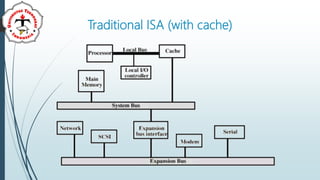
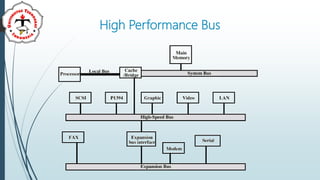
The document discusses bus systems in computer architecture. It describes some problems that can occur with single bus systems, such as propagation delays and performance issues when aggregate data transfer approaches bus capacity. To overcome these problems, most systems use multiple buses. It then covers different bus types (dedicated, multiplexed), bus arbitration methods (centralized, distributed), bus timing (synchronous vs asynchronous), and examples of specific bus standards like PCI bus.