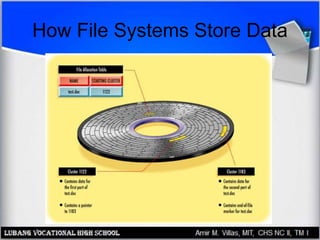
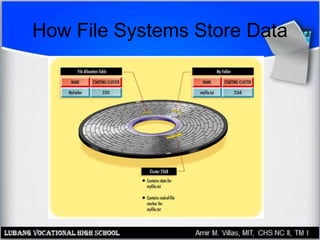
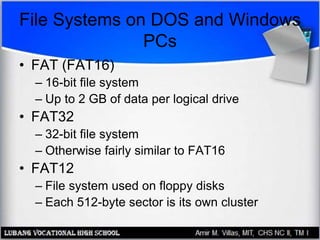
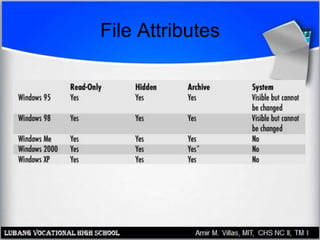
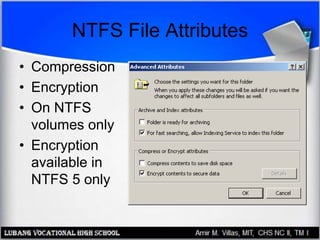
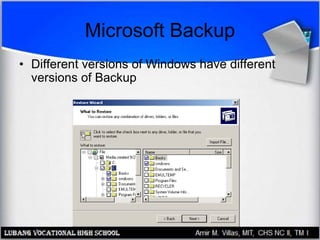
This document provides an overview of file systems and managing files on Windows PCs. It discusses different file systems like FAT, FAT32, NTFS, and CDFS. It covers basic file management tasks in Windows like selecting, copying, moving, deleting and renaming files. It also describes file attributes, troubleshooting common file errors, backing up files, and using command prompt commands to manage files from the command line interface.