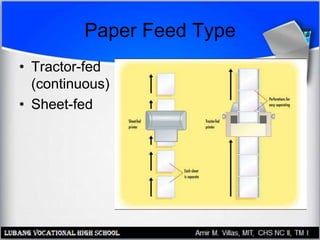
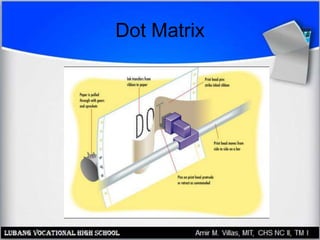
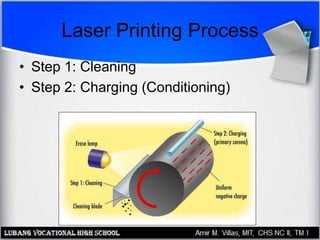
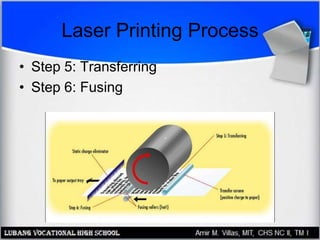
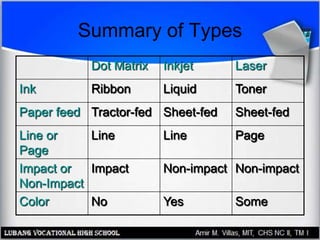
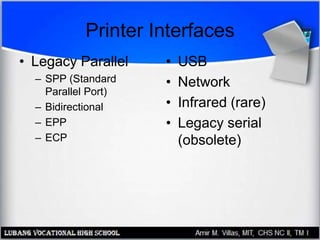
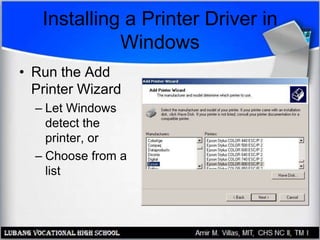
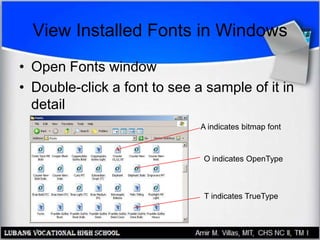
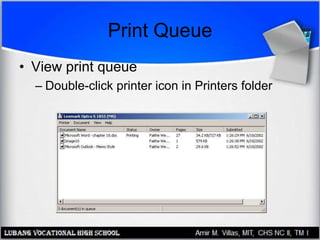
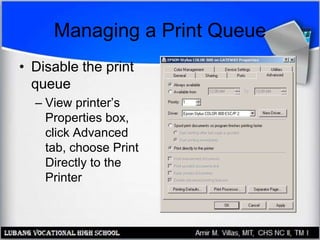
This document provides an overview of PC printer hardware, technologies, and troubleshooting. It discusses the basic functions of printers, different printer classes like line and page printers, and technologies such as laser, inkjet, dot matrix printers. It covers the laser printing process, installing and managing printer drivers, and evaluating factors like cost and print quality. The document also describes how to troubleshoot issues with print jobs, queues, and print quality.